介绍Spark中的stage切分和调度
stage描述
StageInfo
用于描述Stage信息,并可以传递给SparkListener。有以下成员属性用于描述Stage信息
stageIdattemptIdnamenumTasks: 当前stage的Task数量rddInfos:RDDInfo序列,当前Stage的RDD与其窄依赖的所有祖先RDDparentIds: 当前stage的父stage的id序列details: 详细的线程栈信息,字符串taskLocalityPreferences:Seq[Seq[TaskLocation]]维护每个RDD的每个partition的存储本地性偏好submissionTime:DAGScheduler将当前stage提交给TaskScheduler的时间completionTime: 当前stage中的所有task完成的时间或者stage被取消的时间failureReason: 用于记录失败的原因,字符串
有以下方法
stageFailed(): 失败时调用,将失败原因保存到failureReason并记录completionTimefromStage(): 伴生对象中定义的静态方法。用于从stage构建一个StageInfogetStatusString(): 返回当前task状态用于日志记录,failed, succeeded, runningprivate[spark] def getStatusString: String = { if (completionTime.isDefined) { if (failureReason.isDefined) { "failed" } else { "succeeded" } } else { "running" } }
Stage
表示一组可以并行执行并且拥有相同计算函数和相同shuffle依赖的task。DAGScheduler会将Job划分为不同的stage,并构建这些stage的依赖关系。这样可以使得没有依赖关系的stage并行执行,并保证有依赖关系的stage顺序执行。Stage是一个抽象类,下面是重要的成员属性
idrdd: 当前stage包含的rdd。对于shuffle map stage来说是运行map task的RDD,对于result stage来说是执行action的RDDnumTasks: task数量parents: 父Stage列表,一个Stage可以有多个父StagefirstJobId: 第一个提交当前Stage的job id。当使用FIFO调度时,通过firstJobId首先计算来自较早Job的stage,或者在发生故障时更快的恢复numPartitionscallSite: 应用程序中与当前Stage相关联的调用栈信息jobIds:Stage所属的全部job的id序列。一个Stage可以属于多个jobnextAttemptId:Stage下一次attempt id_latestInfo:Stage最近一次尝试的信息,即StageInfofailedAttemptIds:Stage失败的attempt id的集合(set),防止相同stage的多个任务的重复失败
下面是重要的成员方法
clearFailures():清空failedAttemptIdsmakeNewStageAttempt():创建新的Stage尝试。使用nextAttemptId作为attempt id创建一个attempt,创建新的StageInfo赋值给_lastestInfo,并将nextAttemptId自增def makeNewStageAttempt( numPartitionsToCompute: Int, taskLocalityPreferences: Seq[Seq[TaskLocation]] = Seq.empty): Unit = { val metrics = new TaskMetrics metrics.register(rdd.sparkContext) _latestInfo = StageInfo.fromStage( this, nextAttemptId, Some(numPartitionsToCompute), metrics, taskLocalityPreferences) nextAttemptId += 1 }findMissingPartitions():未实现,返回未计算的分区id
Stage有两个子类分别为需要处理Shuffle的ShuffleMapStage和最下游的ResultStage。
ResultStage
使用指定的函数对RDD中的分区进行计算并得出最终结果。DAG调度流程的结尾stage,进行作业的收尾工作(例如,对各个分区的数据收拢、打印到控制台或写入到HDFS)。有以下重要的成员属性
func:(TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,这是一个函数用于partition的计算partitions_activeJob: 处理此Stage的ActiveJob
实现了findMissingPartitions()用于找出当前Job的所有partition中还没有完成的部分,通过ActiveJob.finished()获得
override def findMissingPartitions(): Seq[Int] = {
val job = activeJob.get
(0 until job.numPartitions).filter(id => !job.finished(id))
}
ShuffleMapStage
DAG调度流程的中间Stage,包括一到多个ShuffleMapTask,生成用于Shuffle的数据,交由下游ShuffleMapStage或者ResultStage计算。有以下重要的成员属性
ShuffleDep:ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]类型,RDD间的宽依赖mapOutputTrackerMaster_mapStageJob: 处理此Stage的ActiveJob集合(set)
有以下重要的成员方法
numAvailableOutputs(): 通过mapOutputTrackerMaster获得已经计算完成的partition。isAvailable(): 当数量和numPartitions一致时,说明ShuffleMapStage已经准备完毕addActiveJob(),removeActiveJob(): 在_mapStageJob中添加或者删除ActiveJobfindMissingPartitions(): 在mapOutputTrackerMaster中根据shuffle id获取未计算的partition,默认计算全部partitionoverride def findMissingPartitions(): Seq[Int] = { mapOutputTrackerMaster .findMissingPartitions(shuffleDep.shuffleId) .getOrElse(0 until numPartitions) }
stage划分
所有的组件都通过向DAGScheduler投递DAGSchedulerEvent,DAGScheduler内部的DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop将处理这些DAGSchedulerEvent,并调用DAGScheduler的不同方法。
JobListener用于对作业中每个task执行成功或失败进行监听,JobWaiter实现了JobListener并最终确定作业的成功与失败
JobListener
特质,定义了抽象的taskSucceeded()和jobFailed()回调方法。有JobWaiter和ApproximateActionListener两个实现类。
JobWaiter
用于等待整个Job执行完毕,然后调用给定的处理函数对返回结果(即对ResultStage的每个task执行结果)进行处理。有以下重要的成员属性
dagScheduler:DAGScheduler,当前JobWaiter等待执行完成的Job的调度者jobIdtotalTasks: 等待完成的job中所有的Task数量resultHandler:(Int, T) => Unit,是一个函数,用于执行结果的处理器finishedTasks: 等待完成的Job中已经完成的Task数量jobPromise:Promise。Job完成后的结果。如果totalTasks等于零,则标记为成功完成
有以下重要的成员方法
