聚合操作指的是在原始数据的基础上按照一定的逻辑进行整合从而得到新的数据, 一般通过聚合函数和分组聚合的方式汇总多行的信息
ANTLR4文法定义
// 聚合函数
// function_name(arguments)
primaryExpression
:
qualifiedName '(' (setQuantifier? argument+=expression (',' argument+=expression)*)? ')'
(OVER windowSpec)? #functionCall
| qualifiedName '(' trimOption=(BOTH | LEADING | TRAILING) argument+=expression
FROM argument+=expression ')' #functionCall
;
qualifiedName
: identifier ('.' identifier)*
;
setQuantifier
: DISTINCT
| ALL
;
// 分组聚合
// group by bool_expression [with roolup, with cube, grouping sets(...)]
// group by grouping sets(...)]
aggregation
: GROUP BY groupingExpressions+=expression (',' groupingExpressions+=expression)* (
WITH kind=ROLLUP
| WITH kind=CUBE
| kind=GROUPING SETS '(' groupingSet (',' groupingSet)* ')')?
| GROUP BY kind=GROUPING SETS '(' groupingSet (',' groupingSet)* ')'
;
groupingSet
: '(' (expression (',' expression)*)? ')'
| expression
;
expression
: booleanExpression
;
- 聚合函数:
count(),max(),sum()等 - 分组聚合关键字:
group by(分组),with cube(所有分组维度的可能组合的聚合),with rollup(按照分组维度顺序进行的层次结构的聚合),grouping sets(对分组维度进行分别聚合)
聚合函数
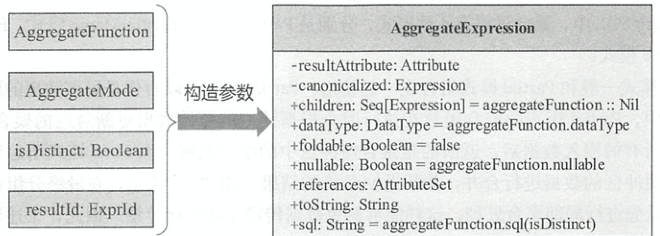
无论是在逻辑算子树还是物理算子树中,聚合函数都是以聚合表达式AggregatcExpression的形式进行封装的,同时聚合函数表达式中也定义了直接生成聚合表达式的方法,其结构如下图所示
缓冲区
聚合查询在计算聚合值的过程中,通常都需要保存相关的中间计算结果。聚合函数缓冲区是指在同一个分组的数据聚合的过程中,用来保存聚合函数计算中间结果的内存空间(一行数据)。因为一次查询中可能包含多个聚合函数,因此聚合函数缓冲区是多个聚合函数所共享的。
