Spark计算引擎中的排序器
Spillable
继承自MemoryConsumer,抽象类Spillable用于当超过内存阈值时,把内存中的集合溢出到磁盘上。有以下成员属性
taskMemoryManagerinitialMemoryThreshold: 对集合的内存使用进行跟踪的内存阈值的初始值。通过spark.shuffle.spill.initialMemoryThreshold属性获取,默认为5MBnumElementsForceSpillThreshold: 当集合中的元素超过此阈值时,将强制将集合中的数据溢出到磁盘。通过spark.shuffle.spill.numElementsForceSpillThreshold属性配置,默认为Long.MAX_VALUEmyMemoryThreshold: 集合内存大于此阈值时才会进行溢出,防止过多的小容量溢出。初始值等于initialMemoryThreshold_elementsRead: 自从上次溢出后已经读取到集合的元素数量,通过addElementsRead()方法进行更新_memoryBytesSpilled: 内存中的数据已经溢出到磁盘的字节总数__spillCount: 集合产生溢出的次数
下面是成员方法
spill()#1: 实现了父类MemoryConsumer的抽象方法。将一些数据强制溢出到磁盘以释放内存,此方法由TaskMemoryManager调用。- 当task内存管理器是堆内内存模式并且不是由此consumer触发才会去溢出
- 调用未实现的
forceSpill()强制溢出内存中的集合到磁盘中,如果溢出失败返回0,如果溢出成功则更新成员属性并且调用父类MemoryConsumer.freeMemory()释放内存
override def spill(size: Long, trigger: MemoryConsumer): Long = { if (trigger != this && taskMemoryManager.getTungstenMemoryMode == MemoryMode.ON_HEAP) { val isSpilled = forceSpill() if (!isSpilled) { 0L } else { val freeMemory = myMemoryThreshold - initialMemoryThreshold _memoryBytesSpilled += freeMemory releaseMemory() freeMemory } } else { 0L } }maybeSpill(): 模板方法。溢出当前内存中的集合到磁盘中,尝试在溢出前获得更多内存。collection表示溢出到磁盘的集合,currentMemory表示估计的集合大小- 如果自从上次溢出后插入到集合中的数量是32的倍数且集合占用内存达到跟踪的阈值
myMemoryThreshold,则调用父类MemoryConsumer.acquireMemory()方法尝试调用taskMemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory()释放内存,使得当前的内存增加一倍,并更新跟踪阈值myMemoryThreshold - 如果没能获取到足够的内存或者插入次数达到了阈值则调用未实现的
spill()#2去溢出集合到磁盘并重置已读取元素阈值
protected def maybeSpill(collection: C, currentMemory: Long): Boolean = { var shouldSpill = false if (elementsRead % 32 == 0 && currentMemory >= myMemoryThreshold) { // Claim up to double our current memory from the shuffle memory pool val amountToRequest = 2 * currentMemory - myMemoryThreshold val granted = acquireMemory(amountToRequest) myMemoryThreshold += granted // If we were granted too little memory to grow further (either tryToAcquire returned 0, // or we already had more memory than myMemoryThreshold), spill the current collection shouldSpill = currentMemory >= myMemoryThreshold } shouldSpill = shouldSpill || _elementsRead > numElementsForceSpillThreshold // Actually spill if (shouldSpill) { _spillCount += 1 logSpillage(currentMemory) spill(collection) _elementsRead = 0 _memoryBytesSpilled += currentMemory releaseMemory() } shouldSpill }- 如果自从上次溢出后插入到集合中的数量是32的倍数且集合占用内存达到跟踪的阈值
ExternalSorter
ExternalSorter是SortShuffleManager的底层组件,继承自Spillable,功能包括将map任务的输出存储到JVM的堆中,如果指定了聚合函数,则还会对数据进行聚合;使用partition计算器首先将key分组到各个partition中,对每个partition中的key进行可选的排序;将每个partition输出到单个文件的不同字节范围中,便于reduce的shuffle获取。
下面是重要的成员属性
context: TaskContextaggregator:Aggregator[K, V, C]对map任务的输出数据进行聚合的聚合器,三种泛型分别表示key类型,value类型和聚合类型ordering:scala.math.Ordering,key的排序器conf:SparkConfnumPartitions: 通过partitioner.numPartitions()方法获得,默认为1shouldPartition: 是否有partition,即numPartitions大于1的情况fileBufferSize: 用于设置DiskBlockObjectWriter内部的文件缓冲大小。通过spark.shuffle.file.buffer属性进行配置,默认是32KBserializerBatchSize: 用于将DiskBlockObjectWriter内部的文件缓冲写到磁盘的大小。