Spark计算引擎中的shuffle管理器
MapStatus
特质MapStatus的定义如下所示,用于表示ShuffleMapTask返回给TaskScheduler的执行结果
private[spark] sealed trait MapStatus {
// task运行的位置
def location: BlockManagerId
// reduce task需要拉取的block大小
def getSizeForBlock(reduceId: Int): Long
}
其伴生对象中定义了apply()静态方法,根据uncompressedSizes的长度是否大于spark.shuffle.minNumPartitionsToHighlyCompress的配置值,默认为2000,分别创建HighlyCompressedMapStatus和CompressedMapStatus,对于较大的数据量使用高度压缩的HighlyCompressedMapStatus,一般的数据量则使用CompressedMapStatus
private lazy val minPartitionsToUseHighlyCompressMapStatus = Option(SparkEnv.get)
.map(_.conf.get(config.SHUFFLE_MIN_NUM_PARTS_TO_HIGHLY_COMPRESS))
.getOrElse(config.SHUFFLE_MIN_NUM_PARTS_TO_HIGHLY_COMPRESS.defaultValue.get)
def apply(loc: BlockManagerId, uncompressedSizes: Array[Long]): MapStatus = {
if (uncompressedSizes.length > minPartitionsToUseHighlyCompressMapStatus) {
HighlyCompressedMapStatus(loc, uncompressedSizes)
} else {
new CompressedMapStatus(loc, uncompressedSizes)
}
}
ShuffleBlockResolver
特质ShuffleBlockResolver定义了对shuffle block进行解析的规范,包括获取、删除、生成shuffle数据文件和索引文件等。目前只有IndexShuffleBlockResolver这唯一的实现类。IndexShuffleBlockResolver用于创建和维护shuffle block与物理文件位置之间的映射关系,下面介绍IndexShuffleBlockResolver
有以下成员属性
blockManagertransportConf: 即与shuffle相关的TransportConf。从spark.shuffle.io.clientThreads获取传输线程数和从spark.shuffle.io.serverThreads获取传输线程数
下面是重要的成员方法
getDataFile(),getIndexFile(): 根据shuffle id和map id(实际上案例类转化为了文件名)调用DiskBlockManager.getFile()获取shuffle的数据和索引文件def getDataFile(shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int): File = { blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile(ShuffleDataBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, NOOP_REDUCE_ID)) } private def getIndexFile(shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int): File = { blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile(ShuffleIndexBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, NOOP_REDUCE_ID)) }removeDataByMap(): 删除指定shuffle id和map id对应的数据文件和索引文件def removeDataByMap(shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int): Unit = { var file = getDataFile(shuffleId, mapId) if (file.exists()) { if (!file.delete()) { logWarning(s"Error deleting data ${file.getPath()}") } } file = getIndexFile(shuffleId, mapId) if (file.exists()) { if (!file.delete()) { logWarning(s"Error deleting index ${file.getPath()}") } } }checkIndexAndDataFile(): 检查索引文件和数据文件是否对应writeIndexFileAndCommit(): map输出的所有bucket会写入到一个数据文件中,将数据文件中各个bucket的偏移量写入索引文件,并将临时shuffle数据文件改名为shuffle数据文件,并在索引文件最后增加一个表示输出文件末尾的偏移量- 调用
getIndexFile()方法获取指定shuffle id和map id的索引文件 - 调用
Utils.tempFileWith()返回临时索引文件的路径,即原始文件名加上.UUID - 由
getDataFile()获得指定shuffle id和map id的数据文件,调用checkIndexAndDataFile()方法对给定的索引文件和数据文件是否匹配进行检查并返回数据文件中各个partition的长度数组existingLengths - 下面使用关键词
synchronized保证同步,如果existingLengths不为空,说明在本尝试获取文件期,其他尝试已经写过map输出了,这时删除临时索引文件并用existingLengths更新lengths - 如果
existingLengths不为空,说明这是task的第一次成功尝试,将输出写到临时索引文件中,并替换原索引文件,并将临时shuffle数据文件改名为shuffle数据文件
def writeIndexFileAndCommit( shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int, lengths: Array[Long], dataTmp: File): Unit = { val indexFile = getIndexFile(shuffleId, mapId) val indexTmp = Utils.tempFileWith(indexFile) try { val dataFile = getDataFile(shuffleId, mapId) // There is only one IndexShuffleBlockResolver per executor, this synchronization make sure // the following check and rename are atomic. synchronized { val existingLengths = checkIndexAndDataFile(indexFile, dataFile, lengths.length) if (existingLengths != null) { // Another attempt for the same task has already written our map outputs successfully, // so just use the existing partition lengths and delete our temporary map outputs. System.arraycopy(existingLengths, 0, lengths, 0, lengths.length) if (dataTmp != null && dataTmp.exists()) { dataTmp.delete() } } else { // This is the first successful attempt in writing the map outputs for this task, // so override any existing index and data files with the ones we wrote. val out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(indexTmp))) Utils.tryWithSafeFinally { // We take in lengths of each block, need to convert it to offsets. var offset = 0L out.writeLong(offset) for (length <- lengths) { offset += length out.writeLong(offset) } } { out.close() } if (indexFile.exists()) { indexFile.delete() } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete() } if (!indexTmp.renameTo(indexFile)) { throw new IOException("fail to rename file " + indexTmp + " to " + indexFile) } if (dataTmp != null && dataTmp.exists() && !dataTmp.renameTo(dataFile)) { throw new IOException("fail to rename file " + dataTmp + " to " + dataFile) } } } } finally { if (indexTmp.exists() && !indexTmp.delete()) { logError(s"Failed to delete temporary index file at ${indexTmp.getAbsolutePath}") } } }- 调用