在AggregateFunction中与聚合缓冲区相关的基本属性包括:聚合缓冲区的Schema信息aggBufferSchema: StructType,聚合缓冲区的数据列信息aggBufferAttributes: Seq[AttributeReference]
聚合模式
在SparkSQL中,聚合过程有4种模式,分别是Partial模式、ParitialMerge模式、Final模式和Complete模式。
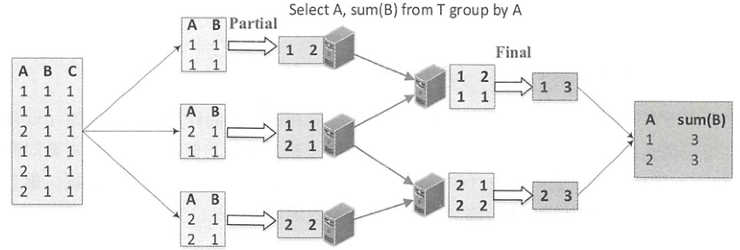
Final模式一般和Partial模式组合在一起使用。如下图所示,Partial模式的聚合函数在执行时会根据读入的原始数据更新对应的聚合缓冲区,当处理完所有的输入数据后,返回的是聚合缓冲区中的中间数据 。 而Final模式所起到的作用是将聚合缓冲区的数据进行合并,然后返回最终的结果
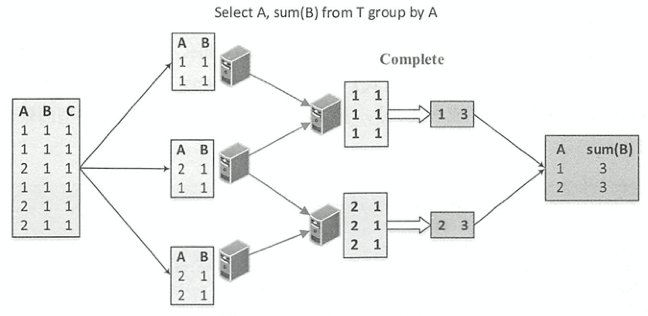
如下图所示,Complete模式相对于Partial/Final组合的分区内聚合,不进行局部聚合计算。Complete模式应用在不支持Partial模式的聚合函数中
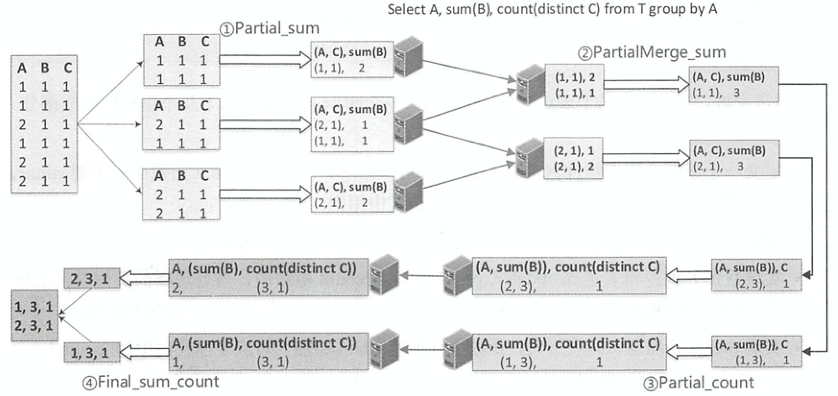
PartialMerge模式的聚合函数主要是对聚合缓冲区进行合并,但此时仍然不是最终的结果。ParitialMerge模式主要应用在distinct语句中
DeclarativeAggregate
DeclarativeAggregate聚合函数是直接由表达式Expressions构建的聚合函数,主要逻辑通过调用 4 个表达式完成,分别是聚合缓冲区初始化表达式initialValues,聚合缓冲区更新表达式updateExpressions,聚合缓冲区合并表达式mergeExpressions,最终结果生成表达式evaluateExpression
下面以count()聚合函数为例介绍
- 定义聚合缓冲区的列信息
aggBufferAttributes,由其子表达式类型确定 - 定义初始值
initialValues,sum()函数的初始值为null - 定义更新表达式
updateExpressions,成员属性sum与子表达式的值相加 - 实现合并表达式
mergeExpressions,将缓冲区的各个sum进行合并相加 - 实现结果输出表达式
evaluateExpression,返回成员属性sum
case class Sum(child: Expression) extends DeclarativeAggregate with ImplicitCastInputTypes {
override def children: Seq[Expression] = child :: Nil
override def nullable: Boolean = true
// Return data type.