jobFinished(),completionFuture(): 对jobPromise方法的进一步封装def jobFinished: Boolean = jobPromise.isCompleted def completionFuture: Future[Unit] = jobPromise.futurecancel(): 调用了dagScheduler.cancelJob(),向DAGScheduler发送信号以取消job的执行taskSucceeded(): 调用了resultHandler函数来处理当前执行成功Task的执行结果,如果所有Task已经完成,标记jobPromise为成功完成jobFailed(): 将jobPromise标记为失败,并抛出warning
ActiveJob
表示已经激活的Job,即被DAGScheduler接收处理的Job。有以下重要属性
jobIdfinalStage: Job的最下游StagecallSite: 应用程序调用栈listener: 监听当前Job的JobListenerpropertiesnumPartitions: 当前Job的partition数量- 如果
finalStage为ResultStage,那么就是ResultStage的partitions属性的长度。 - 如果
finalStage为ShuffleMapStage,那么就是ShuffleMapStage的rdd的partitions属性的长度。
- 如果
finished: 标记每个partition任务是否完成,布尔数组numFinished: 当前Job的所有任务中已完成任务的数量
resetAllPartitions()用于重置finished全部元素为false
DAGScheduler
将DAG中的各个RDD划分到不同的Stage,构建这些Stage之间的父子关系,最后将每个Stage按照partition切分为多个Task,并以TaskSet的形式提交给底层的TaskScheduler
DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop是DAGScheduler中的内部类,与事件总线LiveListenerBus类似,用于循环处理DAGSchedulerEvent事件。内部维护了一个存储事件的阻塞队列,onReceive()方法根据事件的类型调用对应DAGScheduler的方法进行处理。post()方法用于向阻塞队列中添加事件。调用start()方法会开启一个线程不断从阻塞队列中取出事件交给OnReceive()处理。stop()用于停止消费阻塞队列,除了使用标志位来结束线程还调用了Thread.interrupt()方法防止线程一直阻塞在阻塞队列上。
DAGScheduler中包含以下成员属性
sc:SparkContexttaskScheduler:TaskSchedulerlistenerBus:LiveListenerBusmapOutputTracker:MapOutputTrackerMasterenv::SparkEnvclock: 时钟对象SystemClocknextJobId:AtomicInteger,用于生成下一个job idnumTotalJobs:总共提交的作业数量。实际读取了nextJobId的当前值nextStageId:AtomicInteger,用于生成下一个stage idjobIdToStageIds:HashMap[Int,HashSet[Int]]用于缓存job id与stage id之间的映射关系,一对多的关系stageIdToStage:HashMap[Int, Stage]用于缓存stage id与Stage之间的映射关系shuffleIdToMapStage:HashMap[Int, ShuffleMapStage]用于缓存shuffle id与ShuffleMapStage之间的映射关系jobIdToActiveJob:HashMap[Int, ActiveJob]用于缓存job id与ActiveJob之间的映射关系waitingStages: 处于等待状态的Stage集合(set)runningStages: 处于运行状态的Stage集合(set)failedStages: 处于失败状态的Stage集合(set)activeJobs: 所有激活的Job的集合(set)cacheLocs:HashMap[Int,IndexedSeq[Seq[TaskLocation]]]缓存每个RDD的所有partition的位置信息(每个partition有多个位置)outputCommitCoordinator:OutputCommitCoordinatormessageScheduler: 只有一个线程的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,创建的线程以dag-scheduler-message开头。用于对失败的stage进行重试eventProcessLoop:DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop
下面是一些重要的成员方法
updateJobIdStageIdMaps(): 注册job和stage的对应关系,包括当前stage的所有祖先stage也都注册到这个job中private def updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId: Int, stage: Stage): Unit = { @tailrec def updateJobIdStageIdMapsList(stages: List[Stage]) { if (stages.nonEmpty) { val s = stages.head s.jobIds += jobId jobIdToStageIds.getOrElseUpdate(jobId, new HashSet[Int]()) += s.id val parentsWithoutThisJobId = s.parents.filter { ! _.jobIds.contains(jobId) } updateJobIdStageIdMapsList(parentsWithoutThisJobId ++ stages.tail) } } updateJobIdStageIdMapsList(List(stage)) }activeJobForStage(): 找到Stage最早创建的ActiveJob,即job id最小的jobprivate def activeJobForStage(stage: Stage): Option[Int] = { val jobsThatUseStage: Array[Int] = stage.jobIds.toArray.sorted jobsThatUseStage.find(jobIdToActiveJob.contains) }getCacheLocs(): 获取RDD各个partition的TaskLocation序列- 如果
cacheLocs包含对应的位置则直接返回,否则 - 如果未定义存储级别,那么直接返回空的序列,因为该RDD没有被缓存
- 如果定义存储级别,那么由RDD id和分区索引构造
BlockId,由此可以看出block和RDD的partition是一一对应的 - 由
blockManagerMaster获取位置信息并封装为TaskLocation,更新cacheLocs后返回
private[scheduler] def getCacheLocs(rdd: RDD[_]): IndexedSeq[Seq[TaskLocation]] = cacheLocs.synchronized { // Note: this doesn't use `getOrElse()` because this method is called O(num tasks) times if (!cacheLocs.contains(rdd.id)) { // Note: if the storage level is NONE, we don't need to get locations from block manager. val locs: IndexedSeq[Seq[TaskLocation]] = if (rdd.getStorageLevel == StorageLevel.NONE) { IndexedSeq.fill(rdd.partitions.length)(Nil) } else { val blockIds = rdd.partitions.indices.map(index => RDDBlockId(rdd.id, index)).toArray[BlockId] blockManagerMaster.getLocations(blockIds).map { bms => bms.map(bm => TaskLocation(bm.host, bm.executorId)) } } cacheLocs(rdd.id) = locs } cacheLocs(rdd.id) }- 如果
