Tungsten是一种内存分配与释放的实现,包括堆内内存和堆外内存。Tungsten使用sun.misc.Unsafe直接操作系统内存,避免了在JVM中加载额外的类,也不用创建额外的对象,因而减少了不必要的内存开销,降低了GC扫描和回收的频率,提升了处理性能。堆外内存可以被精确地申请和释放,而且序列化的数据占用的空间可以被精确计算,所以相比堆内存来说降低了管理的难度,也降低了误差。
MemoryBlock
MemoryBlock继承自MemoryLocation。当跟踪堆外分配时,obj为空,此时offset表示堆外内存地址。当跟踪堆内分配时,堆内内存地址为obj+offset(对象内偏移量)
public class MemoryLocation {
@Nullable
Object obj;
long offset;
public MemoryLocation(@Nullable Object obj, long offset) {
this.obj = obj;
this.offset = offset;
}
public MemoryLocation() {
this(null, 0);
}
public void setObjAndOffset(Object newObj, long newOffset) {
this.obj = newObj;
this.offset = newOffset;
}
public final Object getBaseObject() {
return obj;
}
public final long getBaseOffset() {
return offset;
}
}
MemoryBlock是Tungsten中实现了一种与操作系统的内存page非常相似的数据结构,可能是堆内内存也可能是堆外内存。MemoryBlock继承了MemoryLocation,表示从MemoryLocation开始的连续内存的block,具体存储的数据放在obj中,一般为long数组。有以下成员属性
length: 内存block大小pageNumber: 由MemoryBlock分配的页号,这个字段是公有的FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER: -3,表示此页已经被MemoryAllocator释放,用于检测重复释放NO_PAGE_NUMBER: -1,表示未分配的页FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER: -2,表示此页已经被TaskMemoryManager释放,防止在调用TaskMemoryManager.freePage()后又调用MemoryAllocator.free()
主要有两个成员方法
fromLongArray(): 创建一个指向long数组使用内存的MemoryBlockpublic static MemoryBlock fromLongArray(final long[] array) { return new MemoryBlock(array, Platform.LONG_ARRAY_OFFSET, array.length * 8L); }fill(): 使用Spark封装的sun.misc.Unsafe包下的方法填充整个MemoryBlockpublic void fill(byte value) { Platform.setMemory(obj, offset, length, value); }
MemoryManager
管理存储内存和计算内存。有以下与计算内存相关的成员属性
tungstenMemoryMode: 读取spark.memory.offHeap.enabled(默认为false)和spark.memory.offHeap.size来决定Tungsten使用堆内还是堆外内存pageSizeBytes: Tungsten采用的page默认大小。默认通过spark.buffer.pageSize来指定,否则通过如下方式来计算val pageSizeBytes: Long = { val minPageSize = 1L * 1024 * 1024 // 1MB val maxPageSize = 64L * minPageSize // 64MB val cores = if (numCores > 0) numCores else Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors() // Because of rounding to next power of 2, we may have safetyFactor as 8 in worst case val safetyFactor = 16 val maxTungstenMemory: Long = tungstenMemoryMode match { case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.poolSize case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.poolSize } val size = ByteArrayMethods.nextPowerOf2(maxTungstenMemory / cores / safetyFactor) val default = math.min(maxPageSize, math.max(minPageSize, size)) conf.getSizeAsBytes("spark.buffer.pageSize", default) }tungstenMemoryAllocator: Tungsten采用的内存分配器MemoryAllocator,根据tungstenMemoryMode确定是堆外还是堆内内存分配器
MemoryAllocator
接口MemoryAllocator主要定义了两个抽象方法,allocate()用于分配MemoryBlock,free()用于释放MemoryBlock。定义了两个成员,UNSAFE表示堆外内存分配器,HEAP表示堆内内存分配器,分别对应着这个接口的两个实现类
HeapMemoryAllocator
