介绍Spark中的RDD
RDD
弹性分布式数据集代表可进行并行操作元素的不可变分区集合,下面是重要成员属性
_sc:SparkContext。不会被序列化deps:Seq[Dependency[_]]当前RDD的依赖。不会被序列化- ` dependencies_
: 与deps`含义一样。可以被序列化 id: RDD的唯一标识。通过sc.newRddId()生成name: RDD的名称。不会被序列化partitions_:Array[Partition]RDD的所有分区。不会被序列化partitioner: 分区器。不会被序列化storageLevel: 存储级别creationSite: 创建此RDD的用户代码,通过sc.getCallSite()获得。不会被序列化scope: 创建此RDD的操作作用域。不会被序列化checkpointData: RDD检查点数据outputDeterministicLevel: RDD的compute输出的结果的确定性级别- DETERMINATE: RDD的输出始终是相同顺序的数据集
- UNORDERED: RDD的输出始终是相同的数据集,但顺序不同
- INDETERMINATE. RDD的输出始终可能不同
RDD应用了模板方法模式,抽象类RDD定义了以下接口,在子类中实现
compute(): 用于对RDD的某个分区计算getPartitions(): 获取当前RDD的所有分区getDependencies(); 获取当前RDD的所有依赖getPreferredLocations(): 获得某一分区的偏好位置
抽象类RDD实现了以下模板方法
partitions(): 优先从RDD检查点数据中获取分区,否则调用未实现的方法getPartitions()final def partitions: Array[Partition] = { checkpointRDD.map(_.partitions).getOrElse { if (partitions_ == null) { stateLock.synchronized { if (partitions_ == null) { partitions_ = getPartitions partitions_.zipWithIndex.foreach { case (partition, index) => require(partition.index == index, s"partitions($index).partition == ${partition.index}, but it should equal $index") } } } } partitions_ } }preferredLocations(): 获得某一分区的偏好位置。优先从RDD检查点数据中获取偏好位置,否则调用子类中实现的getPreferredLocations()final def preferredLocations(split: Partition): Seq[String] = { checkpointRDD.map(_.getPreferredLocations(split)).getOrElse { getPreferredLocations(split) } }dependencies(): 优先从RDD检查点数据中获取依赖,否则为depsprotected def getDependencies: Seq[Dependency[_]] = deps final def dependencies: Seq[Dependency[_]] = { checkpointRDD.map(r => List(new OneToOneDependency(r))).getOrElse { if (dependencies_ == null) { stateLock.synchronized { if (dependencies_ == null) { dependencies_ = getDependencies } } } dependencies_ } }getNarrowAncestors(): 获取与当前RDD是窄依赖的所有祖先RDD。visit()用于获取当前RDD的所有窄依赖的父RDD,并且递归调用visit()获取所有窄依赖的祖先RDD并且去重,最后去除当前RDD。private[spark] def getNarrowAncestors: Seq[RDD[_]] = { val ancestors = new mutable.HashSet[RDD[_]] def visit(rdd: RDD[_]): Unit = { val narrowDependencies = rdd.dependencies.filter(_.isInstanceOf[NarrowDependency[_]]) val narrowParents = narrowDependencies.map(_.rdd) val narrowParentsNotVisited = narrowParents.filterNot(ancestors.contains) narrowParentsNotVisited.foreach { parent => ancestors.add(parent) visit(parent) } } visit(this) // In case there is a cycle, do not include the root itself ancestors.filterNot(_ == this).toSeq }isBarrier(): 是否使用了屏障调度,即一个stage的所有task是否必须同时启动
Dependency
表示RDD间的依赖关系,抽象类Dependency是个泛型类,只有rdd()这一个未实现的方法。有以下继承关系
NarrowDependency:窄依赖,定义了抽象的getParents()方法用于获取子partition对应的父partition,定义了构造器传入一个RDDOneToOneDependency:父RDD与子RDD的partition是一一对应的关系。所以实现的getParents()方法为直接返回输入的partitionIdRangeDependency:如下图所示,父RDD与子RDD的一定范围内的partition是一一对应的关系。所以构造器传入了父RDD及与子RDD的partition对应范围的特征值,并且实现了getParents()方法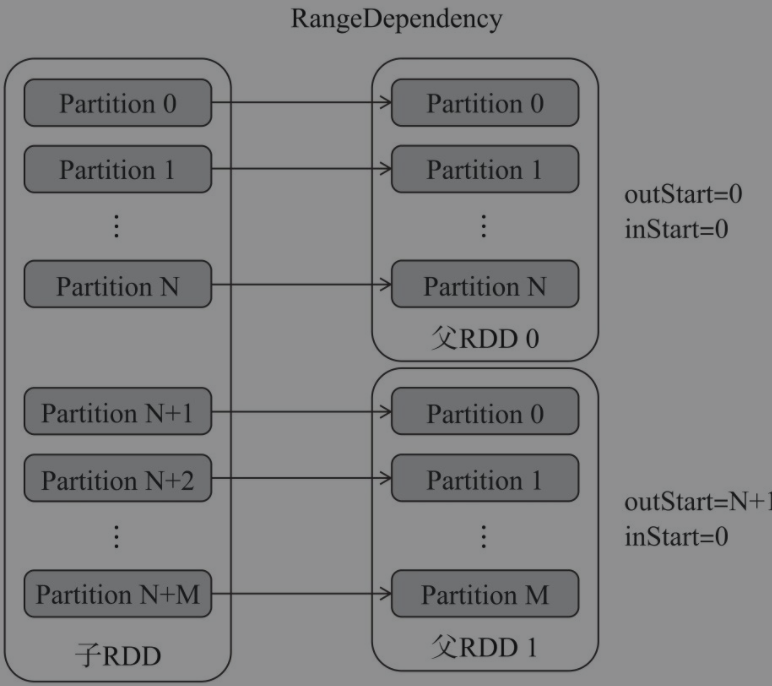