getBlockData(): 获取reduce task需要读入的数据- 首先调用
getIndexFile()获得指定shuffle id和map id的任务输出索引文件 - 读取索引文件输入流,由reduce id确定bucket位置
- 读入索引文件中reduce task所需map数据的偏移量和长度,并和
getDataFile()返回的数据文件一起构造FileSegmentManagedBuffer
override def getBlockData(blockId: ShuffleBlockId): ManagedBuffer = { // The block is actually going to be a range of a single map output file for this map, so // find out the consolidated file, then the offset within that from our index val indexFile = getIndexFile(blockId.shuffleId, blockId.mapId) val channel = Files.newByteChannel(indexFile.toPath) channel.position(blockId.reduceId * 8L) val in = new DataInputStream(Channels.newInputStream(channel)) try { val offset = in.readLong() val nextOffset = in.readLong() val actualPosition = channel.position() val expectedPosition = blockId.reduceId * 8L + 16 if (actualPosition != expectedPosition) { throw new Exception(s"SPARK-22982: Incorrect channel position after index file reads: " + s"expected $expectedPosition but actual position was $actualPosition.") } new FileSegmentManagedBuffer( transportConf, getDataFile(blockId.shuffleId, blockId.mapId), offset, nextOffset - offset) } finally { in.close() } }- 首先调用
ShuffleHandle
抽象类ShuffleHandle是不透明的shuffle句柄,ShuffleManager使用它向Task传递shuffle信息
@DeveloperApi
abstract class ShuffleHandle(val shuffleId: Int) extends Serializable {}
BaseShuffleHandle是ShuffleHandle的直接子类,仅用于ShuffleManager.registerShuffle()方法的参数
private[spark] class BaseShuffleHandle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
val numMaps: Int,
val dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C])
extends ShuffleHandle(shuffleId)
BaseShuffleHandle有BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle和SerializedShuffleHandle两个子类。SerializedShuffleHandle用于确定何时选择使用序列化的shuffle, BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle则用于确定何时选择绕开合并和排序的shuffle
private[spark] class SerializedShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, V])
extends BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency) {
}
private[spark] class BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, V])
extends BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency) {
}
ShuffleWriter
抽象类ShuffleWriter定义了将map任务的中间结果输出到磁盘上的功能规范,给SortShuffleManager提供的服务
private[spark] abstract class ShuffleWriter[K, V] {
// 将map task的结果写到磁盘
@throws[IOException]
def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit
// 关闭此writer
def stop(success: Boolean): Option[MapStatus]
}
ShuffleWriter一共有三个子类,分别为SortShuffleWriter、UnsafeShuffleWriter及BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter
SortShuffleWriter
提供了对shuffle数据的排序功能。底层使用ExternalSorter作为排序器。有以下重要的成员属性
shuffleBlockResolver:IndexShuffleBlockResolverhandle:BaseShuffleHandlecontext:TaskContextdep:handle.dependency,类型为ShuffleDependencysorter:ExternalSorterstopping: 是否正在停止
有以下重要的成员方法
write(): 将map task的结果写到shuffle数据文件和索引文件中,依赖于ExternalSorter排序器和IndexShuffleBlockResolver解析器- 如果
ShuffleDependency.mapSideCombine为true,说明允许在map端进行合并,则创建ExternalSorter时,将ShuffleDependency.aggregator和ShuffleDependency.keyOrdering传递,否则不进行传递。这也间接决定了ExternalSorter内部数据结构是PartitionedAppendOnlyMap还是PartitionedPairBuffer - 调用
ExternalSorter.insertAll()方法将map task的输出插入到排序器中 - 调用
IndexShuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile()方法获取shuffle数据文件,并调用ExternalSorter.writePartitionedFile()方法将排序器中的数据写入到临时shuffle数据文件中 - 调用
IndexShuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit()方法生成数据文件对应的索引文件,并替换临时shuffle数据文件。索引文件记录map输出的各个partition在数据文件中对应的偏移量,以便于reduce任务拉取时使用 - 构造
MapStatus
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = { sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) { new ExternalSorter[K, V, C]( context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer) } else { // In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't // care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side // if the operation being run is sortByKey. new ExternalSorter[K, V, V]( context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer) } sorter.insertAll(records) val output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId) val tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output) try { val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, IndexShuffleBlockResolver.NOOP_REDUCE_ID) val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp) shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp) mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths) } finally { if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) { logError(s"Error while deleting temp file ${tmp.getAbsolutePath}") } } }- 如果