堆内内存分配器。成员属性bufferPoolsBySize,类型为Map<Long, LinkedList<WeakReference<long[]>>>,保存了内存block大小和long数组弱引用池的对应关系,用于MemoryBlock的分配。有以下成员方法
shouldPool(): 判断对于指定大小的MemoryBlock是否需要采用池化机制,即是否需要缓存MemoryBlock中的long数组。当MemoryBlock大于1M则需要池化allocate(): 分配指定大小的MemoryBlock- 如果
MemoryBlock需要池化则从bufferPoolsBySize取出指定大小且未GC的long数组并封装成MemoryBlock返回,如果弱引用池中没有long数组则从bufferPoolsBySize中移除 - 如果不需要池化或者对应大小的弱引用池为空,则创建新的long数组并封装成
MemoryBlock并返回
@Override public MemoryBlock allocate(long size) throws OutOfMemoryError { int numWords = (int) ((size + 7) / 8); long alignedSize = numWords * 8L; assert (alignedSize >= size); if (shouldPool(alignedSize)) { synchronized (this) { final LinkedList<WeakReference<long[]>> pool = bufferPoolsBySize.get(alignedSize); if (pool != null) { while (!pool.isEmpty()) { final WeakReference<long[]> arrayReference = pool.pop(); final long[] array = arrayReference.get(); if (array != null) { assert (array.length * 8L >= size); MemoryBlock memory = new MemoryBlock(array, Platform.LONG_ARRAY_OFFSET, size); if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) { memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_CLEAN_VALUE); } return memory; } } bufferPoolsBySize.remove(alignedSize); } } } long[] array = new long[numWords]; MemoryBlock memory = new MemoryBlock(array, Platform.LONG_ARRAY_OFFSET, size); if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) { memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_CLEAN_VALUE); } return memory; }- 如果
free(): 释放指定的MemoryBlock- 将内存block的页号置为
FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER用于避免重复释放 - 将
MemoryBlock中long数组的内容置空,此时内存block已经释放完毕 - 如果这个大小的内存block采用了池化,则将之前释放的long数组放入弱引用池中,用于下一个
allocate()方法的分配,省去了一个GC再创建的花费
@Override public void free(MemoryBlock memory) { assert (memory.obj != null) : "baseObject was null; are you trying to use the on-heap allocator to free off-heap memory?"; assert (memory.pageNumber != MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER) : "page has already been freed"; assert ((memory.pageNumber == MemoryBlock.NO_PAGE_NUMBER) || (memory.pageNumber == MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER)) : "TMM-allocated pages must first be freed via TMM.freePage(), not directly in allocator " + "free()"; final long size = memory.size(); if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) { memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_FREED_VALUE); } // Mark the page as freed (so we can detect double-frees). memory.pageNumber = MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER; // As an additional layer of defense against use-after-free bugs, we mutate the // MemoryBlock to null out its reference to the long[] array. long[] array = (long[]) memory.obj; memory.setObjAndOffset(null, 0); long alignedSize = ((size + 7) / 8) * 8; if (shouldPool(alignedSize)) { synchronized (this) { LinkedList<WeakReference<long[]>> pool = bufferPoolsBySize.get(alignedSize); if (pool == null) { pool = new LinkedList<>(); bufferPoolsBySize.put(alignedSize, pool); } pool.add(new WeakReference<>(array)); } } else { // Do nothing } }- 将内存block的页号置为