通过spark.shuffle.spill.batchSize属性进行配置,默认是10000map:PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]buffer:PartitionedPairBuffer[K,C]_diskBytesSpilled: 总溢出大小_peakMemoryUsedBytes: 内存中数据结构大小的峰值isShuffleSort: 是否对shuffle数据进行排序forceSpillFiles: 缓存强制溢出的文件数组ArrayBuffer[SpilledFile]。用于当此排序器需要溢出时,溢出迭代器SpillableIterator中的数据至文件。案例类SpilledFile保存了溢出文件的信息private[this] case class SpilledFile( file: File, blockId: BlockId, serializerBatchSizes: Array[Long], elementsPerPartition: Array[Long])readingIterator:SpillableIterator,读取一个溢出文件并返回一个按顺序读取partition的迭代器keyComparator: 与ordering变量含义相同。用于在partition内对中间结果按照key进行排序,以便于聚合。默认比较器为按照两个key的哈希值进行比较private val keyComparator: Comparator[K] = ordering.getOrElse(new Comparator[K] { override def compare(a: K, b: K): Int = { val h1 = if (a == null) 0 else a.hashCode() val h2 = if (b == null) 0 else b.hashCode() if (h1 < h2) -1 else if (h1 == h2) 0 else 1 } })spills: 缓存已溢出的文件数组ArrayBuffer[SpilledFile]
下面是重要的成员方法
insertAll(): 如果定义了聚合器,则对records聚合后插入map中,否则直接插入到buffer中,每次迭代插入时调用maybeSpillCollection()进行可能的溢出- 如果指定了聚合器,则获取聚合器的
mergeValue()函数(用于将新的value合并到聚合结果中)和createCombiner()函数(用于创建聚合结果的初始值) - 定义闭包
update(因为引用了外部变量kv),当有新的value时,调用mergeValue()函数将函数参数oldValue和刚更新的kv._2进行合并,否则说明刚刚开始聚合,此时调用createCombiner()函数生成初始值 - 迭代map输出结果,调用父类
Spillable.addElementsRead()方法增加已读取元素数,调用map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update)将获取到的键值对添加到PartitionedAppendOnlyMap中。PartitionedAppendOnlyMap负责保存(partition id, key)和对应的聚合值,update()函数负责将获取到的value和原聚合值进行合并,最后调用maybeSpillCollection()方法进行可能的磁盘溢出 - 如果没有指定聚合器,则迭代map输出结果,调用父类
Spillable.addElementsRead()方法增加已读取元素数,将调用buffer.insert(getPartition(kv._1), kv._1, kv._2.asInstanceOf[C])获取到的键值对放入PartitionedPairBuffer中,最后调用maybeSpillCollection()方法进行可能的磁盘溢出
def insertAll(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = { val shouldCombine = aggregator.isDefined if (shouldCombine) { // Combine values in-memory first using our AppendOnlyMap val mergeValue = aggregator.get.mergeValue val createCombiner = aggregator.get.createCombiner var kv: Product2[K, V] = null val update = (hadValue: Boolean, oldValue: C) => { if (hadValue) mergeValue(oldValue, kv._2) else createCombiner(kv._2) } while (records.hasNext) { addElementsRead() kv = records.next() map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update) maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true) } } else { // Stick values into our buffer while (records.hasNext) { addElementsRead() val kv = records.next() buffer.insert(getPartition(kv._1), kv._1, kv._2.asInstanceOf[C]) maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = false) } } } private def getPartition(key: K): Int = { if (shouldPartition) partitioner.get.getPartition(key) else 0 }- 如果指定了聚合器,则获取聚合器的
maybeSpillCollection(): 在溢出前尝试获取更多的内存,否则溢出- 如果正在使用
PartitionedAppendOnlyMap,则进行大小估算并调用父类Spillable.maybeSpill()尝试在溢出前获得更多内存,否则调用spill()#2溢出集合并创建一个新的PartitionedAppendOnlyMap - 如果正在使用
PartitionedPairBuffer,与PartitionedAppendOnlyMap的处理流程相同 - 最后更新峰值内存使用
_peakMemoryUsedBytes