shouldBypassMergeSort(): 这是一个静态方法,判断是否绕开合并和排序。如果依赖不需要map端合并,且依赖的分区器中的分区数量小于等于spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold的属性值,默认200,则可以跳过合并和排序,否则不可以def shouldBypassMergeSort(conf: SparkConf, dep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = { // We cannot bypass sorting if we need to do map-side aggregation. if (dep.mapSideCombine) { false } else { val bypassMergeThreshold: Int = conf.getInt("spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold", 200) dep.partitioner.numPartitions <= bypassMergeThreshold } }
BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter
当map端不需要在持久化数据之前进行聚合、排序等操作时,使用BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter。
有以下成员属性
fileBufferSize: 文件缓冲大小。通过spark.shuffle.file.buffer属性配置,默认为32KBtransferToEnabled: 是否采用NIO的从文件流到文件流的复制方式。通过spark.file.transferTo属性配置,默认为trueshuffleBlockResolver:IndexShuffleBlockResolverpartitionWriters:DiskBlockObjectWriter数组,每一个DiskBlockObjectWriter处理一个partition的数据partitionWriterSegments:FileSegment数组,每一个FileSegment对应一个DiskBlockObjectWriter处理的文件片partitionLengths: 各partition的大小stopping: 是否正在停止中
下面是重要的成员方法
write(): 将map task的结果写到shuffle数据文件和索引文件中,依赖于IndexShuffleBlockResolver- 如果没有输出结果,生成空的
partitionLengths,调用shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit()生成只有0偏移量的索引文件,创建MapStatus并返回 - 否则,创建
partitionWriters和partitionWriterSegments。调用blockManager.diskBlockManager().createTempShuffleBlock()为每个partition生成写入的文件,并创建对应的DiskBlockObjectWriter放入partitionWriters - 迭代待输出的记录,使用分区器并通过每条记录的key,获取记录的partition id,调用此paritition对应的
DiskBlockObjectWriter.write()方法,向partition对应的临时shuffle文件的输出流中写入键值对 - 调用每个parititon对应的
DiskBlockObjectWriter.commitAndGet()方法,将临时shuffle文件的输出流中的数据写入到磁盘,并将返回的FileSegment放入partitionWriterSegments数组中 - 调用
IndexShuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile()方法获取shuffle数据文件,调用writePartitionedFile()方法将每个partition的FileSegment合并到临时shuffle数据文件中 - 调用
IndexShuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit()生成数据文件对应的索引文件,并替换临时shuffle数据文件,记录每个partition的偏移量 - 构造并返回
MapStatus
@Override public void write(Iterator<Product2<K, V>> records) throws IOException { assert (partitionWriters == null); if (!records.hasNext()) { partitionLengths = new long[numPartitions]; shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, null); mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths); return; } final SerializerInstance serInstance = serializer.newInstance(); final long openStartTime = System.nanoTime(); partitionWriters = new DiskBlockObjectWriter[numPartitions]; partitionWriterSegments = new FileSegment[numPartitions]; for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) { final Tuple2<TempShuffleBlockId, File> tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile = blockManager.diskBlockManager().createTempShuffleBlock(); final File file = tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile._2(); final BlockId blockId = tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile._1(); partitionWriters[i] = blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, file, serInstance, fileBufferSize, writeMetrics); } // Creating the file to write to and creating a disk writer both involve interacting with // the disk, and can take a long time in aggregate when we open many files, so should be // included in the shuffle write time. writeMetrics.incWriteTime(System.nanoTime() - openStartTime); while (records.hasNext()) { final Product2<K, V> record = records.next(); final K key = record._1(); partitionWriters[partitioner.getPartition(key)].write(key, record._2()); } for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) { final DiskBlockObjectWriter writer = partitionWriters[i]; partitionWriterSegments[i] = writer.commitAndGet(); writer.close(); } File output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(shuffleId, mapId); File tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output); try { partitionLengths = writePartitionedFile(tmp); shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp); } finally { if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) { logger.error("Error while deleting temp file {}", tmp.getAbsolutePath()); } } mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths); }- 如果没有输出结果,生成空的
writePartitionedFile(): 将partitionWriterSegments中的文件写入到参数outputFile中- 创建
lengths用于跟踪每个partition的长度以生成对应的索引文件 - 打开shuffle数据文件的文件输出流
- 遍历
partitionWriterSegments,打开每个partition对应文件的输入流,并拷贝到shuffle数据文件中并记录lengths - 返回
lengths