UnsafeMemoryAllocator
堆外内存分配器。有以下实现的方法
allocate(): 分配指定大小的MemoryBlock。使用了Spark封装的sun.misc.Unsafe方法,将地址和大小封装为MemoryBlock返回@Override public MemoryBlock allocate(long size) throws OutOfMemoryError { long address = Platform.allocateMemory(size); MemoryBlock memory = new MemoryBlock(null, address, size); if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) { memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_CLEAN_VALUE); } return memory; }free(): 释放MemoryBlock。同样使用了Spark封装的sun.misc.Unsafe方法去释放内存,并标记页号表示已经被释放,避免重复释放@Override public void free(MemoryBlock memory) { assert (memory.obj == null) : "baseObject not null; are you trying to use the off-heap allocator to free on-heap memory?"; assert (memory.pageNumber != MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER) : "page has already been freed"; assert ((memory.pageNumber == MemoryBlock.NO_PAGE_NUMBER) || (memory.pageNumber == MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER)) : "TMM-allocated pages must be freed via TMM.freePage(), not directly in allocator free()"; if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) { memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_FREED_VALUE); } Platform.freeMemory(memory.offset); // As an additional layer of defense against use-after-free bugs, we mutate the // MemoryBlock to reset its pointer. memory.offset = 0; // Mark the page as freed (so we can detect double-frees). memory.pageNumber = MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER; }
TaskMemoryManager
管理单个task尝试的内存分配与释放,多个TaskMemoryManager共享MemoryManager提供的内存管理能力。
包含以下重要的成员属性
PAGE_NUMBER_BITS: 用于保存编码后的存储页号的位数。初始值为13,在64位的长整型中将使用高位的13位存储页号OFFSET_BITS: 用于保存编码后的页内偏移量的位数。初始值为51,在64位的长整型中将使用低位的51位存页内储偏移量PAGE_TABLE_SIZE: 页表中的page数量。初始值为8192,实际是将1向左位移13位所得的值,1 << PAGE_NUMBER_BITSMAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES: 最大的page大小。初始值为 $(2^{32}-1)\times 8$MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS: 长整型的低51位的位掩码,用于计算页内偏移量。初始值为十六进制0x7FFFFFFFFFFFFpageTable: 页表。MemoryBlock[PAGE_TABLE_SIZE]allocatedPages: 跟踪空闲page的位图。BitSet(PAGE_TABLE_SIZE)taskAttemptId:TaskMemoryManageridtungstenMemoryMode: Tungsten的内存模式。使用了成员属性memoryManager的内存模式consumers: 跟踪可溢出的内存消费者。HashSet<MemoryConsumer>acquiredButNotUsed: task尝试已经获得但是并未使用的内存大小
有以下重要的成员方法
acquireExecutionMemory(): 为获得指定大小的内存。当此task尝试没有足够内存时,调用MemoryConsumer.spill()溢出数据至硬盘以释放内存- 首先,调用
MemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory()尝试为当前task尝试分配指定内存模式的计算内存 - 如果已经获得了当前期望的内存,则直接将内存消费者添加进