ShuffleDependency:宽依赖。ShuffleDependency在构造的过程中还将自己注册到SparkContext的ContextCleaner中。有以下重要的成员属性_rdd:RDD[_ <: Product2[K, V]]类型,即数据集中的类型必须是Product2[K, V]及其子类,代表必须是键值对类型的RDDkeyOrdering:Option[Ordering[K]]对key进行排序的排序器aggregator: 对map任务的输出数据进行聚合的聚合器mapSideCombine: 是否在map端进行合并,默认为falseshuffleHandle:ShuffleHandle
@DeveloperApi abstract class Dependency[T] extends Serializable { def rdd: RDD[T] } @DeveloperApi abstract class NarrowDependency[T](_rdd: RDD[T]) extends Dependency[T] { def getParents(partitionId: Int): Seq[Int] override def rdd: RDD[T] = _rdd } @DeveloperApi class OneToOneDependency[T](rdd: RDD[T]) extends NarrowDependency[T](rdd) { override def getParents(partitionId: Int): List[Int] = List(partitionId) } @DeveloperApi class RangeDependency[T](rdd: RDD[T], inStart: Int, outStart: Int, length: Int) extends NarrowDependency[T](rdd) { override def getParents(partitionId: Int): List[Int] = { if (partitionId >= outStart && partitionId < outStart + length) { List(partitionId - outStart + inStart) } else { Nil } } } @DeveloperApi class ShuffleDependency[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, C: ClassTag]( @transient private val _rdd: RDD[_ <: Product2[K, V]], val partitioner: Partitioner, val serializer: Serializer = SparkEnv.get.serializer, val keyOrdering: Option[Ordering[K]] = None, val aggregator: Option[Aggregator[K, V, C]] = None, val mapSideCombine: Boolean = false) extends Dependency[Product2[K, V]] { if (mapSideCombine) { require(aggregator.isDefined, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!") } override def rdd: RDD[Product2[K, V]] = _rdd.asInstanceOf[RDD[Product2[K, V]]] private[spark] val keyClassName: String = reflect.classTag[K].runtimeClass.getName private[spark] val valueClassName: String = reflect.classTag[V].runtimeClass.getName // Note: It's possible that the combiner class tag is null, if the combineByKey // methods in PairRDDFunctions are used instead of combineByKeyWithClassTag. private[spark] val combinerClassName: Option[String] = Option(reflect.classTag[C]).map(_.runtimeClass.getName) val shuffleId: Int = _rdd.context.newShuffleId() val shuffleHandle: ShuffleHandle = _rdd.context.env.shuffleManager.registerShuffle( shuffleId, _rdd.partitions.length, this) _rdd.sparkContext.cleaner.foreach(_.registerShuffleForCleanup(this)) }
Partitioner
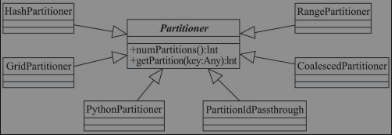
规定了键值对类型RDD的分区规则。抽象类Partitioner中定义了未实现的numPartitions()和getPartition()。其中getPartition()表示将本RDD的key映射成子RDD的从0到numPartitions-1这一范围中的某一个partition。如图所示,Partitioner的继承体系
HashPartitioner
HashPartitioner对key的hashCode()和numPartitions进行取模计算出对应的partition ID,如果余数小于0则用numPartitions+余数作为partition ID。所以HashPartitioner不是一个均匀的分区器,可能导致数据倾斜,并且经过分区后父子RDD间的依赖关系为宽依赖
// Utils.scala