override def dataType: DataType = resultType
override def inputTypes: Seq[AbstractDataType] = Seq(NumericType)
override def checkInputDataTypes(): TypeCheckResult =
TypeUtils.checkForNumericExpr(child.dataType, "function sum")
private lazy val resultType = child.dataType match {
case DecimalType.Fixed(precision, scale) =>
DecimalType.bounded(precision + 10, scale)
case _: IntegralType => LongType
case _ => DoubleType
}
private lazy val sumDataType = resultType
private lazy val sum = AttributeReference("sum", sumDataType)()
private lazy val zero = Cast(Literal(0), sumDataType)
override lazy val aggBufferAttributes = sum :: Nil
override lazy val initialValues: Seq[Expression] = Seq(
/* sum = */ Literal.create(null, sumDataType)
)
override lazy val updateExpressions: Seq[Expression] = {
if (child.nullable) {
Seq(
/* sum = */
coalesce(coalesce(sum, zero) + child.cast(sumDataType), sum)
)
} else {
Seq(
/* sum = */
coalesce(sum, zero) + child.cast(sumDataType)
)
}
}
override lazy val mergeExpressions: Seq[Expression] = {
Seq(
/* sum = */
coalesce(coalesce(sum.left, zero) + sum.right, sum.left)
)
}
override lazy val evaluateExpression: Expression = sum
}
ImperativeAggregate
ImperativeAggregate聚合函数需要显式地实现initialize(), update(), merge()方法来操作聚合缓冲区中的数据 。ImperativeAggregate聚合函数所处理的聚合缓冲区本质上是基于行InternalRow。
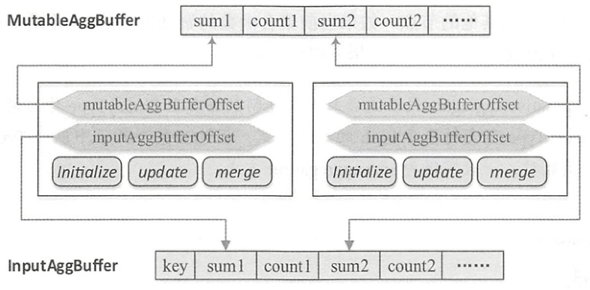
如下图所示,聚合缓冲区是共享的,可能对应多个聚合函数,因此特定的ImperativeAggregate聚合函数会通过偏移量mutableAggBufferOffset在可变缓冲区MutableAggBuffer中进行定位。在合并聚合缓冲区时,通过将输入缓冲区InputAggBuffer的值更新到可变缓冲区MutableAggBuffer中,需要通过偏移量inputAggBuferOffset来访问特定的聚合值。
TypedAggregateExpression
TypedimperativeAggregate[T]聚合函数允许使用用户自定义的 Java 对象作为内部的聚合缓冲区
逻辑计划
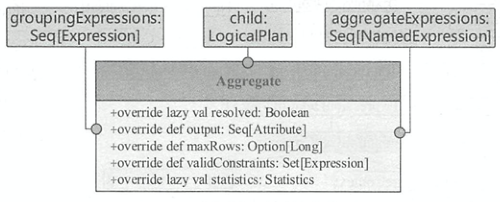
Aggregate逻辑算子树节点继承于UnaryNode。由分组表达式列表groupingExpressions、聚合表达式列表aggregateExpressions和子节点由造而成,输出函数output()对应聚合表达式列表中的所有属性值。 判断一个聚合算子是否已经被解析过需要满足 3 个条件
- 该算子中的所有表达式都已经被解析过了
- 其子节点已经被解析过了
- 该节点中不包含窗口函数表达式
物理计划
AggregationIterator
聚合迭代器包含聚合函数初始化initializeAggregateFunctions()、数据处理函数生成generateProcessRow()和聚合结果输出函数生成generateResultProjection()。其子类SortBasedAggregationlterator和TungstenAggregationlterator分别由SortAggregateExec和 HashAggregateExec两种执行方式调用processCurrentSortedGroup()与processlnputs()得到最聚合结果。
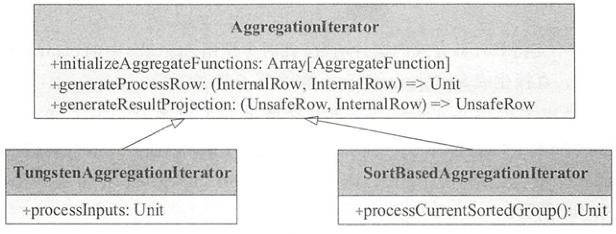
initializeAggregateFunctions(): 聚合函数初始化。为ImperativeAggregate类型的聚合函数设置输入缓冲区偏移量inputBufferOffset和可变缓冲区偏移量mutableAggBufferOffsetgenerateProcessRow(): 返回数据处理函数processRow: (InternalRow, InternalRow) => Unit,处理当前的聚合缓冲区和输入数据行。数据处理函数的核心操作是对于Partial和Complete模式,处理的是原始输入数据,因此采用的是update函数;而对于Final和PartialMerge模式,处理的是聚合缓冲区,因此采用的是 merge函数protected def generateProcessRow( expressions: Seq[AggregateExpression], functions: Seq[AggregateFunction], inputAttributes: Seq[Attribute]): (InternalRow, InternalRow) => Unit = { val joinedRow = new JoinedRow if (expressions.nonEmpty) { val mergeExpressions = functions.zipWithIndex.flatMap { case (ae: DeclarativeAggregate, i) => expressions(i).mode match { case Partial | Complete => ae.updateExpressions case PartialMerge | Final => ae.mergeExpressions } case (agg: AggregateFunction, _) => Seq.fill(agg.aggBufferAttributes.length)(NoOp) } val updateFunctions = functions.zipWithIndex.collect { case (ae: ImperativeAggregate, i) => expressions(i).mode match { case Partial | Complete => (buffer: InternalRow, row: InternalRow) => ae.update(buffer, row) case PartialMerge | Final => (buffer: InternalRow, row: InternalRow) => ae.merge(buffer, row) } }.toArray // This projection is used to merge buffer values for all expression-based aggregates. val aggregationBufferSchema = functions.flatMap(_.aggBufferAttributes) val updateProjection = newMutableProjection(mergeExpressions, aggregationBufferSchema ++ inputAttributes) (currentBuffer: InternalRow, row: InternalRow) => { // Process all expression-based aggregate functions. updateProjection.target(currentBuffer)(joinedRow(currentBuffer, row)) // Process all imperative aggregate functions. var i = 0 while (i < updateFunctions.length) { updateFunctions(i)(currentBuffer, row) i += 1 } } } else { // Grouping only. (currentBuffer: InternalRow, row: InternalRow) => {} } }generateResultProjection(): 返回最终计算结果函数generateOutput: (UnsafeRow, InternalRow) => UnsafeRow。