private def maybeSpillCollection(usingMap: Boolean): Unit = { var estimatedSize = 0L if (usingMap) { estimatedSize = map.estimateSize() if (maybeSpill(map, estimatedSize)) { map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C] } } else { estimatedSize = buffer.estimateSize() if (maybeSpill(buffer, estimatedSize)) { buffer = new PartitionedPairBuffer[K, C] } } if (estimatedSize > _peakMemoryUsedBytes) { _peakMemoryUsedBytes = estimatedSize } }- 如果正在使用
spill()#2: 实现了父类Spillable中的方法。将内存中的集合溢出到排序好的文件中用于以后合并- 调用
WritablePartitionedPairCollection.destructiveSortedWritablePartitionedIterator()方法返回按顺序写入磁盘的迭代器 - 调用
spillMemoryIteratorToDisk()写入排序好并按partition顺序写入溢出文件- 调用
DiskBlockManager.createTempShuffleBlock()方法创建唯一的用于保存shuffle中间数据的block - 不断调用迭代器的
writeNext()方法,并传入DiskBlockObjectWriter分批次将每个partition写入磁盘 - 在迭代写入的过程,保存
objectsWritten(已写入分区数),elementsPerPartition(统计partition内的元素),batchSizes(总批次数)
- 调用
- 添加到
spillFile中
override protected[this] def spill(collection: WritablePartitionedPairCollection[K, C]): Unit = { val inMemoryIterator = collection.destructiveSortedWritablePartitionedIterator(comparator) val spillFile = spillMemoryIteratorToDisk(inMemoryIterator) spills += spillFile } private[this] def spillMemoryIteratorToDisk(inMemoryIterator: WritablePartitionedIterator) : SpilledFile = { // Because these files may be read during shuffle, their compression must be controlled by // spark.shuffle.compress instead of spark.shuffle.spill.compress, so we need to use // createTempShuffleBlock here; see SPARK-3426 for more context. val (blockId, file) = diskBlockManager.createTempShuffleBlock() // These variables are reset after each flush var objectsWritten: Long = 0 val spillMetrics: ShuffleWriteMetrics = new ShuffleWriteMetrics val writer: DiskBlockObjectWriter = blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, file, serInstance, fileBufferSize, spillMetrics) // List of batch sizes (bytes) in the order they are written to disk val batchSizes = new ArrayBuffer[Long] // How many elements we have in each partition val elementsPerPartition = new Array[Long](numPartitions) // Flush the disk writer's contents to disk, and update relevant variables. // The writer is committed at the end of this process. def flush(): Unit = { val segment = writer.commitAndGet() batchSizes += segment.length _diskBytesSpilled += segment.length objectsWritten = 0 } var success = false try { while (inMemoryIterator.hasNext) { val partitionId = inMemoryIterator.nextPartition() require(partitionId >= 0 && partitionId < numPartitions, s"partition Id: ${partitionId} should be in the range [0, ${numPartitions})") inMemoryIterator.writeNext(writer) elementsPerPartition(partitionId) += 1 objectsWritten += 1 if (objectsWritten == serializerBatchSize) { flush() } } if (objectsWritten > 0) { flush() } else { writer.revertPartialWritesAndClose() } success = true } finally { if (success) { writer.close() } else { // This code path only happens if an exception was thrown above before we set success; // close our stuff and let the exception be thrown further writer.revertPartialWritesAndClose() if (file.exists()) { if (!file.delete()) { logWarning(s"Error deleting ${file}") } } } } SpilledFile(file, blockId, batchSizes.toArray, elementsPerPartition) }- 调用