private long[] writePartitionedFile(File outputFile) throws IOException { // Track location of the partition starts in the output file final long[] lengths = new long[numPartitions]; if (partitionWriters == null) { // We were passed an empty iterator return lengths; } final FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outputFile, true); final long writeStartTime = System.nanoTime(); boolean threwException = true; try { for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) { final File file = partitionWriterSegments[i].file(); if (file.exists()) { final FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); boolean copyThrewException = true; try { lengths[i] = Utils.copyStream(in, out, false, transferToEnabled); copyThrewException = false; } finally { Closeables.close(in, copyThrewException); } if (!file.delete()) { logger.error("Unable to delete file for partition {}", i); } } } threwException = false; } finally { Closeables.close(out, threwException); writeMetrics.incWriteTime(System.nanoTime() - writeStartTime); } partitionWriters = null; return lengths; }- 创建
UnsafeShuffleWriter
底层使用ShuffleExternalSorter作为外部排序器,所以相对于SortShuffleWriter,不具有聚合功能且使用了Tungsten的内存作为缓存
有以下成员属性
shuffleBlockResolver:IndexShuffleBlockResolvermemoryManager:TaskMemoryManagertransferToEnabled: 是否采用NIO的从文件流到文件流的复制方式。通过spark.file.transferTo属性配置,默认为trueinitialSortBufferSize: 初始化的排序缓冲大小。可通过spark.shuffle.sort.initialBufferSize属性配置,默认为4096sorter:ShuffleExternalSorterpeakMemoryUsedBytes: 使用内存的峰值serBuffer:MyByteArrayOutputStream,提供了暴露ByteArrayOutputStream内部存储数据的字节数组buf.getBuf()方法serOutputStream:SerializationStream,实际是将serBuffer序列化包装后的输出流stopping: 是否正在停止中
有以下重要的成员方法
closeAndWriteOutput(): 将map task的结果写到shuffle数据文件和索引文件中,依赖于ShuffleExternalSorter,IndexShuffleBlockResolver- 更新
ShuffleExternalSorter的内存使用峰值 - 关闭
ShuffleExternalSorter,并获得溢出的文件信息数组 - 调用
IndexShuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile()方法,获取正式的shuffle数据文件 - 调用
mergeSpills()合并所有溢出文件临时shuffle数据文件 - 调用
IndexShuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit()方法生成数据文件对应的索引文件,并替换临时shuffle文件 - 返回
MapStatus
@VisibleForTesting void closeAndWriteOutput() throws IOException { assert(sorter != null); updatePeakMemoryUsed(); serBuffer = null; serOutputStream = null; final SpillInfo[] spills = sorter.closeAndGetSpills(); sorter = null; final long[] partitionLengths; final File output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(shuffleId, mapId); final File tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output); try { try { partitionLengths = mergeSpills(spills, tmp); } finally { for (SpillInfo spill : spills) { if (spill.file.exists() && ! spill.file.delete()) { logger.error("Error while deleting spill file {}", spill.file.getPath()); } } } shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp); } finally { if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) { logger.error("Error while deleting temp file {}", tmp.getAbsolutePath()); } } mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths); }- 更新
insertRecordIntoSorter(): 将记录插入排序器中- 使用分区器由记录的key计算出patition id
- 重置
serBuffer,将记录写入到serOutputStream当中 - 调用
ShuffleExternalSorter.insertRecord()方法,将serBuffer底层的字节数组插入到Tungsten的内存中
@VisibleForTesting void insertRecordIntoSorter(Product2<K, V> record) throws IOException { assert(sorter != null); final K key = record._1(); final int partitionId = partitioner.getPartition(key); serBuffer.reset(); serOutputStream.writeKey(key, OBJECT_CLASS_TAG); serOutputStream.writeValue(record._2(), OBJECT_CLASS_TAG); serOutputStream.flush(); final int serializedRecordSize = serBuffer.size(); assert (serializedRecordSize > 0); sorter.insertRecord( serBuffer.getBuf(), Platform.BYTE_ARRAY_OFFSET, serializedRecordSize, partitionId); }write(): 先排序再将map task的结果写到shuffle数据文件和索引文件中,依赖于ShuffleExternalSorter,IndexShuffleBlockResolver- 迭代输入的每条记录,并调用
insertRecordIntoSorter()方法将记录插入排序器 - 调用
closeAndWriteOutput()方法将map任务输出的数据持久化到磁盘
@Override public void write(scala.collection.Iterator<Product2<K, V>> records) throws IOException { // Keep track of success so we know if we encountered an exception // We do this rather than a standard try/catch/re-throw to handle // generic throwables. boolean success = false; try { while (records.hasNext()) { insertRecordIntoSorter(records.next()); } closeAndWriteOutput(); success = true; } finally { if (sorter != null) { try { sorter.cleanupResources(); } catch (Exception e) { // Only throw this error if we won't be masking another // error. if (success) { throw e; } else { logger.error("In addition to a failure during writing, we failed during " + "cleanup.", e); } } } } }- 迭代输入的每条记录,并调用
ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator
继承自Iterator[(BlockId, InputStream)],用于获取多个shuffle block的迭代器。如果block在本地,那么从本地的BlockManager获取;如果block在远端,那么通过ShuffleClient请求远端节点上的BlockTransferService获取
有以下重要的成员变量