对于Partial或PartialMerge模式的聚合函数,因为只是中间结果,所以需要保存分组语句与聚合缓冲属性;对于Final和Complete模式,直接对应resultExpressions表达式protected def generateResultProjection(): (UnsafeRow, InternalRow) => UnsafeRow = { val joinedRow = new JoinedRow val modes = aggregateExpressions.map(_.mode).distinct val bufferAttributes = aggregateFunctions.flatMap(_.aggBufferAttributes) if (modes.contains(Final) || modes.contains(Complete)) { val evalExpressions = aggregateFunctions.map { case ae: DeclarativeAggregate => ae.evaluateExpression case agg: AggregateFunction => NoOp } val aggregateResult = new SpecificInternalRow(aggregateAttributes.map(_.dataType)) val expressionAggEvalProjection = newMutableProjection(evalExpressions, bufferAttributes) expressionAggEvalProjection.target(aggregateResult) val resultProjection = UnsafeProjection.create(resultExpressions, groupingAttributes ++ aggregateAttributes) resultProjection.initialize(partIndex) (currentGroupingKey: UnsafeRow, currentBuffer: InternalRow) => { // Generate results for all expression-based aggregate functions. expressionAggEvalProjection(currentBuffer) // Generate results for all imperative aggregate functions. var i = 0 while (i < allImperativeAggregateFunctions.length) { aggregateResult.update( allImperativeAggregateFunctionPositions(i), allImperativeAggregateFunctions(i).eval(currentBuffer)) i += 1 } resultProjection(joinedRow(currentGroupingKey, aggregateResult)) } } else if (modes.contains(Partial) || modes.contains(PartialMerge)) { val resultProjection = UnsafeProjection.create( groupingAttributes ++ bufferAttributes, groupingAttributes ++ bufferAttributes) resultProjection.initialize(partIndex) // TypedImperativeAggregate stores generic object in aggregation buffer, and requires // calling serialization before shuffling. See [[TypedImperativeAggregate]] for more info. val typedImperativeAggregates: Array[TypedImperativeAggregate[_]] = { aggregateFunctions.collect { case (ag: TypedImperativeAggregate[_]) => ag } } (currentGroupingKey: UnsafeRow, currentBuffer: InternalRow) => { // Serializes the generic object stored in aggregation buffer var i = 0 while (i < typedImperativeAggregates.length) { typedImperativeAggregates(i).serializeAggregateBufferInPlace(currentBuffer) i += 1 } resultProjection(joinedRow(currentGroupingKey, currentBuffer)) } } else { // Grouping-only: we only output values based on grouping expressions. val resultProjection = UnsafeProjection.create(resultExpressions, groupingAttributes) resultProjection.initialize(partIndex) (currentGroupingKey: UnsafeRow, currentBuffer: InternalRow) => { resultProjection(currentGroupingKey) } } }
HashAggregateExec
基于哈希表的聚合物理计划。HashAggregateExec可能因为内存不足的原因退化为SortAggregateExec。在其doExecute()方法中每个分区内都构建了TungstenAggregationIterator迭代器,将聚合的具体逻辑交由迭代器处理。
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = attachTree(this, "execute") {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
val peakMemory = longMetric("peakMemory")
val spillSize = longMetric("spillSize")
val avgHashProbe = longMetric("avgHashProbe")
val aggTime = longMetric("aggTime")
child.execute().mapPartitionsWithIndex { (partIndex, iter) =>
val beforeAgg = System.nanoTime()
val hasInput = iter.hasNext
val res = if (!hasInput && groupingExpressions.nonEmpty) {
// This is a grouped aggregate and the input iterator is empty,
// so return an empty iterator.