getPreferredLocs(): 获取RDD指定partition的偏好位置visit用于缓存当前已经访问过的partition,防止重复访问- 首先通过
getCacheLocs()获取该partition缓存的位置 - 如果没有,则获取RDD中保存的偏好位置
- 如果没有,则将窄依赖中的父RDD的对应partition再次传入
getPreferredLocs()方法中递归查找
private[spark] def getPreferredLocs(rdd: RDD[_], partition: Int): Seq[TaskLocation] = { getPreferredLocsInternal(rdd, partition, new HashSet) } private def getPreferredLocsInternal( rdd: RDD[_], partition: Int, visited: HashSet[(RDD[_], Int)]): Seq[TaskLocation] = { // If the partition has already been visited, no need to re-visit. // This avoids exponential path exploration. SPARK-695 if (!visited.add((rdd, partition))) { // Nil has already been returned for previously visited partitions. return Nil } // If the partition is cached, return the cache locations val cached = getCacheLocs(rdd)(partition) if (cached.nonEmpty) { return cached } // If the RDD has some placement preferences (as is the case for input RDDs), get those val rddPrefs = rdd.preferredLocations(rdd.partitions(partition)).toList if (rddPrefs.nonEmpty) { return rddPrefs.map(TaskLocation(_)) } // If the RDD has narrow dependencies, pick the first partition of the first narrow dependency // that has any placement preferences. Ideally we would choose based on transfer sizes, // but this will do for now. rdd.dependencies.foreach { case n: NarrowDependency[_] => for (inPart <- n.getParents(partition)) { val locs = getPreferredLocsInternal(n.rdd, inPart, visited) if (locs != Nil) { return locs } } case _ => } Nil }
下面与创建Stage有关的方法
getShuffleDependencies(): 获取该RDD的直接ShuffleDependency(一级shuffle依赖),即获取所有非shuffle RDD的ShuffleDependency- 从该RDD开始深搜,如果搜索到
ShuffleDependency,加入返回集合,且就不会顺着这条依赖继续搜索下去 - 如果搜索到非
ShuffleDependency的依赖,则会继续搜索下去直到找到ShuffleDependency
private[scheduler] def getShuffleDependencies( rdd: RDD[_]): HashSet[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]] = { val parents = new HashSet[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]] val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]] val waitingForVisit = new ArrayStack[RDD[_]] waitingForVisit.push(rdd) while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) { val toVisit = waitingForVisit.pop() if (!visited(toVisit)) { visited += toVisit toVisit.dependencies.foreach { case shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] => parents += shuffleDep case dependency => waitingForVisit.push(dependency.rdd) } } } parents }- 从该RDD开始深搜,如果搜索到
getMissingAncestorShuffleDependencies(): 找到所有还未注册过ShuffleMapStage的祖先ShuffleDependency,返回一个栈,从栈顶到栈尾是按照依赖的先后顺序- 从该RDD开始深搜,调用
getShuffleDependencies()找到RDD的所有直接shuffle dependency - 如果当前依赖未注册到
shuffleIdToMapStage中,则添加到返回栈中,并继续向上深搜寻找未注册的shuffle dependency
private def getMissingAncestorShuffleDependencies( rdd: RDD[_]): ArrayStack[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]] = { val ancestors = new ArrayStack[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]] val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]] // We are manually maintaining a stack here to prevent StackOverflowError // caused by recursively visiting val waitingForVisit = new ArrayStack[RDD[_]] waitingForVisit.push(rdd) while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) { val toVisit = waitingForVisit.pop() if (!visited(toVisit)) { visited += toVisit getShuffleDependencies(toVisit).foreach { shuffleDep => if (!shuffleIdToMapStage.contains(shuffleDep.shuffleId)) { ancestors.push(shuffleDep) waitingForVisit.push(shuffleDep.rdd) } // Otherwise, the dependency and its ancestors have already been registered. } } } ancestors }- 从该RDD开始深搜,调用
getOrCreateShuffleMapStage(): 创建当前ShuffleDependency的ShuffleMapStage,以及其未注册的祖先shuffle依赖的ShuffleMapStage,若已注册则返回注册的ShuffleDependency- 根据当前
ShuffleDependency找到注册在shuffleIdToMapStage的ShuffleMapStage并返回 - 如果没有,则调用