groupByPartition(): 给((parition, key), value)的迭代器生成一个嵌套迭代器,外部按照partition迭代,内部按照key迭代- 每个
IteratorForPartition都使用了相同的数据源,但是仍然能区分出当前partition的数据 - 外层迭代器是按照partition顺序返回的
IteratorForPartition迭代器,所以内层数据源迭代器data总是按照partition顺序遍历的
private def groupByPartition(data: Iterator[((Int, K), C)]) : Iterator[(Int, Iterator[Product2[K, C]])] = { // BufferedIterator相比于普通迭代器多了一个head方法,返回当前值并且不会丢弃 val buffered = data.buffered (0 until numPartitions).iterator.map(p => (p, new IteratorForPartition(p, buffered))) } private[this] class IteratorForPartition(partitionId: Int, data: BufferedIterator[((Int, K), C)]) extends Iterator[Product2[K, C]] { override def hasNext: Boolean = data.hasNext && data.head._1._1 == partitionId override def next(): Product2[K, C] = { if (!hasNext) { throw new NoSuchElementException } val elem = data.next() (elem._1._2, elem._2) } }- 每个
partitionedIterator(): 将集合(内存中的和溢出文件中的)进行聚合排序,并且调用groupByPartition()按照partition id分组生成嵌套迭代器- 由是否使用聚合函数来确定当前使用的数据结构
- 如果
spills中没有缓存溢出到磁盘的文件,即所有的数据依然都在内存中。调用数据结构的partitionedDestructiveSortedIterator()方法返回排序的迭代器,并调用destructiveIterator()方法返回可以溢出的迭代器,并调用groupByPartition()方法对partition进行分组 - 如果存在溢出到磁盘的文件,即有些数据存在磁盘上。调用
merge()方法将spills中的文件和内存中的排序好的迭代器进行归并排序,具体通过mergeSort()方法实现- 首先构建了关于partition的外部迭代器,在此迭代器内部接着从
spills取出所有溢出文件中的对应patition的迭代器和内存中的对应partition的迭代器,这样就构建了一个partition的迭代器序列 - 构建partition内部迭代器,使用优先队列维护这个迭代器序列,比较迭代器的第一个元素进行排序。每当调用
next()方法时,从优先队列中取出第一个迭代器,返回其第一个元素(这个元素肯定是全局最小的),接着将此迭代器放入优先队列中(重新根据迭代器的第一个元素进行排序)
- 首先构建了关于partition的外部迭代器,在此迭代器内部接着从
def partitionedIterator: Iterator[(Int, Iterator[Product2[K, C]])] = { val usingMap = aggregator.isDefined val collection: WritablePartitionedPairCollection[K, C] = if (usingMap) map else buffer if (spills.isEmpty) { // Special case: if we have only in-memory data, we don't need to merge streams, and perhaps // we don't even need to sort by anything other than partition ID if (!ordering.isDefined) { // The user hasn't requested sorted keys, so only sort by partition ID, not key groupByPartition(destructiveIterator(collection.partitionedDestructiveSortedIterator(None))) } else { // We do need to sort by both partition ID and key groupByPartition(destructiveIterator( collection.partitionedDestructiveSortedIterator(Some(keyComparator)))) } } else { // Merge spilled and in-memory data merge(spills, destructiveIterator( collection.partitionedDestructiveSortedIterator(comparator))) } } def destructiveIterator(memoryIterator: Iterator[((Int, K), C)]): Iterator[((Int, K), C)] = { if (isShuffleSort) { memoryIterator } else { readingIterator = new SpillableIterator(memoryIterator) readingIterator } } private def merge(spills: Seq[SpilledFile], inMemory: Iterator[((Int, K), C)]) : Iterator[(Int, Iterator[Product2[K, C]])] = { val readers = spills.map(new SpillReader(_)) val inMemBuffered = inMemory.buffered (0 until numPartitions).iterator.map { p => val inMemIterator = new IteratorForPartition(p, inMemBuffered) val iterators = readers.map(_.readNextPartition()) ++ Seq(inMemIterator) if (aggregator.isDefined) { // Perform partial