Iterator.empty
} else {
val aggregationIterator =
new TungstenAggregationIterator(
partIndex,
groupingExpressions,
aggregateExpressions,
aggregateAttributes,
initialInputBufferOffset,
resultExpressions,
(expressions, inputSchema) =>
newMutableProjection(expressions, inputSchema, subexpressionEliminationEnabled),
child.output,
iter,
testFallbackStartsAt,
numOutputRows,
peakMemory,
spillSize,
avgHashProbe)
if (!hasInput && groupingExpressions.isEmpty) {
numOutputRows += 1
Iterator.single[UnsafeRow](aggregationIterator.outputForEmptyGroupingKeyWithoutInput())
} else {
aggregationIterator
}
}
aggTime += (System.nanoTime() - beforeAgg) / 1000000
res
}
}
如下所示,TungstenAggregationiterator.processlnputs()方法触发聚合操作。
- 不断获取输入数据
newInput,然后得到分组键值groupingKey,在hashMap: UnsafeFixedWidthAggregationMap中获取对应的聚合操作缓冲区buffer - 如果
buffer不为空,则直接调用processRow()处理 - 如获取不到对应的
buffer,则意味着hashMap内存空间己满无法创建新的缓冲区,调用destructAndCreateExternalSorter()方法将内存数据溢出到磁盘以释放内存空间。每次溢出的结果会以sorter: UnsafeKVExternalSorter数据结构访问,多次spill的外部数据还会进行合并操作。然后,再次从hashMap获取聚合缓冲区,此时如果无法获取,则会抛出OOM - 当输入数据都处理完时,如果
externalSorter不为空则意味着聚合操作过程因为内存不足没能执行成功,部分数据存储在磁盘上。 此时,将hashMap中最后的数据溢出到磁盘并与externalSorter中的数据合并,然后调用hashMap.free()方法释放内存中的数据 ,调用switchToSortBasedAggregation()方法切换到基于排序的聚合执行方式
private def processInputs(fallbackStartsAt: (Int, Int)): Unit = {
if (groupingExpressions.isEmpty) {
// If there is no grouping expressions, we can just reuse the same buffer over and over again.
// Note that it would be better to eliminate the hash map entirely in the future.
val groupingKey = groupingProjection.apply(null)
val buffer: UnsafeRow = hashMap.getAggregationBufferFromUnsafeRow(groupingKey)
while (inputIter.hasNext) {
val newInput = inputIter.next()
processRow(buffer, newInput)
}
} else {
var i = 0
while (inputIter.hasNext) {
val newInput = inputIter.next()
val groupingKey = groupingProjection.apply(newInput)
var buffer: UnsafeRow = null
if (i < fallbackStartsAt._2) {
buffer = hashMap.getAggregationBufferFromUnsafeRow(groupingKey)
}
if (buffer == null) {
val sorter = hashMap.destructAndCreateExternalSorter()
if (externalSorter == null) {
externalSorter = sorter
} else {
externalSorter.merge(sorter)
}
i = 0
buffer = hashMap.getAggregationBufferFromUnsafeRow(groupingKey)
if (buffer == null) {
// failed to allocate the first page
throw new SparkOutOfMemoryError("No enough memory for aggregation")
}
}
processRow(buffer, newInput)
i += 1
}
if (externalSorter != null) {
val sorter = hashMap.destructAndCreateExternalSorter()
externalSorter.merge(sorter)
hashMap.free()
switchToSortBasedAggregation()
}
}
}
SortAggregateExec
基于排序的聚合物理计划。在进行聚合之前,会根据分组键进行shuffle,所以会添加Exchange物理计划。requiredChildOrdering要求分组表达式列表中的每个表达式都必须满足升序排列,因此在SortAggregateExec节点之前通常都会添加一个SortExec节点
对于SortAggregateExec来说,只需要顺序遍历整个分区内的数据,即可得到聚合结果。在其doExecute()方法中每个分区内都构建了SortBasedAggregationIterator迭代器,将聚合的具体逻辑交由迭代器处理
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = attachTree(this, "execute") {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
child.execute().mapPartitionsWithIndexInternal { (partIndex, iter) =>
// Because the constructor of an aggregation iterator will read at least the first row,
// we need to get the value of iter.hasNext first.