consumers并返回获得的内存大小,如果不能获得期望的内存,则做以下工作 - 遍历
consumers,在本task尝试的所有consumer中,将已使用了内存且内存模式相同的consumer与其使用内存大小放入类型为TreeMap<Long, List<MemoryConsumer>>的sortedConsumers变量中(底层为红黑树,按照已使用内存有序排列) - 循环做以下操作,每次挑出使用内存最接近所需内存的consumer进行释放,这样可以避免频繁spill相同的consumer从而产生许多小文件
- 从
sortedConsumers中取出刚好大于仍需内存(大于仍需内存的最小内存)的consumer列表(可能有多个consumer拥有相同的已使用内存),如果不存在这个键值对则取最后一个即使用内存最大的那个consumer列表 - 取出列表中最后一个consumer并调用
MemoryConsumer.spill()尝试释放所需内存。根据返回值判断如果释放了内存则调用MemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory()去获取刚刚释放的内存并更新所需内存值。如果没有释放内存则从sortedConsumers中移除这个consumer,因为它已经没有内存可以释放了
- 从
- 如果还不能满足内存需要则释放当前的内存消费者的使用内存
public long acquireExecutionMemory(long required, MemoryConsumer consumer) { assert(required >= 0); assert(consumer != null); MemoryMode mode = consumer.getMode(); synchronized (this) { long got = memoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory(required, taskAttemptId, mode); // Try to release memory from other consumers first, then we can reduce the frequency of // spilling, avoid to have too many spilled files. if (got < required) { // Call spill() on other consumers to release memory // Sort the consumers according their memory usage. So we avoid spilling the same consumer // which is just spilled in last few times and re-spilling on it will produce many small // spill files. TreeMap<Long, List<MemoryConsumer>> sortedConsumers = new TreeMap<>(); for (MemoryConsumer c: consumers) { if (c != consumer && c.getUsed() > 0 && c.getMode() == mode) { long key = c.getUsed(); List<MemoryConsumer> list = sortedConsumers.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>(1)); list.add(c); } } while (!sortedConsumers.isEmpty()) { // Get the consumer using the least memory more than the remaining required memory. Map.Entry<Long, List<MemoryConsumer>> currentEntry = sortedConsumers.ceilingEntry(required - got); // No consumer has used memory more than the remaining required memory. // Get the consumer of largest used memory. if (currentEntry == null) { currentEntry = sortedConsumers.lastEntry(); } List<MemoryConsumer> cList = currentEntry.getValue(); MemoryConsumer c = cList.get(cList.size() - 1); try { long released = c.spill(required - got, consumer); if (released > 0) { logger.debug("Task {} released {} from {} for {}", taskAttemptId, Utils.bytesToString(released), c, consumer); got += memoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory(required - got, taskAttemptId, mode); if (got >= required) { break; } } else { cList.remove(cList.size() - 1); if (cList.isEmpty()) { sortedConsumers.remove(currentEntry.getKey()); } } } catch (ClosedByInterruptException e) { // This called by user to kill a task (e.g: speculative task). logger.error("error while calling spill() on " + c, e); throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage()); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("error while calling spill() on " + c, e); throw new SparkOutOfMemoryError("error while calling spill() on " + c + " : " + e.getMessage()); } } } // call spill() on itself if (got < required) { try { long released = consumer.spill(required - got, consumer); if (released > 0) { logger.debug("Task {} released {} from itself ({})", taskAttemptId, Utils.bytesToString(released), consumer); got += memoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory(required - got, taskAttemptId, mode); } } catch (ClosedByInterruptException e) { // This called by user to kill a task (e.g: speculative task). logger.error("error while calling spill() on " + consumer, e); throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage()); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("error while calling spill() on " + consumer, e); throw new SparkOutOfMemoryError("error while calling spill() on " + consumer + " : " + e.getMessage()); } } consumers.add(consumer); logger.debug("Task {} acquired {} for {}", taskAttemptId, Utils.bytesToString(got), consumer); return got; } }- 首先,调用
releaseExecutionMemory(): 调用了MemoryManager.releaseExecutionMemory()释放内存public void releaseExecutionMemory(long size, MemoryConsumer consumer) { logger.debug("Task {} release {} from {}", taskAttemptId, Utils.bytesToString(size), consumer); memoryManager.releaseExecutionMemory(size, taskAttemptId, consumer.getMode()); }showMemoryUsage(): 将task尝试、各个MemoryConsumer及MemoryManager管理的执行内存和存储内存的使用情况打印到日志allocatePage(): 给内存消费者分配指定大小的MemoryBlock- 调用
acquireExecutionMemory()方法为consumer获得内存,如果获取不了足够的内存则返回null - 从
allocatedPages获得最小的未分配的页号作为当前分配的页号 - 调用
MemoryAllocator.allocate()获取封装成MemoryBlock的页 - 如果OOM则说明物理内存大小小于
MemoryManager认为自己管理的逻辑内存大小,此时需要更新acquiredButNotUsed,从allocatedPages中清除此页号并再次调用allocatePage()方法 - 将
MemoryBlock放入pageTable中并返回
public MemoryBlock allocatePage(long size, MemoryConsumer consumer) { assert(consumer != null); assert(consumer.getMode() == tungstenMemoryMode); if (size > MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES) { throw new TooLargePageException(size); } long acquired = acquireExecutionMemory(size, consumer); if (acquired <= 0) { return null; } final int pageNumber; synchronized (this) { pageNumber = allocatedPages.nextClearBit(0); if (pageNumber >= PAGE_TABLE_SIZE) { releaseExecutionMemory(acquired, consumer); throw new IllegalStateException( "Have already allocated a maximum of " + PAGE_TABLE_SIZE + " pages"); } allocatedPages.set(pageNumber); } MemoryBlock page = null; try { page = memoryManager.tungstenMemoryAllocator().allocate(acquired); } catch (OutOfMemoryError e) { logger.warn("Failed to allocate a page ({} bytes), try again.", acquired); // there is no enough memory