context:TaskContextblocksByAddress:Iterator[(BlockManagerId, Seq[(BlockId, Long)])],要获取的block(id, size)与所在位置的BlockManager的对应关系maxBytesInFlight: 单批次请求的最大字节数。为了提高请求的并发度,保证至少向5个不同的节点发送请求获取数据,最大限度地利用各节点的资源,每个请求的字节数不能超过maxBytesInFlight的1/5。通过参数spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight来控制大小,默认为48MBmaxReqsInFlight: 单批次的最多请求数。通过spark.reducer.maxReqsInFlight属性配置,默认为Integer.MAX_VALUEmaxBlocksInFlightPerAddress: 单批次中请求最大的block大小numBlocksToFetch: 一共要获取的block数量numBlocksProcessed: 已经处理的block数量startTime: 启动时间localBlocks:LinkedHashSet[BlockId]。本地BlockManager中要请求的blockremoteBlocks:HashSet[BlockId]。远端BlockManager中要请求的blockresults:LinkedBlockingQueue[FetchResult]。用于保存已获取block的结果信息private[storage] sealed trait FetchResult { val blockId: BlockId val address: BlockManagerId }currentResult: 当前正在处理的FetchResultfetchRequests:Queue[FetchRequest]。block请求信息队列。FetchRequest.size属性表示FetchRequest要下载的所有block的大小之和case class FetchRequest(address: BlockManagerId, blocks: Seq[(BlockId, Long)]) { val size = blocks.map(_._2).sum }deferredFetchRequests: 提取请求队列在第一次出队时无法发出。当获取限制满足时,将再次尝试这些请求bytesInFlight: 当前批次的请求的字节数reqsInFlight: 当前批次的请求的数量isZombie:ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator是否处于激活状态。如果isZombie为true,则ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator处于非激活状态
下面是重要的成员方法
splitLocalRemoteBlocks(): 划分远端block和本地block。本地block放入localBlocks中,远端block按请求限制分组包装并放入remoteRequests- 遍历
blocksByAddress中缓存的按照BlockManagerId分组的block id列表 - 如果
BlockManagerId所在的executor与当前executor一致,将所有block id放入localBlocks列表中 - 如果不一致,迭代要获取的远端executor上的block id列表,将所有大小大于0的block id放入
remoteBlocks中,并将block大小累加到curRequestSize中,直到curRequestSize大于maxBytesInFlight的五分之一,或者当前block大于maxBlocksInFlightPerAddress,将已遍历的block放入一个FetchRequest并保存到remoteRequests列表中。末尾剩余的block也会放入一个FetchRequest并保存到remoteRequests列表中
private[this] def splitLocalRemoteBlocks(): ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest] = { // Make remote requests at most maxBytesInFlight / 5 in length; the reason to keep them // smaller than maxBytesInFlight is to allow multiple, parallel fetches from up to 5 // nodes, rather than blocking on reading output from one node. val targetRequestSize = math.max(maxBytesInFlight / 5, 1L) logDebug("maxBytesInFlight: " + maxBytesInFlight + ", targetRequestSize: " + targetRequestSize + ", maxBlocksInFlightPerAddress: " + maxBlocksInFlightPerAddress) // Split local and remote blocks. Remote blocks are further split into FetchRequests of size // at most maxBytesInFlight in order to limit the amount of data in flight. val remoteRequests = new ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest] for ((address, blockInfos) <- blocksByAddress) { if (address.executorId == blockManager.blockManagerId.executorId) { blockInfos.find(_._2 <= 0) match { case Some((blockId, size)) if size < 0 => throw new BlockException(blockId, "Negative block size " + size) case Some((blockId, size)) if size == 0 => throw new BlockException(blockId, "Zero-sized blocks should be excluded.") case None => // do nothing. } localBlocks ++= blockInfos.map(_._1) numBlocksToFetch += localBlocks.size } else { val iterator = blockInfos.iterator var curRequestSize = 0L var curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)] while (iterator.hasNext) { val (blockId, size) = iterator.next() if (size < 0) { throw new BlockException(blockId, "Negative block size " + size) } else if (size == 0) { throw new BlockException(blockId, "Zero-sized blocks should be excluded.") } else { curBlocks += ((blockId, size)) remoteBlocks += blockId numBlocksToFetch += 1 curRequestSize += size } if (curRequestSize >= targetRequestSize || curBlocks.size >= maxBlocksInFlightPerAddress) { // Add this FetchRequest remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks) logDebug(s"Creating fetch request of $curRequestSize at $address " + s"with ${curBlocks.size} blocks") curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)] curRequestSize = 0 } } // Add in the final request if (curBlocks.nonEmpty) { remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks) } } } logInfo(s"Getting $numBlocksToFetch non-empty blocks including ${localBlocks.size}" + s" local blocks and ${remoteBlocks.size} remote blocks") remoteRequests }- 遍历
fetchLocalBlocks(): 获取本地block- 遍历
splitLocalRemoteBlocks()方法划分的本地block列表localBlocks - 调用本地的
BlockManager.getBlockData()获取block - 创建
SuccessFetchResult对象,并添加到results中
private[this] def fetchLocalBlocks() { logDebug(s"Start fetching local blocks: ${localBlocks.mkString(", ")}") val iter = localBlocks.iterator while (iter.hasNext) { val blockId = iter.next() try { val buf = blockManager.getBlockData(blockId) shuffleMetrics.incLocalBlocksFetched(1) shuffleMetrics.incLocalBytesRead(buf.size) buf.retain() results.put(new SuccessFetchResult(blockId, blockManager.blockManagerId, buf.size(), buf, false)) } catch { case e: Exception => // If we see an exception, stop immediately. logError(s"Error occurred while fetching local blocks", e) results.put(new FailureFetchResult(blockId, blockManager.blockManagerId, e)) return } } }- 遍历
fetchUpToMaxBytes(): 向远端发送不超过maxReqsInFlight和maxBytesInFlight的限制的获取block的请求initialize(): 为此迭代器获取用于迭代的数据- 给