val hasInput = iter.hasNext
if (!hasInput && groupingExpressions.nonEmpty) {
// This is a grouped aggregate and the input iterator is empty,
// so return an empty iterator.
Iterator[UnsafeRow]()
} else {
val outputIter = new SortBasedAggregationIterator(
partIndex,
groupingExpressions,
child.output,
iter,
aggregateExpressions,
aggregateAttributes,
initialInputBufferOffset,
resultExpressions,
(expressions, inputSchema) =>
newMutableProjection(expressions, inputSchema, subexpressionEliminationEnabled),
numOutputRows)
if (!hasInput && groupingExpressions.isEmpty) {
// There is no input and there is no grouping expressions.
// We need to output a single row as the output.
numOutputRows += 1
Iterator[UnsafeRow](outputIter.outputForEmptyGroupingKeyWithoutInput())
} else {
outputIter
}
}
}
}
如下代码所示,迭代器的initialize()方法,会在迭代器构造时调用。currentGroupingKey和nextGroupingKey分别表示当前的分组表达式和下一个分组表达式,sortBasedAggregationBuffer为其聚合缓冲区。
protected def initialize(): Unit = {
if (inputIterator.hasNext) {
initializeBuffer(sortBasedAggregationBuffer)
val inputRow = inputIterator.next()
nextGroupingKey = groupingProjection(inputRow).copy()
firstRowInNextGroup = inputRow.copy()
sortedInputHasNewGroup = true
} else {
// This inputIter is empty.
sortedInputHasNewGroup = false
}
}
如下代码所示,迭代器的processCurrentSortedGroup()方法,会在其next()方法内调用。不断获取输入行,执行groupingProjection()得到groupingKey分组键值。 如果当前的分组键值currentGroupingKey和groupingKey相同,那么意味着当前输入数据仍然属 同一个分组内部,因此调用Aggregationlterator.processRow()函数来处理当前数据,否则就要重新初始化缓冲区进行聚合
protected def processCurrentSortedGroup(): Unit = {
currentGroupingKey = nextGroupingKey
// Now, we will start to find all rows belonging to this group.
// We create a variable to track if we see the next group.
var findNextPartition = false
// firstRowInNextGroup is the first row of this group. We first process it.
processRow(sortBasedAggregationBuffer, firstRowInNextGroup)
// The search will stop when we see the next group or there is no
// input row left in the iter.
while (!findNextPartition && inputIterator.hasNext) {
// Get the grouping key.
val currentRow = inputIterator.next()
val groupingKey = groupingProjection(currentRow)
// Check if the current row belongs the current input row.
if (currentGroupingKey == groupingKey) {
processRow(sortBasedAggregationBuffer, currentRow)
} else {
// We find a new group.
findNextPartition = true
nextGroupingKey = groupingKey.copy()
firstRowInNextGroup = currentRow.copy()
}
}
// We have not seen a new group. It means that there is no new row in the input
// iter. The current group is the last group of the iter.