actually, it means the actual free memory is smaller than // MemoryManager thought, we should keep the acquired memory. synchronized (this) { acquiredButNotUsed += acquired; allocatedPages.clear(pageNumber); } // this could trigger spilling to free some pages. return allocatePage(size, consumer); } page.pageNumber = pageNumber; pageTable[pageNumber] = page; if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Allocate page number {} ({} bytes)", pageNumber, acquired); } return page; }- 调用
freePage(): 释放分配给MemoryConsumer的MemoryBlock- 清理
pageTable和allocatedPages中的信息 - 标记页号并调用
MemoryAllocator.free()释放物理内存 - 调用
releaseExecutionMemory()方法
public void freePage(MemoryBlock page, MemoryConsumer consumer) { assert (page.pageNumber != MemoryBlock.NO_PAGE_NUMBER) : "Called freePage() on memory that wasn't allocated with allocatePage()"; assert (page.pageNumber != MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER) : "Called freePage() on a memory block that has already been freed"; assert (page.pageNumber != MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER) : "Called freePage() on a memory block that has already been freed"; assert(allocatedPages.get(page.pageNumber)); pageTable[page.pageNumber] = null; synchronized (this) { allocatedPages.clear(page.pageNumber); } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Freed page number {} ({} bytes)", page.pageNumber, page.size()); } long pageSize = page.size(); // Clear the page number before passing the block to the MemoryAllocator's free(). // Doing this allows the MemoryAllocator to detect when a TaskMemoryManager-managed // page has been inappropriately directly freed without calling TMM.freePage(). page.pageNumber = MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER; memoryManager.tungstenMemoryAllocator().free(page); releaseExecutionMemory(pageSize, consumer); }- 清理
encodePageNumberAndOffset(): 根据给定的MemoryBlock和页内偏移量,返回页号和页内偏移量的编码值- 如果是堆外内存,则
offsetInPage是操作系统内存的绝对地址,offsetInPage与MemoryBlock的起始地址之差就是相对于起始地址的偏移量 - 通过位运算将页号存储到64位长整型的高13位中,并将偏移量存储到64位长整型的低51位中,返回生成的64位的长整型
@VisibleForTesting public static long encodePageNumberAndOffset(int pageNumber, long offsetInPage) { assert (pageNumber >= 0) : "encodePageNumberAndOffset called with invalid page"; return (((long) pageNumber) << OFFSET_BITS) | (offsetInPage & MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS); } public long encodePageNumberAndOffset(MemoryBlock page, long offsetInPage) { if (tungstenMemoryMode == MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP) { // offset offsetInPage -= page.getBaseOffset(); } return encodePageNumberAndOffset(page.pageNumber, offsetInPage); }- 如果是堆外内存,则