TaskContext添加任务完成的监听器,以便于任务执行完成后调用cleanup()方法进行一些清理工作 - 使用
splitLocalRemoteBlocks()方法划分从本地读取和需要远程读取的block的请求 - 将返回的远端请求
FetchRequest随机排序后存入fetchRequests - 调用
fetchUpToMaxBytes()方法发送请求获取远端block,并调用fetchLocalBlocks()方法获取本地block
private[this] def initialize(): Unit = { // Add a task completion callback (called in both success case and failure case) to cleanup. context.addTaskCompletionListener[Unit](_ => cleanup()) // Split local and remote blocks. val remoteRequests = splitLocalRemoteBlocks() // Add the remote requests into our queue in a random order fetchRequests ++= Utils.randomize(remoteRequests) assert ((0 == reqsInFlight) == (0 == bytesInFlight), "expected reqsInFlight = 0 but found reqsInFlight = " + reqsInFlight + ", expected bytesInFlight = 0 but found bytesInFlight = " + bytesInFlight) // Send out initial requests for blocks, up to our maxBytesInFlight fetchUpToMaxBytes() val numFetches = remoteRequests.size - fetchRequests.size logInfo("Started " + numFetches + " remote fetches in" + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime)) // Get Local Blocks fetchLocalBlocks() logDebug("Got local blocks in " + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime)) }- 给
next(): 重载了Iterator.next(),不断返回(BlockId, InputStream)。每次从results队列中取出一个非空的FetchResult,解析后返回(BlockId, InputStream),在返回前会调用fetchUpToMaxBytes()触发下一批次的请求override def hasNext: Boolean = numBlocksProcessed < numBlocksToFetch override def next(): (BlockId, InputStream) = { if (!hasNext) { throw new NoSuchElementException } numBlocksProcessed += 1 var result: FetchResult = null var input: InputStream = null // Take the next fetched result and try to decompress it to detect data corruption, // then fetch it one more time if it's corrupt, throw FailureFetchResult if the second fetch // is also corrupt, so the previous stage could be retried. // For local shuffle block, throw FailureFetchResult for the first IOException. while (result == null) { val startFetchWait = System.currentTimeMillis() result = results.take() val stopFetchWait = System.currentTimeMillis() shuffleMetrics.incFetchWaitTime(stopFetchWait - startFetchWait) result match { case r @ SuccessFetchResult(blockId, address, size, buf, isNetworkReqDone) => if (address != blockManager.blockManagerId) { numBlocksInFlightPerAddress(address) = numBlocksInFlightPerAddress(address) - 1 shuffleMetrics.incRemoteBytesRead(buf.size) if (buf.isInstanceOf[FileSegmentManagedBuffer]) { shuffleMetrics.incRemoteBytesReadToDisk(buf.size) } shuffleMetrics.incRemoteBlocksFetched(1) } if (!localBlocks.contains(blockId)) { bytesInFlight -= size } if (isNetworkReqDone) { reqsInFlight -= 1 logDebug("Number of requests in flight " + reqsInFlight) } if (buf.size == 0) { val msg = s"Received a zero-size buffer for block $blockId from $address " + s"(expectedApproxSize = $size, isNetworkReqDone=$isNetworkReqDone)" throwFetchFailedException(blockId, address, new IOException(msg)) } val in = try { buf.createInputStream() } catch { // The exception could only be throwed by local shuffle block case e: IOException => assert(buf.isInstanceOf[FileSegmentManagedBuffer]) logError("Failed to create input stream from local block", e) buf.release() throwFetchFailedException(blockId, address, e) } var isStreamCopied: Boolean = false try { input = streamWrapper(blockId, in) // Only copy the stream if it's wrapped by compression or encryption, also the size of // block is small (the decompressed block is smaller than maxBytesInFlight) if (detectCorrupt && !input.eq(in) && size < maxBytesInFlight / 3) { isStreamCopied = true val out = new ChunkedByteBufferOutputStream(64 * 1024, ByteBuffer.allocate) Utils.copyStream(input, out, closeStreams = true) input = out.toChunkedByteBuffer.toInputStream(dispose = true) } } catch { case e: IOException => buf.release() if (buf.isInstanceOf[FileSegmentManagedBuffer] || corruptedBlocks.contains(blockId)) { throwFetchFailedException(blockId, address, e) } else { logWarning(s"got an corrupted block $blockId from $address, fetch again", e) corruptedBlocks += blockId fetchRequests += FetchRequest(address, Array((blockId, size))) result = null } } finally { // TODO: release the buf here to free memory earlier if (isStreamCopied) { in.close() } } case FailureFetchResult(blockId, address, e) => throwFetchFailedException(blockId, address, e) } // Send fetch requests up to maxBytesInFlight fetchUpToMaxBytes() } currentResult = result.asInstanceOf[SuccessFetchResult] (currentResult.blockId, new BufferReleasingInputStream(input, this)) }
BlockStoreShuffleReader
用于shuffle执行过程中,reduce task从其他节点的shuffle数据文件中读取由起始partition和结束partition的指定范围内的数据
有以下成员属性
handle:BaseShuffleHandlestartPartition: 要读取的起始partition idendPartition: 要读取的结束partition idcontext:TaskContextdep:BaseShuffleHandle.dependency,ShuffleDependency