getMissingAncestorShuffleDependencies()找到所有还未注册(同时也未创建过ShuffleMapStage)的ShuffleMapStage的祖先ShuffleDependency,调用createShuffleMapStage()创建并注册这些祖先ShuffleDependency和当前ShuffleDependency的ShuffleMapStage - 这个方法存在递归调用,具体看
createShuffleMapStage()中的分析
private def getOrCreateShuffleMapStage( shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _], firstJobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = { shuffleIdToMapStage.get(shuffleDep.shuffleId) match { case Some(stage) => stage case None => // Create stages for all missing ancestor shuffle dependencies. getMissingAncestorShuffleDependencies(shuffleDep.rdd).foreach { dep => // Even though getMissingAncestorShuffleDependencies only returns shuffle dependencies // that were not already in shuffleIdToMapStage, it's possible that by the time we // get to a particular dependency in the foreach loop, it's been added to // shuffleIdToMapStage by the stage creation process for an earlier dependency. See // SPARK-13902 for more information. if (!shuffleIdToMapStage.contains(dep.shuffleId)) { createShuffleMapStage(dep, firstJobId) } } // Finally, create a stage for the given shuffle dependency. createShuffleMapStage(shuffleDep, firstJobId) } }- 根据当前
getOrCreateParentStages(): 创建当前RDD的所有ShuffleMapStage,以及其未注册的祖先shuffle依赖的ShuffleMapStage,若已注册则返回注册的ShuffleDependency。执行流程如下图所示,方框表示RDD,虚线表示ShuffleDependency,实线表示NarrowDependency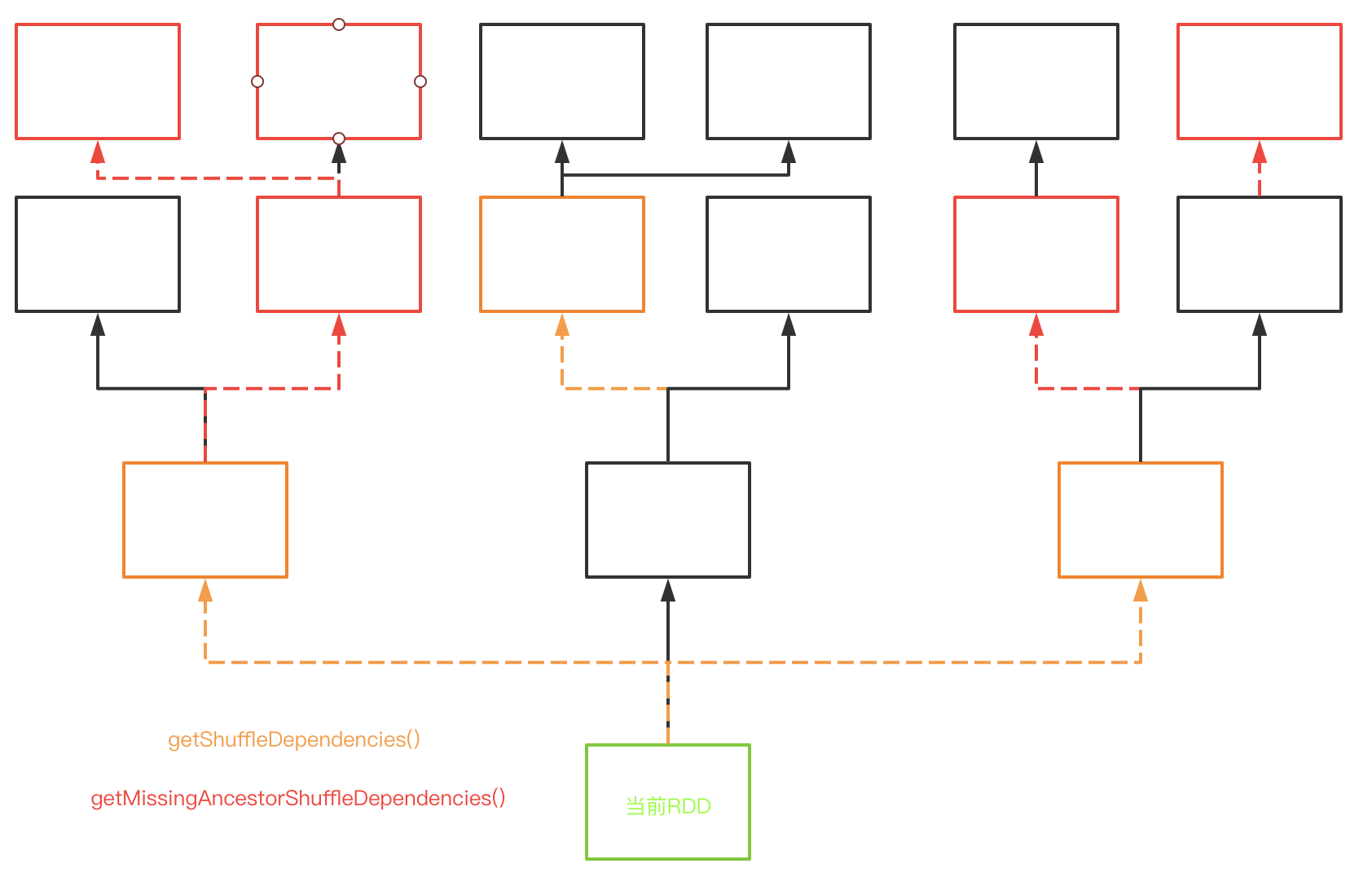
- 从当前RDD(绿色)开始,调用
getShuffleDependencies()获取该RDD的所有直接ShuffleDependency(橙色) - 调用
getOrCreateShuffleMapStage(),里面首先调用getMissingAncestorShuffleDependencies()从橙色的依赖开始找到祖先ShuffleDependency(红色),再由所有这些依赖创建ShuffleMapStage - 这个方法存在递归调用,具体看
createShuffleMapStage()中的分析
private def getOrCreateParentStages(rdd: RDD[_], firstJobId: Int): List[Stage] = { getShuffleDependencies(rdd).map { shuffleDep => getOrCreateShuffleMapStage(shuffleDep, firstJobId) }.toList }- 从当前RDD(绿色)开始,调用
createShuffleMapStage(): 创建并注册ShuffleMapStage- 首先检查屏障调度的运行条件,调用
getOrCreateParentStages()创建未注册的当前和所有祖先shuffle依赖的Stage。 - 这里存在递归调用的情况,
createShuffleMapStage()->getOrCreateParentStages()->getOrCreateShuffleMapStage()->createShuffleMapStage()。因为每个ShuffleMapStage的属性parents需要其所有的shuffle依赖,想要获得层级结构,只有递归调用才能做到。此外由于是递归调用,其创建顺序是从最古老的祖先shuffle依赖开始,并且已经创建的ShuffleMapStage并不会重复创建,所以减少了不必要的重复创建stage。这里举个小例子,设当前的ShuffleDependency为A,其祖先ShuffleDependency为B,在此方法中由于递归调用,会先创建B和其shuffle祖先依赖的stage并注册。当创建A时,原本需要创建和B相重叠的shuffle依赖(即B的祖先依赖)的stage,由于之前已经注册过了所以并不会真正创建而是直接使用已经注册过的stage - 构建
ShuffleMapStage后,在stageIdToStage,shuffleIdToMapStage,jobIdToStageIds中注册。 - 如果
MapOutputTrackerMaster中没有注册则注册,并返回当前stage
def createShuffleMapStage(shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _], jobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = { val rdd = shuffleDep.rdd checkBarrierStageWithDynamicAllocation(rdd) checkBarrierStageWithNumSlots(rdd) checkBarrierStageWithRDDChainPattern(rdd, rdd.getNumPartitions) val numTasks = rdd.partitions.length val parents = getOrCreateParentStages(rdd, jobId) val id = nextStageId.getAndIncrement() val stage = new ShuffleMapStage( id, rdd, numTasks, parents, jobId, rdd.creationSite, shuffleDep, mapOutputTracker) stageIdToStage(id) = stage shuffleIdToMapStage(shuffleDep.shuffleId) = stage updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage) if (!mapOutputTracker.containsShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId)) { // Kind of ugly: need to register RDDs with the cache and map output tracker here // since we can't do it in the RDD constructor because # of partitions is unknown logInfo(s"Registering RDD ${rdd.id} (${rdd.getCreationSite}) as input to " + s"shuffle ${shuffleDep.shuffleId}") mapOutputTracker.registerShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId, rdd.partitions.length) } stage }- 首先检查屏障调度的运行条件,调用
createResultStage(): 创建并注册ResultStage- 调用
getOrCreateParentStages()方法,创建了当前RDD的所有祖先shuffle依赖的stage,并获得当前RDD的Stage - 创建
ResultStage并注册