decodePageNumber(): 返回编码值的页号@VisibleForTesting public static int decodePageNumber(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { return (int) (pagePlusOffsetAddress >>> OFFSET_BITS); }decodeOffset(): 通过51位的掩码按位进行与运算获得编码值的页内偏移量private static long decodeOffset(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { return (pagePlusOffsetAddress & MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS); }getPage(): 由编码值获取页内的对象(long数组),只对堆内内存模式有用,调用了decodePageNumberpublic Object getPage(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { if (tungstenMemoryMode == MemoryMode.ON_HEAP) { final int pageNumber = decodePageNumber(pagePlusOffsetAddress); assert (pageNumber >= 0 && pageNumber < PAGE_TABLE_SIZE); final MemoryBlock page = pageTable[pageNumber]; assert (page != null); assert (page.getBaseObject() != null); return page.getBaseObject(); } else { return null; } }getOffsetInPage(): 由编码值获取堆内内存的页内偏移量和堆外内存的绝对起始地址- 堆内内存模式直接返回
decodeOffset()解码值即可,因为可以根据getPage()方法获取的页内对象直接定位到内存地址 - 堆外内存模式还需要取出
MemoryBlock,返回MemoryBlock在操作系统内存中的地址与偏移量之和作为偏移量,这样才能定位到内存地址
public long getOffsetInPage(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { final long offsetInPage = decodeOffset(pagePlusOffsetAddress); if (tungstenMemoryMode == MemoryMode.ON_HEAP) { return offsetInPage; } else { // In off-heap mode, an offset is an absolute address. In encodePageNumberAndOffset, we // converted the absolute address into a relative address. Here, we invert that operation: final int pageNumber = decodePageNumber(pagePlusOffsetAddress); assert (pageNumber >= 0 && pageNumber < PAGE_TABLE_SIZE); final MemoryBlock page = pageTable[pageNumber]; assert (page != null); return page.getBaseOffset() + offsetInPage; } }- 堆内内存模式直接返回
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory(): 清空所有page及其内存public long cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory() { synchronized (this) { for (MemoryConsumer c: consumers) { if (c != null && c.getUsed() > 0) { // In case of failed task, it's normal to see leaked memory logger.debug("unreleased " + Utils.bytesToString(c.getUsed()) + " memory from " + c); } } consumers.clear(); for (MemoryBlock page : pageTable) { if (page != null) { logger.debug("unreleased page: " + page + " in task " + taskAttemptId); page.pageNumber = MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER; memoryManager.tungstenMemoryAllocator().free(page); } } Arrays.fill(pageTable, null); } // release the memory that is not used by any consumer (acquired for pages in tungsten mode). memoryManager.releaseExecutionMemory(acquiredButNotUsed, taskAttemptId, tungstenMemoryMode); return memoryManager.releaseAllExecutionMemoryForTask(taskAttemptId); }
MemoryConsumer
抽象类MemoryConsumer定义了内存消费者的规范,它通过TaskMemoryManager在计算内存上申请或释放内存,如下所示为其子类
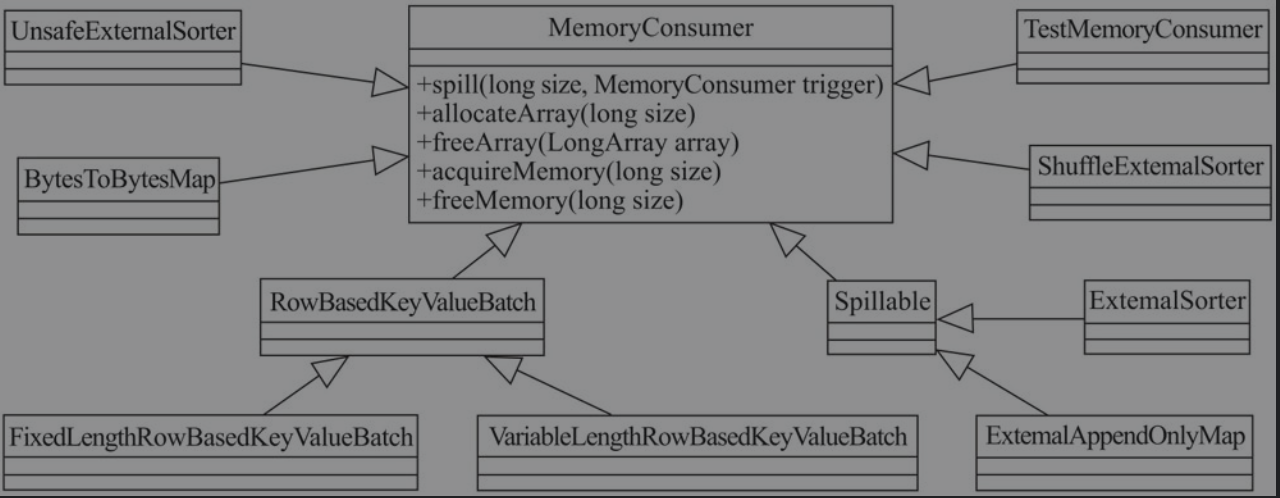
有以下成员属性