aggregation across partitions (p, mergeWithAggregation( iterators, aggregator.get.mergeCombiners, keyComparator, ordering.isDefined)) } else if (ordering.isDefined) { // No aggregator given, but we have an ordering (e.g. used by reduce tasks in sortByKey); // sort the elements without trying to merge them (p, mergeSort(iterators, ordering.get)) } else { (p, iterators.iterator.flatten) } } } private def mergeSort(iterators: Seq[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]], comparator: Comparator[K]) : Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = { val bufferedIters = iterators.filter(_.hasNext).map(_.buffered) type Iter = BufferedIterator[Product2[K, C]] val heap = new mutable.PriorityQueue[Iter]()(new Ordering[Iter] { // Use the reverse order because PriorityQueue dequeues the max override def compare(x: Iter, y: Iter): Int = comparator.compare(y.head._1, x.head._1) }) heap.enqueue(bufferedIters: _*) // Will contain only the iterators with hasNext = true new Iterator[Product2[K, C]] { override def hasNext: Boolean = !heap.isEmpty override def next(): Product2[K, C] = { if (!hasNext) { throw new NoSuchElementException } val firstBuf = heap.dequeue() val firstPair = firstBuf.next() if (firstBuf.hasNext) { heap.enqueue(firstBuf) } firstPair } } }writePartitionedFile(): 将此外部排序器中的数据写入文件中并返回partition大小数组(用于生成索引文件)- 创建
lengths用于对每个partition的长度进行跟踪 - 如果
spills中没有缓存溢出到磁盘的文件,即所有的数据依然都在内存中- 确定集合类型,如果定义了聚合器则应该是
PartitionedAppendOnlyMap,如果未定义聚合器则应该是PartitionedPairBuffer - 由自身的比较器获取
WritablePartitionedIterator迭代器,此迭代器对partiton进行了排序并且每个partition内部对key进行了排序 - 遍历此迭代器,按照排序好的顺序调用
writeNext()方法通过DiskObjectWriter写入到outputFile中,并且更新lengths
- 确定集合类型,如果定义了聚合器则应该是
- 否则,调用
partitionedIterator()生成溢出文件和内存数据合并的迭代器,通过DiskObjectWriter写入到outputFile中,并且更新lengths
def writePartitionedFile( blockId: BlockId, outputFile: File): Array[Long] = { // Track location of each range in the output file val lengths = new Array[Long](numPartitions) val writer = blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, outputFile, serInstance, fileBufferSize, context.taskMetrics().shuffleWriteMetrics) if (spills.isEmpty) { // Case where we only have in-memory data val collection = if (aggregator.isDefined) map else buffer val it = collection.destructiveSortedWritablePartitionedIterator(comparator) while (it.hasNext) { val partitionId = it.nextPartition() while (it.hasNext && it.nextPartition() == partitionId) { it.writeNext(writer) } val segment = writer.commitAndGet() lengths(partitionId) = segment.length } } else { // We must perform merge-sort; get an iterator by partition and write everything directly. for ((id, elements) <- this.partitionedIterator) { if (elements.hasNext) { for (elem <- elements) { writer.write(elem._1, elem._2) } val segment = writer.commitAndGet() lengths(id) = segment.length } } } writer.close() context.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(memoryBytesSpilled) context.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(diskBytesSpilled) context.taskMetrics().incPeakExecutionMemory(peakMemoryUsedBytes) lengths }- 创建