private def createResultStage( rdd: RDD[_], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _, partitions: Array[Int], jobId: Int, callSite: CallSite): ResultStage = { checkBarrierStageWithDynamicAllocation(rdd) checkBarrierStageWithNumSlots(rdd) checkBarrierStageWithRDDChainPattern(rdd, partitions.toSet.size) val parents = getOrCreateParentStages(rdd, jobId) val id = nextStageId.getAndIncrement() val stage = new ResultStage(id, rdd, func, partitions, parents, jobId, callSite) stageIdToStage(id) = stage updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage) stage }- 调用
getMissingParentStages(): 获取当前Stage的所有未提交的父Stage- 从当前
Stage的RDD开始深搜,调用getCacheLocs(),如果出现partition丢失,则需重新计算这个RDD - 将所有不可用(
mapStage.isAvailable)的shuffle依赖的Stage添加进miss序列并返回
private def getMissingParentStages(stage: Stage): List[Stage] = { val missing = new HashSet[Stage] val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]] // We are manually maintaining a stack here to prevent StackOverflowError // caused by recursively visiting val waitingForVisit = new ArrayStack[RDD[_]] def visit(rdd: RDD[_]) { if (!visited(rdd)) { visited += rdd val rddHasUncachedPartitions = getCacheLocs(rdd).contains(Nil) if (rddHasUncachedPartitions) { for (dep <- rdd.dependencies) { dep match { case shufDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] => val mapStage = getOrCreateShuffleMapStage(shufDep, stage.firstJobId) if (!mapStage.isAvailable) { missing += mapStage } case narrowDep: NarrowDependency[_] => waitingForVisit.push(narrowDep.rdd) } } } } } waitingForVisit.push(stage.rdd) while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) { visit(waitingForVisit.pop()) } missing.toList }- 从当前
下面介绍提交job以及stage提交有关的方法
submitJob(): 提交一个job- 检查提交的partition是否合法,生成下一个job id
- 如果partition数量为0,则直接返回
JobWaiter,该JobWaiter的jobPromise将被置为success,这样就意味着这个job已经完成 - 否则,构建
JobWaiter,并向eventProcessLoop发送JobSubmitted事件,这将交由DagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted异步执行
def submitJob[T, U]( rdd: RDD[T], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U, partitions: Seq[Int], callSite: CallSite, resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit, properties: Properties): JobWaiter[U] = { // Check to make sure we are not launching a task on a partition that does not exist. val maxPartitions = rdd.partitions.length partitions.find(p => p >= maxPartitions || p < 0).foreach { p => throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Attempting to access a non-existent partition: " + p + ". " + "Total number of partitions: " + maxPartitions) } val jobId = nextJobId.getAndIncrement() if (partitions.size == 0) { // Return immediately if the job is running 0 tasks return new JobWaiter[U](this, jobId, 0, resultHandler) } assert(partitions.size > 0) val func2 = func.asInstanceOf[(TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _] val waiter = new JobWaiter(this, jobId, partitions.size, resultHandler) eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted( jobId, rdd, func2, partitions.toArray, callSite, waiter, SerializationUtils.clone(properties))) waiter }runJob(): 调用了submitJob()的同步方法,通过返回的JobWaiter等待job执行完,如果执行失败则抛出异常
下面介绍与处理job有关的方法
handleJobSubmitted(): 处理job提交事件,进行stage切分- 调用
createResultStage()创建ResultStage,此时已经处理好了此stage的所有shuffle依赖,即已经进行了stage划分 - 创建并注册
ActiveJob并清空cacheLocs - 获取当前Job的所有
Stage对应的StageInfo(不只是当前的Stage,由于调用了createResultStage(),所以还包括依赖的父Stage),并向LiveListenerBus投递SparkListenerJobStart事件,进而引发所有关注此事件的监听器执行相应的操作 - 调用
submitStage()提交当前Stage