if (!findNextPartition) {
sortedInputHasNewGroup = false
}
}
选择过程
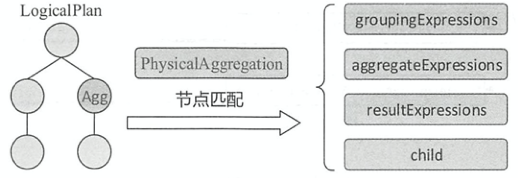
如图所示,PhysicalAggregation匹配策略用来匹配逻辑算子树中的 Aggregate节点并提取该节点中的相关信息,其中resultExpressions表示聚合的结果表达式。 PhysicalAggregation在提取信息时会进行以下转换
- 去重: 对
Aggregate逻辑算子节点中多次重复出现的聚合操作进行去重,收集resultExpressions中的聚合函数表达式,然后执行distinct操作 - 命名: 对未命名的分组表达式套上一个
Alias表达式,方便在后续聚合过程中进行引用 - 分离: 从最后结果中分离出聚合计算本身的值
def unapply(a: Any): Option[ReturnType] = a match {
case logical.Aggregate(groupingExpressions, resultExpressions, child) =>
val equivalentAggregateExpressions = new EquivalentExpressions
val aggregateExpressions = resultExpressions.flatMap { expr =>
expr.collect {
// addExpr() always returns false for non-deterministic expressions and do not add them.
case agg: AggregateExpression
if !equivalentAggregateExpressions.addExpr(agg) => agg
case udf: PythonUDF
if PythonUDF.isGroupedAggPandasUDF(udf) &&
!equivalentAggregateExpressions.addExpr(udf) => udf
}
}
val namedGroupingExpressions = groupingExpressions.map {
case ne: NamedExpression => ne -> ne
case other =>
val withAlias = Alias(other, other.toString)()
other -> withAlias
}
val groupExpressionMap = namedGroupingExpressions.toMap
val rewrittenResultExpressions = resultExpressions.map { expr =>
expr.transformDown {
case ae: AggregateExpression =>
equivalentAggregateExpressions.getEquivalentExprs(ae).headOption
.getOrElse(ae).asInstanceOf[AggregateExpression].resultAttribute
// Similar to AggregateExpression
case ue: PythonUDF if PythonUDF.isGroupedAggPandasUDF(ue) =>
equivalentAggregateExpressions.getEquivalentExprs(ue).headOption
.getOrElse(ue).asInstanceOf[PythonUDF].resultAttribute
case expression =>
groupExpressionMap.collectFirst {
case (expr, ne) if expr semanticEquals expression => ne.toAttribute
}.getOrElse(expression)
}.asInstanceOf[NamedExpression]
}
Some((
namedGroupingExpressions.map(_._2),
aggregateExpressions,
rewrittenResultExpressions,
child))
case _ => None
}
在Aggregation.apply()方法中,匹配到PhysicalAggregation时,会根据聚合表达式是否包含distinct函数,调用AggUtils.planAggregateWithoutDistinct()或者AggUtils.planAggregateWithOneDistinct()来生成对应的物理计划
planAggregateWithoutDistinct(): 对应着partital/final组合和complete模式,可以结合上一小节的流程图理解- O如果是partital/final组合,调用
createAggregate()给所有partial模式聚合函数作为聚合表达式创建物理计划,再调用createAggregate()以partial模式聚合函数的物理计划作为子结点创建所有final模式聚合函数的物理计划 - 如果是complete模式,目前版本的处理方式是,将complete聚合函数当做partital/final组合,与partital/final组合处理方式相同
- O如果是partital/final组合,调用
planAggregateWithOneDistinct(): 对应着PartialMerge模式,可以结合上一小节的流程图理解- 调用
createAggregate()给不包含distinct的partial模式聚合函数作为聚合表达式创建物理计划,resultExpressions为分组字段+distinct字段+聚合字段 - 调用
createAggregate()给不包含distinct的PartialMerge模式聚合函数作为聚合表达式创建物理计划,子结点为上一步创建的物理计划,resultExpressions为分组字段+distinct字段+聚合字段 - 调用
createAggregate()给不包含distinct的PartialMerge模式聚合函数和包含distinct的聚合函数作为聚合表达式创建物理计划,子结点为上一步创建的物理计划,resultExpressions为分组字段+聚合字段+distinct字段 - 调用
createAggregate()给不包含distinct的final模式聚合函数和包含distinct的聚合函数作为聚合表达式创建物理计划,子结点为上一步创建的物理计划,resultExpressions为最终聚合结果
- 调用
createAggregate(): 创建具体的物理计划- 如果聚合缓冲区中的数据列不包含不可变类型,则创建