只有一个成员方法
read(): 读取指定partition内的数据并进行必要的聚合和排序- 创建
ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator,并使用序列化器包装,进行反序列化 - 创建可中断的迭代器
InterruptibleIterator,为了能够支持task尝试的取消操作 - 如果此依赖定义了聚合器
- 如果
dep.mapSideCombine为真,说明value已经被合并过了,value都是聚合过的类型,使用Aggregator.combineCombinersByKey()去聚合
- 如果
- 如果
dep.mapSideCombine为假,说明value没有合并过,value都是原始类型,使用Aggregator.combineValuesByKey()去聚合 - 如果此依赖定义了排序器,则创建
ExternalSorter进行排序,封装为CompletionIterator并返回
// Aggregator def combineValuesByKey( iter: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, V]], context: TaskContext): Iterator[(K, C)] = { val combiners = new ExternalAppendOnlyMap[K, V, C](createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners) combiners.insertAll(iter) updateMetrics(context, combiners) combiners.iterator } // Aggregator def combineCombinersByKey( iter: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, C]], context: TaskContext): Iterator[(K, C)] = { val combiners = new ExternalAppendOnlyMap[K, C, C](identity, mergeCombiners, mergeCombiners) combiners.insertAll(iter) updateMetrics(context, combiners) combiners.iterator } override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = { val wrappedStreams = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator( context, blockManager.shuffleClient, blockManager, mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition), serializerManager.wrapStream, // Note: we use getSizeAsMb when no suffix is provided for backwards compatibility SparkEnv.get.conf.getSizeAsMb("spark.reducer.maxSizeInFlight", "48m") * 1024 * 1024, SparkEnv.get.conf.getInt("spark.reducer.maxReqsInFlight", Int.MaxValue), SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.REDUCER_MAX_BLOCKS_IN_FLIGHT_PER_ADDRESS), SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.MAX_REMOTE_BLOCK_SIZE_FETCH_TO_MEM), SparkEnv.get.conf.getBoolean("spark.shuffle.detectCorrupt", true)) val serializerInstance = dep.serializer.newInstance() // Create a key/value iterator for each stream val recordIter = wrappedStreams.flatMap { case (blockId, wrappedStream) => // Note: the asKeyValueIterator below wraps a key/value iterator inside of a // NextIterator. The NextIterator makes sure that close() is called on the // underlying InputStream when all records have been read. serializerInstance.deserializeStream(wrappedStream).asKeyValueIterator } // Update the context task metrics for each record read. val readMetrics = context.taskMetrics.createTempShuffleReadMetrics() val metricIter = CompletionIterator[(Any, Any), Iterator[(Any, Any)]]( recordIter.map { record => readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1) record }, context.taskMetrics().mergeShuffleReadMetrics()) // An interruptible iterator must be used here in order to support task cancellation val interruptibleIter = new InterruptibleIterator[(Any, Any)](context, metricIter) val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) { if (dep.mapSideCombine) { // We are reading values that are already combined val combinedKeyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]] dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(combinedKeyValuesIterator, context) } else { // We don't know the value type, but also don't care -- the dependency *should* // have made sure its compatible w/ this aggregator, which will convert the value // type to the combined type C val keyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, Nothing)]] dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(keyValuesIterator, context) } } else { interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]] } // Sort the output if there is a sort ordering defined. val resultIter = dep.keyOrdering match { case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) => // Create an ExternalSorter to sort the data. val sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](context, ordering = Some(keyOrd), serializer = dep.serializer) sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter) context.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(sorter.memoryBytesSpilled) context.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(sorter.diskBytesSpilled) context.taskMetrics().incPeakExecutionMemory(sorter.peakMemoryUsedBytes) // Use completion callback to stop sorter if task was finished/cancelled. context.addTaskCompletionListener[Unit](_ => { sorter.stop() }) CompletionIterator[Product2[K, C], Iterator[Product2[K, C]]](sorter.iterator, sorter.stop()) case None => aggregatedIter } resultIter match { case _: InterruptibleIterator[Product2[K, C]] => resultIter case _ => // Use another interruptible iterator here to support task cancellation as aggregator // or(and) sorter may have consumed previous interruptible iterator. new InterruptibleIterator[Product2[K, C]](context, resultIter) } }- 创建