private[scheduler] def handleJobSubmitted(jobId: Int, finalRDD: RDD[_], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _, partitions: Array[Int], callSite: CallSite, listener: JobListener, properties: Properties) { var finalStage: ResultStage = null try { // New stage creation may throw an exception if, for example, jobs are run on a // HadoopRDD whose underlying HDFS files have been deleted. finalStage = createResultStage(finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId, callSite) } catch { case e: BarrierJobSlotsNumberCheckFailed => logWarning(s"The job $jobId requires to run a barrier stage that requires more slots " + "than the total number of slots in the cluster currently.") // If jobId doesn't exist in the map, Scala coverts its value null to 0: Int automatically. val numCheckFailures = barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.compute(jobId, new BiFunction[Int, Int, Int] { override def apply(key: Int, value: Int): Int = value + 1 }) if (numCheckFailures <= maxFailureNumTasksCheck) { messageScheduler.schedule(new Runnable { override def run(): Unit = eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(jobId, finalRDD, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)) }, timeIntervalNumTasksCheck, TimeUnit.SECONDS ) return } else { // Job failed, clear internal data. barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.remove(jobId) listener.jobFailed(e) return } case e: Exception => logWarning("Creating new stage failed due to exception - job: " + jobId, e) listener.jobFailed(e) return } // Job submitted, clear internal data. barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.remove(jobId) val job = new ActiveJob(jobId, finalStage, callSite, listener, properties) clearCacheLocs() logInfo("Got job %s (%s) with %d output partitions".format( job.jobId, callSite.shortForm, partitions.length)) logInfo("Final stage: " + finalStage + " (" + finalStage.name + ")") logInfo("Parents of final stage: " + finalStage.parents) logInfo("Missing parents: " + getMissingParentStages(finalStage)) val jobSubmissionTime = clock.getTimeMillis() jobIdToActiveJob(jobId) = job activeJobs += job finalStage.setActiveJob(job) val stageIds = jobIdToStageIds(jobId).toArray val stageInfos = stageIds.flatMap(id => stageIdToStage.get(id).map(_.latestInfo)) listenerBus.post( SparkListenerJobStart(job.jobId, jobSubmissionTime, stageInfos, properties)) submitStage(finalStage) }- 调用
submitStage(): 提交Stage,将优先提交父Stage- 调用
activeJobForStage()方法,找到Stage最早创建的ActiveJob - 如果不存job,则终止当前
Stage。如果存在job,并且该Stage并不是waiting, runnning, failed状态,则 - 调用
getMissingParentStages()获取所有未提交的父Stage - 如果没有未提交的父
Stage,则调用submitMissingTasks()提交当前Stage的所有未提交Task - 如果存在未提交的父
Stage,则递归调用submitStage()提交父Stage并把当前Stage加入waitingStages
private def submitStage(stage: Stage) { val jobId = activeJobForStage(stage) if (jobId.isDefined) { logDebug(s"submitStage($stage (name=${stage.name};" + s"jobs=${stage.jobIds.toSeq.sorted.mkString(",")}))") if (!waitingStages(stage) && !runningStages(stage) && !failedStages(stage)) { val missing = getMissingParentStages(stage).sortBy(_.id) logDebug("missing: " + missing) if (missing.isEmpty) { logInfo("Submitting " + stage + " (" + stage.rdd + "), which has no missing parents") submitMissingTasks(stage, jobId.get) } else { for (parent <- missing) { submitStage(parent) } waitingStages += stage } } } else { abortStage(stage, "No active job for stage " + stage.id, None) } }- 调用
submitMissingTasks(): 在当前Stage的所有父Stage都可用时,进行task切分并提交当前TaskSet至TaskScheduler- 调用
Stage.findMissingPartitions()找出未计算的partition。将当前Stage加入runningStages - 为每一个未计算的partition获取偏好位置,调用
stage.makeNewStageAttempt()开始进行stage尝试并向listenerBus投递SparkListenerStageSubmitted事件 - 调用
OutputCommitCoordinator.stageStart()方法,启动对当前Stage的输出提交到HDFS的协调 - 如果当前
Stage是ShuffleMapStage,那么对Stage的RDD和ShuffleDependency进行序列化;如果当前Stage是ResultStage,那么对Stage的RDD和计算函数func进行序列化。并且将序列化后的数据添加到广播变量 - 如果当前
Stage是ShuffleMapStage,则为ShuffleMapStage的每一个待计算partition创建一个ShuffleMapTask。如果当前Stage是ResultStage,则为ResultStage的每一个待计算partition创建一个ResultTask - 如果在上一个步骤中创建了
Task,则为刚创建的那批Task创建TaskSet,并调用TaskScheduler.submitTasks()方法提交此TaskSet - 如果没有创建
Task,则标记当前Stage已经完成,并调用submitWaitingChildStages()提交子stage