HashAggregateExec。可变类型为BooleanType,ByteType,DateType,DecimalType,DoubleType,FloatType,IntegerType,LongType,NullType,ShortType,TimestampType, 不可变类型为ArrayType,BinaryType,StringType,CalendarIntervalType,MapType,ObjectType,StructType - 如果
spark.sql.execution.useObjectHashAggregateExec属性开启,并且至少存在一个TypedImperativeAggregate类型的聚合函数,则创建ObjectHashAggregateExec - 其他情况创建
SortAggregateExec
- 如果聚合缓冲区中的数据列不包含不可变类型,则创建
解析过程
如下所示,一条简单的带有聚合的SQL语句SELECT ID, COUNT(NAME) FROM STUDENT GROUP BY ID解析成执行计划的过程
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
// UnresolvedFunction => 'COUNT('NAME)
'Aggregate ['ID], ['ID, unresolvedalias('COUNT('NAME), None)]
+- 'UnresolvedRelation `STUDENT`
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
ID: string, count(NAME): bigint
// AggregateFunction => count(NAME#11)
Aggregate [ID#10], [ID#10, count(NAME#11) AS count(NAME)#22L]
+- SubqueryAlias `student`
+- Relation[ID#10,NAME#11,AGE#12] csv
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Aggregate [ID#10], [ID#10, count(NAME#11) AS count(NAME)#22L]
+- Project [ID#10, NAME#11]
+- Relation[ID#10,NAME#11,AGE#12] csv
== Physical Plan ==
*(2) HashAggregate(keys=[ID#10], functions=[count(NAME#11)])
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(ID#10, 200)
+- *(1) HashAggregate(keys=[ID#10], functions=[partial_count(NAME#11)])
+- *(1) FileScan csv [ID#10,NAME#11] Batched: false, Format: CSV, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/wzx/Documents/tmp/spark_tmp/STUDENT.csv], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [], ReadSchema: struct<ID:string,NAME:string>
- 由ANTLR4将SQL字符串解析成ANTLR4解析树
- 由
SparkSqlParser将ANTLR4解析树转化为Unresolved逻辑计划树 Analyzer对Unresolved逻辑计划树应用解析规则,解析为Analyzed逻辑计划树。对于UnresolvedFunction表达式,Analyzer会根据函数名和函数参数去SessionCatalog中查找,而SessionCatalog会根据FunctionRegistry中已经注册的函数信息得到对应的聚合函数AggregateFunctionOptimizer对Analyzed逻辑计划树应用优化规则。在本例中经过了别名消除EliminateSubqueryAliases规则与列剪裁ColumnPruning规则的处理SparkPlanner对逻辑计划树应用生成物理计划规则,转化为物理计划树。在Aggregation策略中通过PhysicalAggregation模式匹配将Aggregate [ID#10], [ID#10, cast(count(NAME#11) as string) AS count(NAME)#23]提取为PhysicalAggregation [ID#10], [count(NAME#11)], [ID#10, cast(count(NAME#11)#16L as string) AS count(NAME)#23], child- 由于count()聚合函数是complete模式,但是处理方式仍然是partital/final组合的处理方式,所以创建了两个
HashAggregate,并且在预处理阶段加入了shuffle
如下所示,SELECT ID, collect_set(NAME) FROM STUDENT GROUP BY ID的执行计划,这里将spark.sql.execution.useObjectHashAggregateExec设置为false以便可以使用SortAggregateExec物理计划。因为聚合缓冲区的类型为ArrayType,所以使用了SortAggregateExec
SortAggregate(key=[ID#10], functions=[collect_set(NAME#11, 0, 0)])
+- Sort [ID#10 ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(ID#10, 200)
+- SortAggregate(key=[ID#10], functions=[partial_collect_set(NAME#11, 0, 0)])
+- Sort [ID#10 ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
+- FileScan csv [ID#10,NAME#11] Batched: false, Format: CSV, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/wzx/Documents/tmp/spark_tmp/STUDENT.csv], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [], ReadSchema: struct<ID:string,NAME:string>
REFERENCE
- Spark SQL内核剖析
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/11/18/spark-sql-aggregation/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)