ShuffleExternalSorter
用于shuffle数据进行排序的外部排序器,用于将map任务的输出存储到Tungsten中;在记录超过限制时,将数据溢出到磁盘。与ExternalSorter不同,ShuffleExternalSorter本身并没有实现数据的持久化功能,具体的持久化将由ShuffleExternalSorter的调用者UnsafeShuffleWriter来实现。
有以下成员属性
numElementsForSpillThreshold: 磁盘溢出的元素数量。通过spark.shuffle.spill.numElementsForceSpillThreshold属性进行配置,默认为1MBfileBufferSizeBytes:创建的DiskBlockObjectWriter内部的文件缓冲大小。通过spark.shuffle.file.buffer属性进行配置,默认是32KBdiskWriteBufferSize: 将已排序的记录写入磁盘文件时要使用的缓冲区大小。通过spark.shuffle.spill.diskWriteBufferSize属性进行配置,默认1024KBallocatedPages: 已经分配的MemoryBlock列表spills: 溢出文件的元数据信息SpillInfo的列表peakMemoryUsedBytes: 内存中数据结构大小的峰值inMemSorter:ShuffleInMemorySorter,用于在内存中对插入的记录进行排序,ShuffleExternalSorter的排序功能依赖于它currentPage: 当前的MemoryBlockpageCursor:MemoryBlock的游标。实际为用于向Tungsten写入数据时的地址信息
下面是重要的成员方法
insertRecord(): 将map task执行结果记录写入ShuffleExternalSorter,主要进行排序操作。与ExternalSorter非常相似,但是少了聚合的实现。ExternalSorter使用的是堆内内存,ShuffleExternalSorter使用的是Tungsten的内存public void insertRecord(Object recordBase, long recordOffset, int length, int partitionId) throws IOException { // for tests assert(inMemSorter != null); if (inMemSorter.numRecords() >= numElementsForSpillThreshold) { logger.info("Spilling data because number of spilledRecords crossed the threshold " + numElementsForSpillThreshold); spill(); } growPointerArrayIfNecessary(); final int uaoSize = UnsafeAlignedOffset.getUaoSize(); // Need 4 or 8 bytes to store the record length. final int required = length + uaoSize; acquireNewPageIfNecessary(required); assert(currentPage != null); final Object base = currentPage.getBaseObject(); final long recordAddress = taskMemoryManager.encodePageNumberAndOffset(currentPage, pageCursor); UnsafeAlignedOffset.putSize(base, pageCursor, length); pageCursor += uaoSize; Platform.copyMemory(recordBase, recordOffset, base, pageCursor, length); pageCursor += length; inMemSorter.insertRecord(recordAddress, partitionId); }spill(): 父类MemoryConsumer的模板方法。与shuffleExternalSorter的溢出实现非常类似,都在溢出前进行了排序,也都有按照partition id进行排序的实现。但是ExternalSorter由按照partition id和key进行排序,而ShuffleExternalSorter由基于基数排序的实现@override public long spill(long size, MemoryConsumer trigger) throws IOException { if (trigger != this || inMemSorter == null || inMemSorter.numRecords() == 0) { return 0L; } logger.info("Thread {} spilling sort data of {} to disk ({} {} so far)", Thread.currentThread().getId(), Utils.bytesToString(getMemoryUsage()), spills.size(), spills.size() > 1 ? " times" : " time"); writeSortedFile(false); final long spillSize = freeMemory(); inMemSorter.reset(); // Reset the in-memory sorter's pointer array only after freeing up the memory pages holding the // records. Otherwise, if the task is over allocated memory, then without freeing the memory // pages, we might not be able to get memory for the pointer array. taskContext.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(spillSize); return spillSize; }
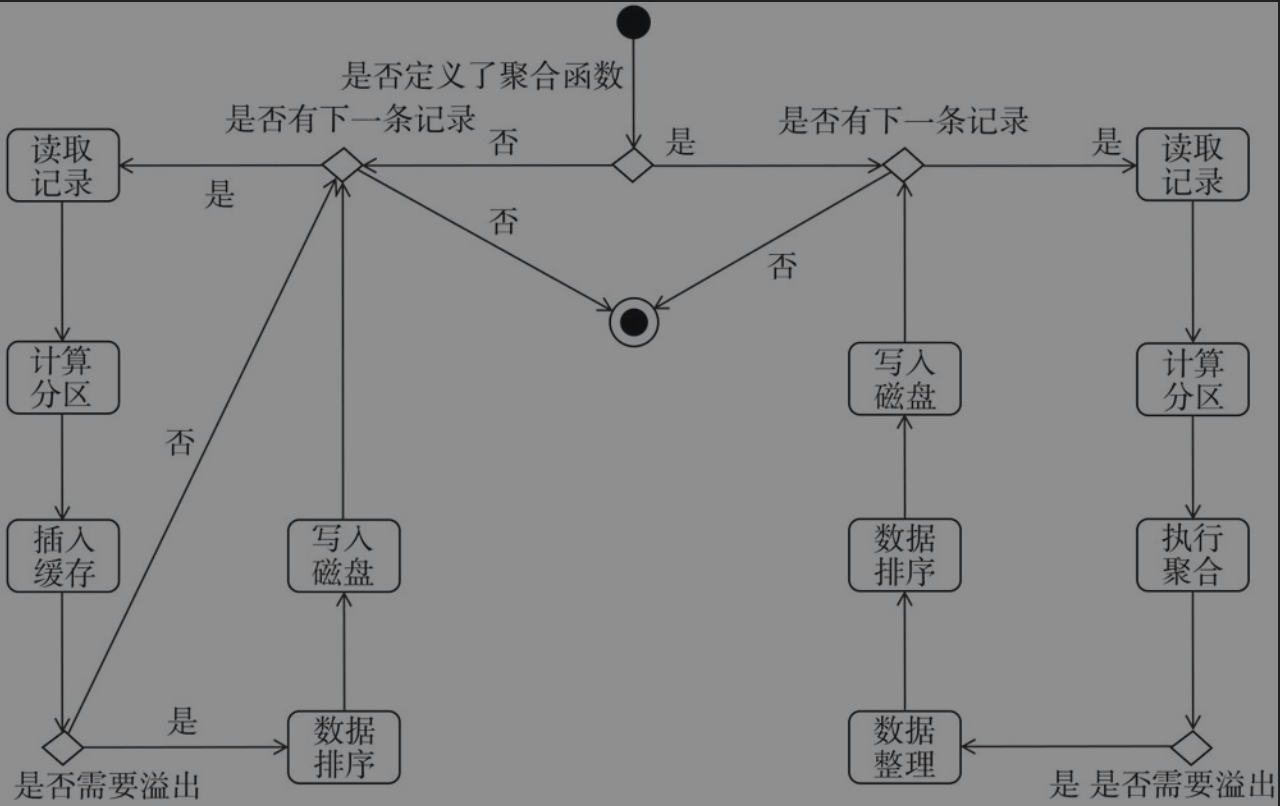
总结
如图所示,表示ExternalSorter实现的map输出写入文件的整个过程
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/09/28/calculation-sorter/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)