private def submitMissingTasks(stage: Stage, jobId: Int) { logDebug("submitMissingTasks(" + stage + ")") // First figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute. val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions() // Use the scheduling pool, job group, description, etc. from an ActiveJob associated // with this Stage val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties runningStages += stage // SparkListenerStageSubmitted should be posted before testing whether tasks are // serializable. If tasks are not serializable, a SparkListenerStageCompleted event // will be posted, which should always come after a corresponding SparkListenerStageSubmitted // event. stage match { case s: ShuffleMapStage => outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.numPartitions - 1) case s: ResultStage => outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart( stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.rdd.partitions.length - 1) } val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try { stage match { case s: ShuffleMapStage => partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap case s: ResultStage => partitionsToCompute.map { id => // id难道不是和partition id 对应的吗 val p = s.partitions(id) (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p)) }.toMap } } catch { case NonFatal(e) => stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size) listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties)) abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e\n${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e)) runningStages -= stage return } stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size, taskIdToLocations.values.toSeq) // If there are tasks to execute, record the submission time of the stage. Otherwise, // post the even without the submission time, which indicates that this stage was // skipped. if (partitionsToCompute.nonEmpty) { stage.latestInfo.submissionTime = Some(clock.getTimeMillis()) } listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties)) var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null var partitions: Array[Partition] = null try { // For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep). // For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func). var taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = null // taskBinaryBytes and partitions are both effected by the checkpoint status. We need // this synchronization in case another concurrent job is checkpointing this RDD, so we get a // consistent view of both variables. RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { taskBinaryBytes = stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => JavaUtils.bufferToArray( closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef)) case stage: ResultStage => JavaUtils.bufferToArray(closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef)) } partitions = stage.rdd.partitions } taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes) } catch { // In the case of a failure during serialization, abort the stage. case e: NotSerializableException => abortStage(stage, "Task not serializable: " + e.toString, Some(e)) runningStages -= stage // Abort execution return case e: Throwable => abortStage(stage, s"Task serialization failed: $e\n${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e)) runningStages -= stage // Abort execution return } val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try { val serializedTaskMetrics = closureSerializer.serialize(stage.latestInfo.taskMetrics).array() stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => stage.pendingPartitions.clear() partitionsToCompute.map { id => val locs = taskIdToLocations(id) val part = partitions(id) stage.pendingPartitions += id new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, taskBinary, part, locs, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier()) } case