taskMemoryManagerpageSize:MemoryConsumer要消费的page的大小mode: 内存模式。getMode()方法用于获取这个属性的值used: 当前consumer已经使用的计算内存的大小。getUsed()方法用于获取这个属性的值
除了未实现的spill()方法外,还有以下成员方法
allocateArray(): 分配指定长度的long数组,long类型占用64bit=8Byte- 调用
TaskMemoryManager.allocatePage()给当前consumer分配相应大小的MemoryBlock - 如果得到的
MemoryBlock小于所需大小则调用TaskMemoryManager.freePage()释放MemoryBlock并抛出OOM - 记录到
used中并创建LongArray,此类调用sun.misc.Unsafe的putLong(object, offset,value)和getLong(object, offset)两个方法来模拟实现长整型数组
public LongArray allocateArray(long size) { long required = size * 8L; MemoryBlock page = taskMemoryManager.allocatePage(required, this); if (page == null || page.size() < required) { throwOom(page, required); } used += required; return new LongArray(page); } private void throwOom(final MemoryBlock page, final long required) { long got = 0; if (page != null) { got = page.size(); taskMemoryManager.freePage(page, this); } taskMemoryManager.showMemoryUsage(); throw new SparkOutOfMemoryError("Unable to acquire " + required + " bytes of memory, got " + got); }- 调用
freeArray(): 释放LongArraypublic void freeArray(LongArray array) { freePage(array.memoryBlock()); } protected void freePage(MemoryBlock page) { used -= page.size(); taskMemoryManager.freePage(page, this); }acquireMemory(): 调用TaskMemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory()获得内存public long acquireMemory(long size) { long granted = taskMemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory(size, this); used += granted; return granted; }freeMemory(): 调用TaskMemoryManager.releaseExecutionMemory()释放内存public void freeMemory(long size) { taskMemoryManager.releaseExecutionMemory(size, this); used -= size; }
总结
如下所示,堆内内存分配器HeapMemoryAllocator基于JVM堆内存的分配流程
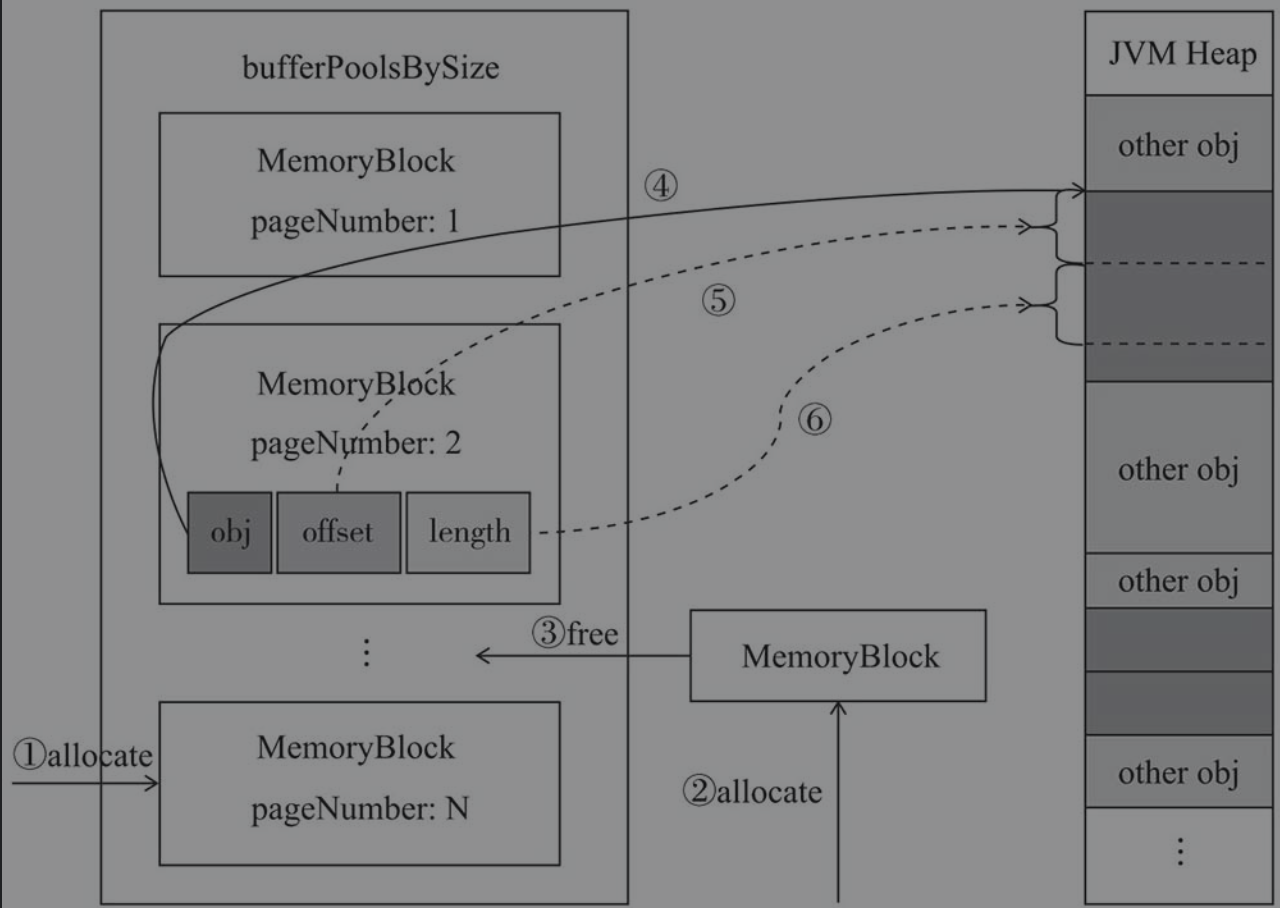
- 当申请超过1M的
MemoryBlock时,此时使用了池化策略,直接从bufferPoolsBySize中取出对应大小的虚引用池,从虚引用池中取出long数组封装为MemoryBlock并返回 - 如果没达到池化的要求或者虚引用池没有,则创建long数组封装为
MemoryBlock并返回 - 释放
MemoryBlock时,如果达到池化要求则将long数组放入bufferPoolsBySize中
序号4表示obj变量保存了对象在堆内内存的地址,序号5表示offset变量保存了MemoryBlock相对于obj地址的偏移量,序号6表示length变量保存了MemoryBlock的大小
如下所示,堆外内存分配器UnsafeMemoryAllocator对堆外内存的分配流程
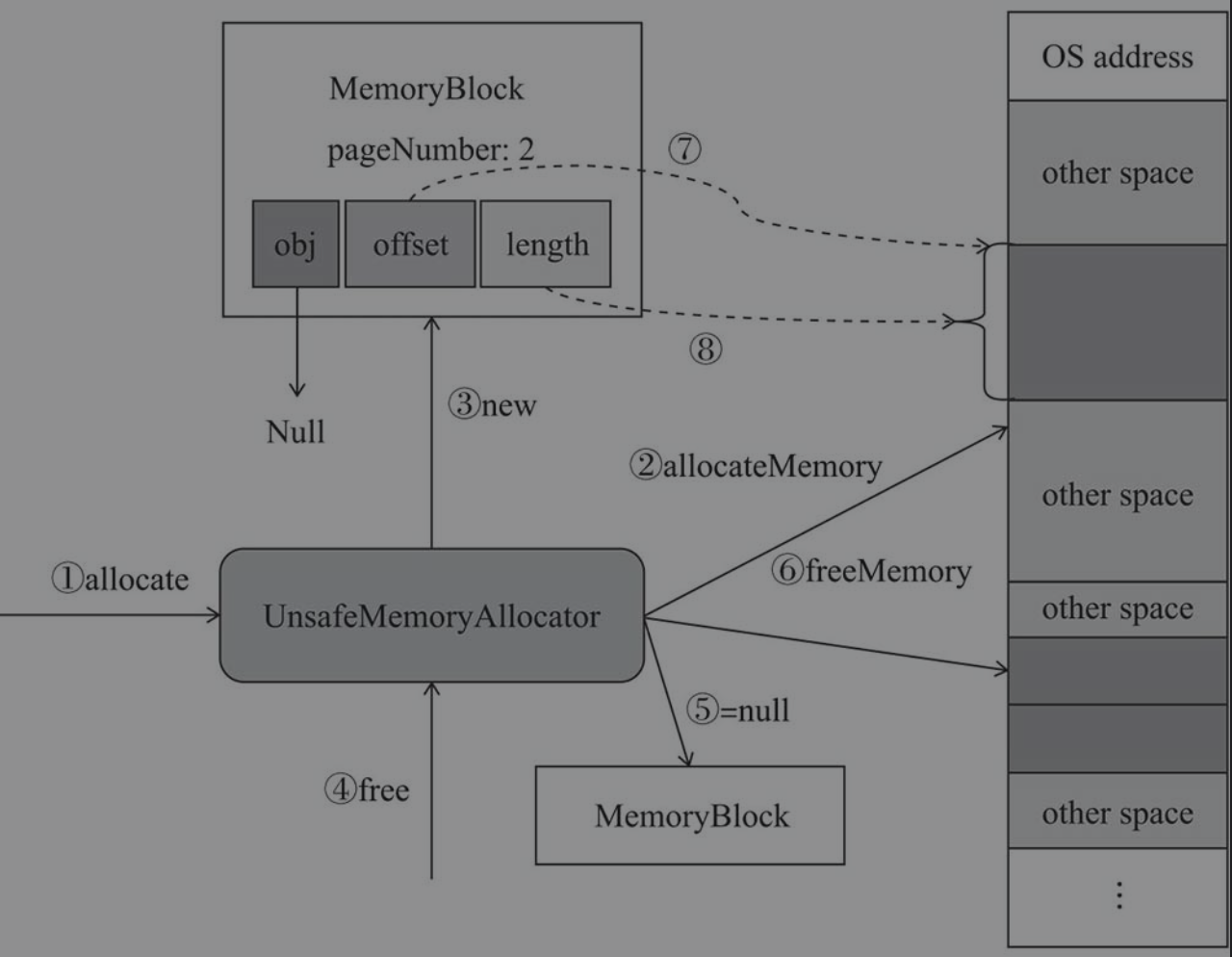
- 如果调用
UnsafeMemeoryAllocator.allocate()请求分配内存 - 方法内部将会调用
sun.misc.Unsafe下的方法请求系统分配内存 UnsafeMemeoryAllocator将返回后的地址封装成MemoryBlock- 如果调用
UnsafeMemoryAllocator.free()释放MemoryBlock - 之前调用方已经将此
MemoryBlock的引用设置为null - 调用
sun.misc.Unsafe下的方法释放内存
序号7表示offset变量保存内存block起始地址,序号8表示length保存内存block大小
如下所示,计算内存的整体架构
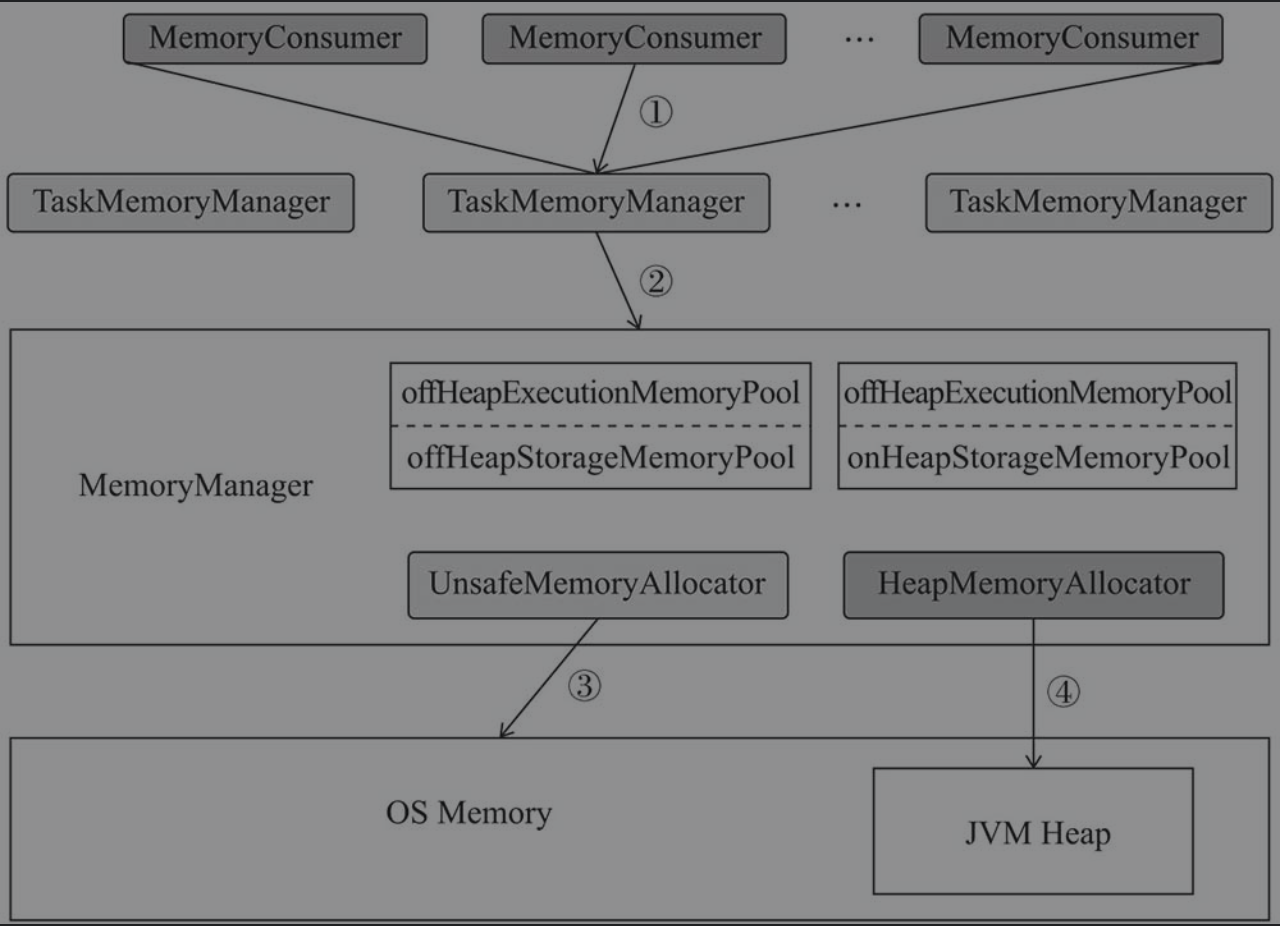
MemoryConsumer通过某个task的TaskMemoryManager获取或者释放计算内存TaskMemoryManager依赖于MemoryManager中的成员MemoryPool实现对计算内存的逻辑操作,成员MemoryAllocator实现对计算内存的物理操作UnsafeMemoryAllocator通过sun.misc.Unsafe操作系统内存HeapMemoryAllocator通过在JVM Heap上分配对象的方式操纵JVM Heap
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/09/24/calculation-memory/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)