def nonNegativeMod(x: Int, mod: Int): Int = {
val rawMod = x % mod
rawMod + (if (rawMod < 0) mod else 0)
}
class HashPartitioner(partitions: Int) extends Partitioner {
require(partitions >= 0, s"Number of partitions ($partitions) cannot be negative.")
def numPartitions: Int = partitions
def getPartition(key: Any): Int = key match {
case null => 0
case _ => Utils.nonNegativeMod(key.hashCode, numPartitions)
}
override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match {
case h: HashPartitioner =>
h.numPartitions == numPartitions
case _ =>
false
}
override def hashCode: Int = numPartitions
}
RangePartitioner
RangePartitioner将一定范围内的key映射到某一个partition内。partition与partition间是有序的,但partition内的元素不一定是有序的。具体使用到了水塘抽样,Leetcode上有类似的题目
如代码所示初始化rangeBounds序列的过程,rangeBounds保存了key和partition id的映射关系
- 总取样大小
sampleSize为 20*partition个数,最大不超过1000000 - 单个分区的取样大小
sampleSizePerPartition为 3*sampleSize/partition个数,采样数量比实际需要的数量多 3 倍,在数据倾斜的情况下尽量使每个分区采样数量足够 sketch()方法对RDD的每个partition进行根据sampleSizePerPartition进行水塘采样,在此方法中的SamplingUtils.reservoirSampleAndCount()实现了水塘抽样- 由于partition中数据量各不相同,所以大partition的采样量是不足的。如果 partition 数据条数 * 抽样率比抽样个数还要大时,则记录partition id之后使用
RDD.sample()方法进行重采样 - 记录采样key和权重(当前partition的数据条数/采样量)
- 调用
determineBounds()方法- 根据采样 key 进行排序
- 根据采样 key 的权重解析出 partition 的划分界限
def sketch[K : ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[K],
sampleSizePerPartition: Int): (Long, Array[(Int, Long, Array[K])]) = {
val shift = rdd.id
// val classTagK = classTag[K] // to avoid serializing the entire partitioner object
val sketched = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex { (idx, iter) =>
val seed = byteswap32(idx ^ (shift << 16))
val (sample, n) = SamplingUtils.reservoirSampleAndCount(
iter, sampleSizePerPartition, seed)
Iterator((idx, n, sample))
}.collect()
val numItems = sketched.map(_._2).sum
(numItems, sketched)
}
def determineBounds[K : Ordering : ClassTag](
candidates: ArrayBuffer[(K, Float)],
partitions: Int): Array[K] = {
val ordering = implicitly[Ordering[K]]
val ordered = candidates.sortBy(_._1)
val numCandidates = ordered.size
val sumWeights = ordered.map(_._2.toDouble).sum
val step = sumWeights / partitions
var cumWeight = 0.0
var target = step
val bounds = ArrayBuffer.empty[K]
var i = 0
var j = 0
var previousBound = Option.empty[K]
while ((i < numCandidates) && (j < partitions - 1)) {
val (key, weight) = ordered(i)
cumWeight += weight
if (cumWeight >= target) {
// Skip duplicate values.
if (previousBound.isEmpty || ordering.gt(key, previousBound.get)) {
bounds += key
target += step
j += 1
previousBound = Some(key)
}
}
i += 1
}
bounds.toArray
}
private var rangeBounds: Array[K] = {
if (partitions <= 1) {
Array.empty
} else {
// This is the sample size we need to have roughly balanced output partitions, capped at 1M.