SortShuffleManager
管理基于排序的shuffle,输入的记录按照目标parition id排序,然后输出到一个单独的map输出文件中。reduce为了读出map输出,需要获取map输出文件的连续内容。当map的输出数据太大已经不适合放在内存中时,排序后的输出子集将被溢出到文件中,这些磁盘上的文件将被合并生成最终的输出文件。
有以下成员属性
numMapsForShuffle:ConcurrentHashMap[Int, Int]()。shuffle id和此shuffle的map数量的映射shuffleBlockResolver:IndexShuffleBlockResolver
有以下成员方法
registerShuffle(): 注册shuffle依赖,根据条件创建不同的ShuffleHandle实例- 调用
SortShuffleWriter.shouldBypassMergeSort()方法,如果可以跳过合并和排序则创建BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle - 如果可以使用序列化的shuffle,那么创建
SerializedShuffleHandle - 其他情况,创建
BaseShuffleHandle
override def registerShuffle[K, V, C]( shuffleId: Int, numMaps: Int, dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]): ShuffleHandle = { if (SortShuffleWriter.shouldBypassMergeSort(conf, dependency)) { new BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K, V]( shuffleId, numMaps, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]]) } else if (SortShuffleManager.canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency)) { // Otherwise, try to buffer map outputs in a serialized form, since this is more efficient: new SerializedShuffleHandle[K, V]( shuffleId, numMaps, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]]) } else { // Otherwise, buffer map outputs in a deserialized form: new BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency) } }- 调用
unregisterShuffle(): 注销shuffle id标记的shuffle。调用shuffleBlockResolver.removeDataByMap()删除此Shuffle过程的所有map任务的数据文件和索引文件override def unregisterShuffle(shuffleId: Int): Boolean = { Option(numMapsForShuffle.remove(shuffleId)).foreach { numMaps => (0 until numMaps).foreach { mapId => shuffleBlockResolver.removeDataByMap(shuffleId, mapId) } } true }getWriter(): 根据ShuffleHandle创建ShuffleWriter并返回override def getWriter[K, V]( handle: ShuffleHandle, mapId: Int, context: TaskContext): ShuffleWriter[K, V] = { numMapsForShuffle.putIfAbsent( handle.shuffleId, handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[_, _, _]].numMaps) val env = SparkEnv.get handle match { case unsafeShuffleHandle: SerializedShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] => new UnsafeShuffleWriter( env.blockManager, shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver], context.taskMemoryManager(), unsafeShuffleHandle, mapId, context, env.conf) case bypassMergeSortHandle: BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] => new BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter( env.blockManager, shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver], bypassMergeSortHandle, mapId, context, env.conf) case other: BaseShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked, _] => new SortShuffleWriter(shuffleBlockResolver, other, mapId, context) } }getReader(): 将ShuffleHandle封装为对shuffle数据文件中从指定partition范围内的数据读取器BlockStoreShuffleReader,供reduce task使用override def getReader[K, C]( handle: ShuffleHandle, startPartition: Int, endPartition: Int, context: TaskContext): ShuffleReader[K, C] = { new BlockStoreShuffleReader( handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C]], startPartition, endPartition, context) }
总结
shuffle用于打通map任务的输出与reduce任务的输入,map任务的中间输出结果按照指定的分区策略分配给处理某一个分区的reduce任务。
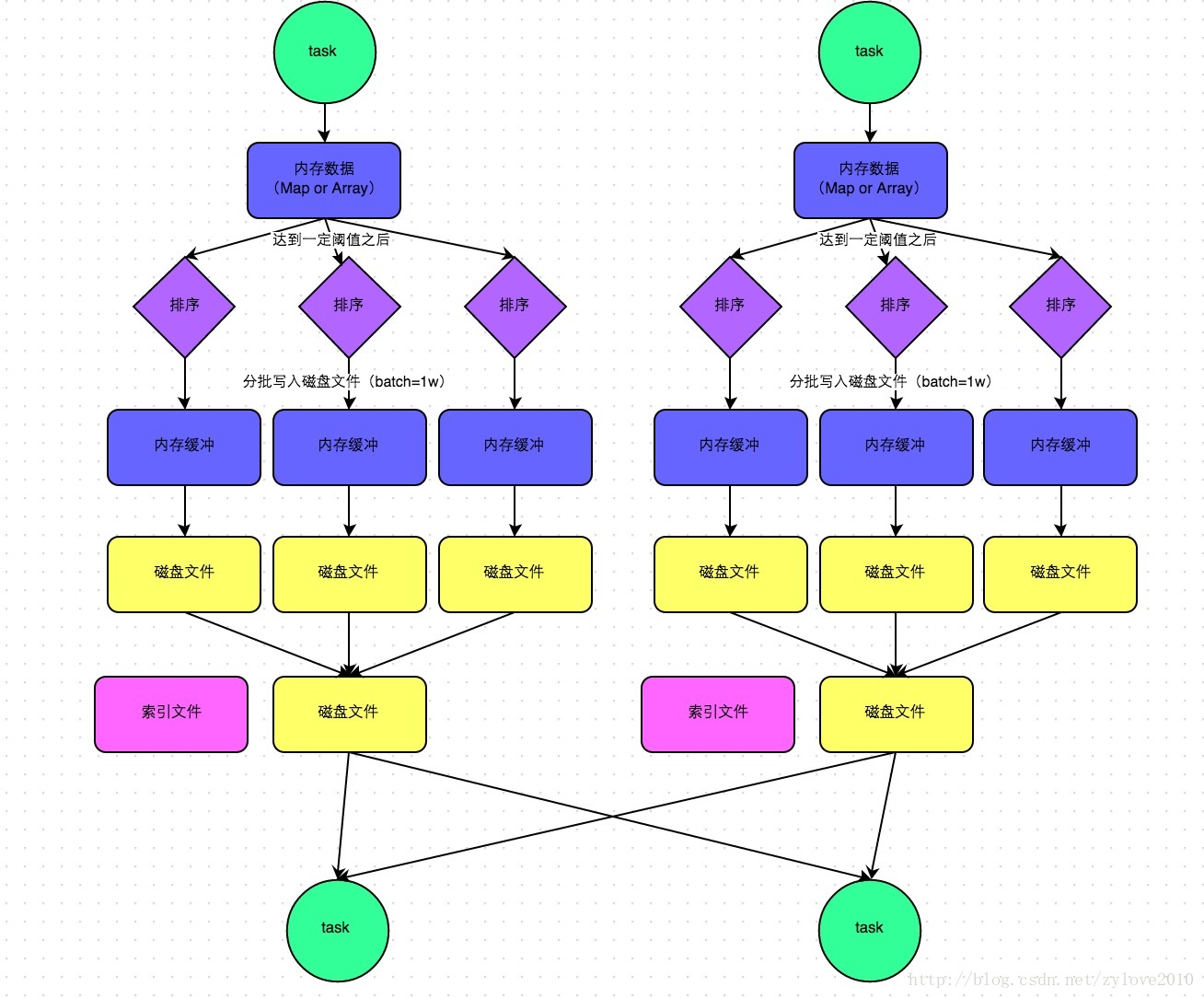
如图所示,Spark的shuffle write和shuffle fetch示意图。这里值得注意的是,如果一个map任务的结果写入了多个bucket中(HashBasedShuffle)或者多个map任务共享一个bucket(HashBasedShuffle引入File Consolidation机制),这些机制在Spark2.0时已经被废弃
map任务在输出时会进行分区计算并生成数据文件和索引文件。将map任务给每个分区的reduce任务输出的bucket合并到同一个文件中,一个结点上的一个map任务只会生成一个shuffle数据文件,这解决了数据本身的体积不大时,造成shuffle频繁,磁盘I/O成为性能瓶颈的问题
map任务逐条输出计算结果,而不是一次性输出到内存,并使用
AppendOnlyMap对中间结果进行聚合和排序,大大减小了中间结果所占的内存大小实现了
SizeTracker特质的数据结构有采样估算功能,当超出溢出限制的大小时,将数据写入磁盘,防止内存溢出reduce任务对拉取到的map任务中间结果逐条读取,而不是一次性读入内存,并在内存中使用
AppendOnlyMap进行聚合和排序,这也大大减小了数据占用的内存大小reduce任务将要拉取的block按照
BlockManager地址划分,然后将同一BlockManager地址中的block累积为少量网络请求,减少网络I/O
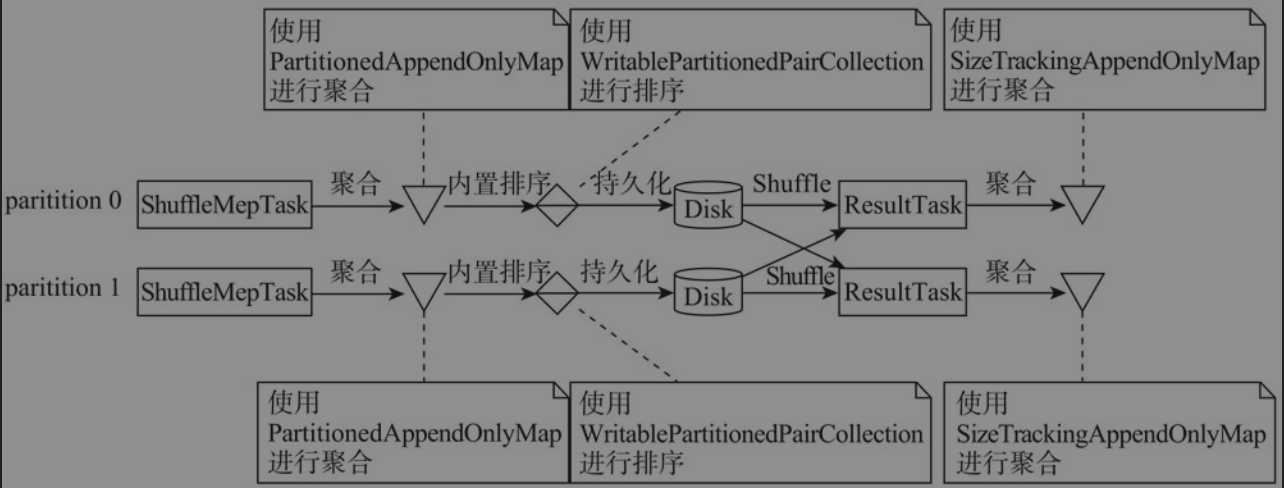
- map端和reduce端都指定了聚合函数
ShuffleDependency.mapSideCombine属性为true,即允许在map端合并BaseShuffleHandle—>SortShuffleWriter- map端和reduce端都会进行聚合和排序
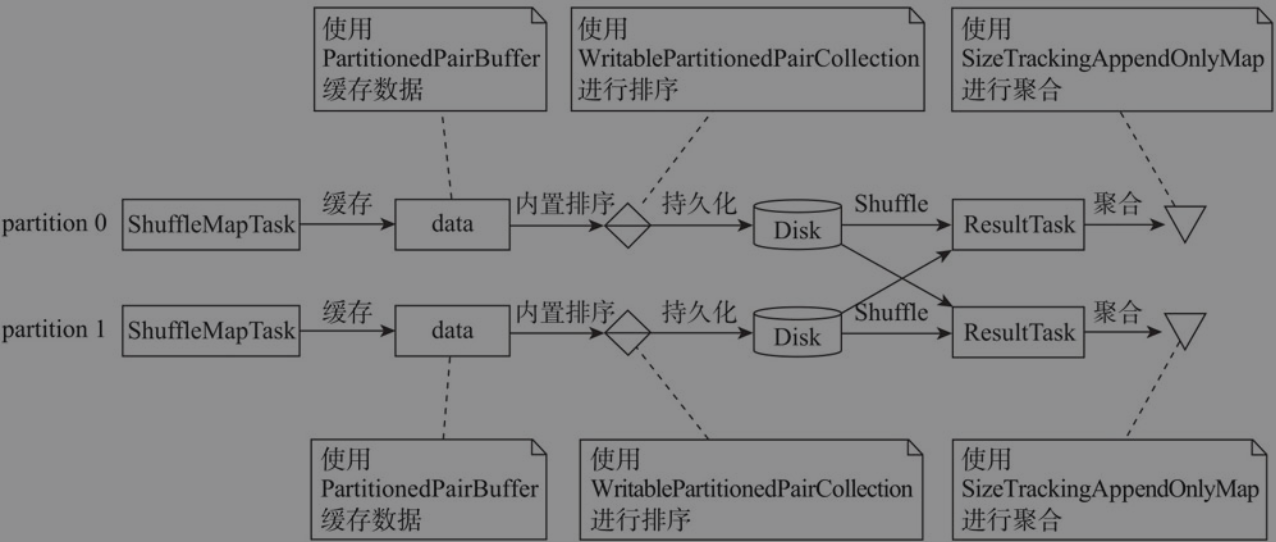
ShuffleDependency的分区数大于spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold属性,map端不会进行聚合和排序BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle—>BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter- map端不会进行聚合和排序,图中所示的排序是对partition排序,partition内部是无序的
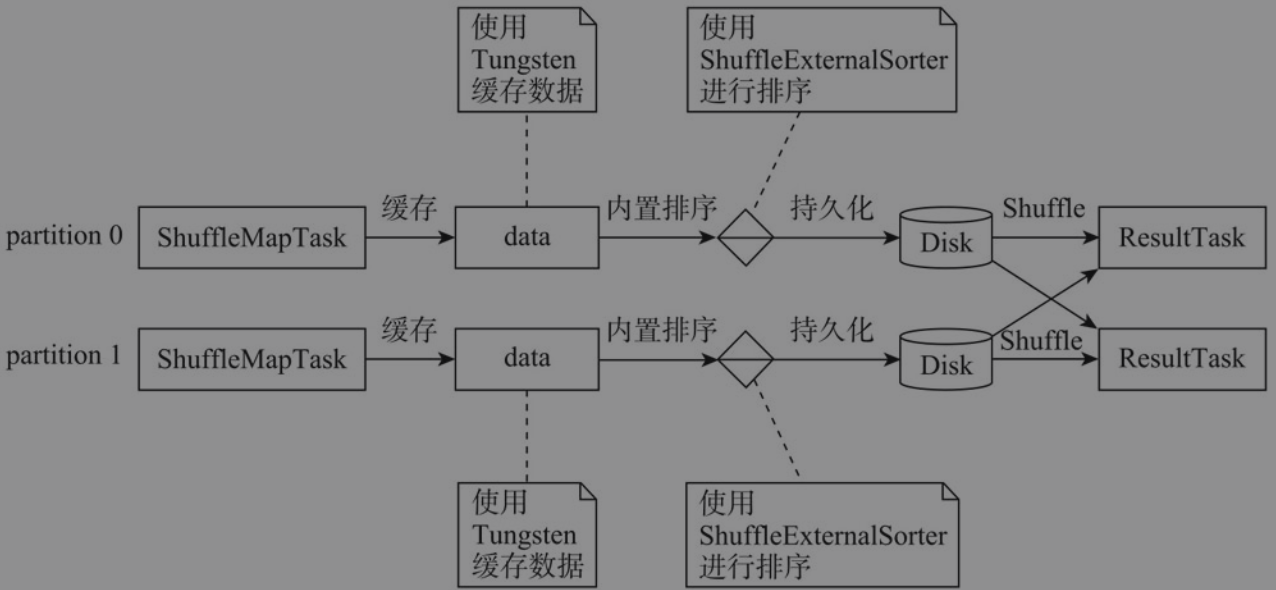
ShuffleDependency.mapSideCombine属性为false,即不允许在map端合并- shuffle可以序列化
SerializedShuffleHandle—>UnsafeShuffleWriter- 使用堆外内存缓存数据
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
- Spark 的Shuffle过程详解——raxanne
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/10/10/calculation-shuffle/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)