stage: ResultStage => partitionsToCompute.map { id => val p: Int = stage.partitions(id) val part = partitions(p) val locs = taskIdToLocations(id) new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, taskBinary, part, locs, id, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier()) } } } catch { case NonFatal(e) => abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e\n${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e)) runningStages -= stage return } if (tasks.size > 0) { logInfo(s"Submitting ${tasks.size} missing tasks from $stage (${stage.rdd}) (first 15 " + s"tasks are for partitions ${tasks.take(15).map(_.partitionId)})") taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet( tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, jobId, properties)) } else { // Because we posted SparkListenerStageSubmitted earlier, we should mark // the stage as completed here in case there are no tasks to run markStageAsFinished(stage, None) stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => logDebug(s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; " + s"(available: ${stage.isAvailable}," + s"available outputs: ${stage.numAvailableOutputs}," + s"partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})") markMapStageJobsAsFinished(stage) case stage : ResultStage => logDebug(s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; (partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})") } submitWaitingChildStages(stage) } }- 调用
submitWaitingChildStages(): 从waitingStages中取出Stage并通过submitStage()提交private def submitWaitingChildStages(parent: Stage) { logTrace(s"Checking if any dependencies of $parent are now runnable") logTrace("running: " + runningStages) logTrace("waiting: " + waitingStages) logTrace("failed: " + failedStages) val childStages = waitingStages.filter(_.parents.contains(parent)).toArray waitingStages --= childStages for (stage <- childStages.sortBy(_.firstJobId)) { submitStage(stage) } }
下面介绍对Task结果处理的方法
taskEnded(): 向DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop投递CompletionEvent事件,实际上交由DAGScheduler.handleTaskCompletion()处理def taskEnded( task: Task[_], reason: TaskEndReason, result: Any, accumUpdates: Seq[AccumulatorV2[_, _]], taskInfo: TaskInfo): Unit = { eventProcessLoop.post( CompletionEvent(task, reason, result, accumUpdates, taskInfo)) }handleTaskCompletion(): 标记当前task已经完成,然后做以下操作- 如果是
ResultTask,如果所有ResultTask都执行成功,则标记ResultStage为成功,并调用JobWaiter.resultHandler()回调函数来处理Job中每个Task的执行结果 - 如果是
ShuffleMapTask,调用MapOutputTrackerMaster.registerMapOutput()将完成信息注册。如果所有partition都执行完了,则判断shuffleStage.isAvailable并进行失败重试,否则标记stage成功并调用submitWaitingChildStages()方法处理子stage
- 如果是
总结
如下图所示,展示了DAGScheduler对job提交的整个流程
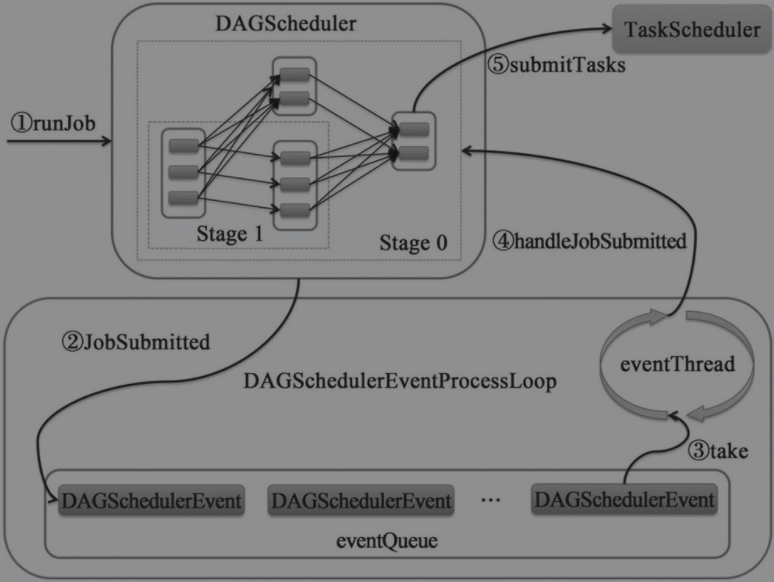
- 应用程序通过对Spark API的调用,进行一系列RDD转换构建出RDD之间的依赖关系后,调用
DAGScheduler.runJob()方法交由DAGScheduler进行调度并等待job执行完成 - 实际调用
DAGScheduler.submitJob()方法向DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop发送JobSubmitted事件并放入事件队列 DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop内部的轮询线程eventThread不断从事件队列中获取DAGSchedulerEvent事件,并调用DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop.doOnReceive()方法对事件进行处理,在方法内通过模式匹配出JobSubmitted并调用DAGScheduler.handleJobSubmitted()进行处理handleJobSubmitted()方法将对RDD的所有祖先依赖切分成stage,具体过程如下一张图所示DAGScheduler首先创建最上游的Stage的TaskSet并调用TaskScheduler.submitTasks()提交给TaskScheduler,对所有Task进行调度。待所有task执行完毕后,handleEnd()方法将被调用接着与步骤3类似的方式最终交由handleTaskCompletion()方法处理,创建下游的Stage的TaskSet并提交给TaskScheduler。直至最后的ResultTask都执行完毕,即可使用JobWaiter中的回调函数对结果进行处理
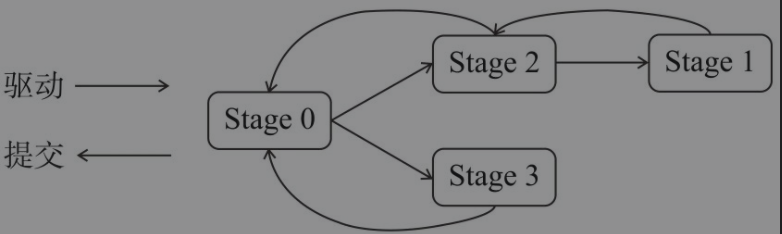
如图所示,每个stage都是对shuffle依赖和父rdd和祖先stage的封装,所以stage的切分标准是shuffle依赖。最开始提交的是stage0,DAGScheduler会由stage0反向驱动直至寻找到最古老的祖先stage1,再由stage1开始逐步正向提交至stage0
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/09/14/schedule-stage/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)