// Cast to double to avoid overflowing ints or longs
val sampleSize = math.min(samplePointsPerPartitionHint.toDouble * partitions, 1e6)
// Assume the input partitions are roughly balanced and over-sample a little bit.
val sampleSizePerPartition = math.ceil(3.0 * sampleSize / rdd.partitions.length).toInt
val (numItems, sketched) = RangePartitioner.sketch(rdd.map(_._1), sampleSizePerPartition)
if (numItems == 0L) {
Array.empty
} else {
// If a partition contains much more than the average number of items, we re-sample from it
// to ensure that enough items are collected from that partition.
val fraction = math.min(sampleSize / math.max(numItems, 1L), 1.0)
val candidates = ArrayBuffer.empty[(K, Float)]
val imbalancedPartitions = mutable.Set.empty[Int]
sketched.foreach { case (idx, n, sample) =>
if (fraction * n > sampleSizePerPartition) {
imbalancedPartitions += idx
} else {
// The weight is 1 over the sampling probability.
val weight = (n.toDouble / sample.length).toFloat
for (key <- sample) {
candidates += ((key, weight))
}
}
}
if (imbalancedPartitions.nonEmpty) {
// Re-sample imbalanced partitions with the desired sampling probability.
val imbalanced = new PartitionPruningRDD(rdd.map(_._1), imbalancedPartitions.contains)
val seed = byteswap32(-rdd.id - 1)
val reSampled = imbalanced.sample(withReplacement = false, fraction, seed).collect()
val weight = (1.0 / fraction).toFloat
candidates ++= reSampled.map(x => (x, weight))
}
RangePartitioner.determineBounds(candidates, math.min(partitions, candidates.size))
}
}
}
如代码所示getPartition()方法。如果初始化后的rangeBounds长度小于128,则用顺序查找否则使用二分查找,找到当前key应在的partition。
def getPartition(key: Any): Int = {
val k = key.asInstanceOf[K]
var partition = 0
if (rangeBounds.length <= 128) {
// If we have less than 128 partitions naive search
while (partition < rangeBounds.length && ordering.gt(k, rangeBounds(partition))) {
partition += 1
}
} else {
// Determine which binary search method to use only once.
partition = binarySearch(rangeBounds, k)
// binarySearch either returns the match location or -[insertion point]-1
if (partition < 0) {
partition = -partition-1
}
if (partition > rangeBounds.length) {
partition = rangeBounds.length
}
}
if (ascending) {
partition
} else {
rangeBounds.length - partition
}
}
RDDInfo
用于描述RDD的信息。有以下成员属性用于描述信息
idnamenumPartitions: 分区数量storageLevel: 存储级别parentIds: 父RDD的id序列。这说明一个RDD会有零到多个父RDDcallSite: RDD的用户调用栈信息scope: RDD的操作范围numCachedPartitions:缓存的分区数量。memSize:使用的内存大小diskSize:使用的磁盘大小externalBlockStoreSize: block存储在外部的大小
有以下成员方法
isCached(): 是否缓存,如果占用了内存或磁盘同时占用了外部存储空间即判定为缓存了。(memSize + diskSize > 0) && numCachedPartitions > 0fromRdd(): 伴生对象中定义的静态方法。从RDD构造RDDInfodef fromRdd(rdd: RDD[_]): RDDInfo = { val rddName = Option(rdd.name).getOrElse(Utils.getFormattedClassName(rdd)) val parentIds = rdd.dependencies.map(_.rdd.id) val callsiteLongForm = Option(SparkEnv.get) .map(_.conf.get(EVENT_LOG_CALLSITE_LONG_FORM)) .getOrElse(false) val callSite = if (callsiteLongForm) { rdd.creationSite.longForm } else { rdd.creationSite.shortForm } new RDDInfo(rdd.id, rddName, rdd.partitions.length, rdd.getStorageLevel, parentIds, callSite, rdd.scope) }
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/09/14/schedule-RDD/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)