介绍Spark中的block内存存储。Hadoop只将内存作为计算资源,Spark除将内存作为计算资源外,还将内存的一部分纳入到存储体系中。
MemoryMode
Spark将内存分为堆内内存(Java堆的一部分)和堆外内存。由MemoryMode枚举变量给定。
@Private
public enum MemoryMode {
ON_HEAP,
OFF_HEAP
}
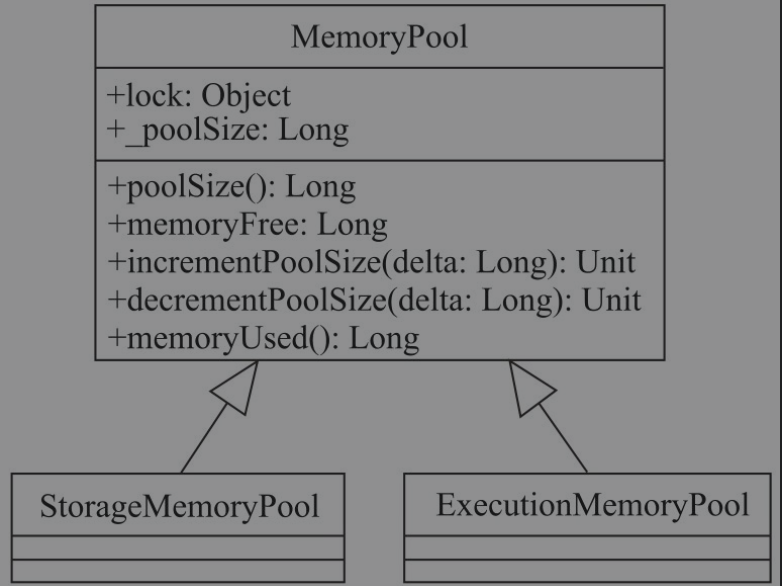
MemoryPool
抽象类,管理和调整内存区域的内存池。
有以下重要的成员变量
lock: 对内存池提供线程安全保证的锁对象。_poolSize: 内存池大小,Byte
有以下基本方法
poolSize(): 返回_poolSize的值memoryUsed(): 返回已使用的内存大小。由MemoryPool的子类实现memoryFree(): 返回内存池的空闲空间大小。_poolSize - memoryUsedincrementPoolSize(): 给内存池拓展delta大小的空间decrementPoolSize(): 缩小内存池delta大小的空间
如下图所示,有以下的继承关系,StorageMemoryPool是存储体系中用到的内存池,ExecutionMemoryPool是计算引擎中用到的内存池。
StorageMemoryPool
下面是特有的成员变量,大部分成员方法都使用lock.synchronized保证线程安全
memoryMode:MemoryModepoolName: 如果是堆内内存则名称为on-heap storage,如果是堆外内存则名称是off-heap storage_memoryUsed: 已使用的内存大小_memoryStore:MemoryStore
下面是一些特有和实现的方法
memoryUsed: 直接返回_memoryUsedreleaseAllMemory(): 将_memoryUsed赋值为0acquireMemory(): 获得内存去缓存给定的block,必要时会腾出其他block占用的内存- 计算出需要腾出的内存大小
numBytesToFree - 如果空闲内存不足,调用
MemoryStore.evictBlocksToFreeSpace()驱逐内存中的block以释放内存 - 更新已使用内存量,返回是否成功获得内存空间
def acquireMemory(blockId: BlockId, numBytes: Long): Boolean = lock.synchronized { val numBytesToFree = math.max(0, numBytes - memoryFree) acquireMemory(blockId, numBytes, numBytesToFree) } def acquireMemory( blockId: BlockId, numBytesToAcquire: Long, numBytesToFree: Long): Boolean = lock.synchronized { assert(numBytesToAcquire >= 0) assert(numBytesToFree >= 0) assert(memoryUsed <= poolSize) if (numBytesToFree > 0) { memoryStore.evictBlocksToFreeSpace(Some(blockId), numBytesToFree, memoryMode) } // NOTE: If the memory store evicts blocks, then those evictions will synchronously call // back into this StorageMemoryPool in order to free memory. Therefore, these variables // should have been updated. val enoughMemory = numBytesToAcquire <= memoryFree if (enoughMemory) { _memoryUsed += numBytesToAcquire } enoughMemory }- 计算出需要腾出的内存大小
releaseMemory(): 释放指定大小的内存,实际上只是更改_memoryUsed的值def releaseMemory(size: Long): Unit = lock.synchronized { if (size > _memoryUsed) { logWarning(s"Attempted to release $size bytes of storage " + s"memory when we only have ${_memoryUsed} bytes") _memoryUsed = 0 } else { _memoryUsed -= size } }freeSpaceToShrinkPool(): 释放spaceToFree大小的空间以缩小内存池大小,只会释放空间并不会缩小内存池大小- 计算
spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory,通过释放未使用内存从而减小内存池大小的最大可释放空间 - 计算
remainingSpaceToFree,还需要释放已使用内存以补齐spaceToFree的大小 - 如果
remainingSpaceToFree大于0则需要释放已使用内存,调用MemoryStore.evictBlocksToFreeSpace()释放内存 - 如果
remainingSpaceToFree小于0则不需要释放已使用内存 - 返回从该内存池中移除的内存大小
def freeSpaceToShrinkPool(spaceToFree: Long): Long = lock.synchronized { val spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory = math.min(spaceToFree, memoryFree) val remainingSpaceToFree = spaceToFree - spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory if (remainingSpaceToFree > 0) { // If reclaiming free memory did not adequately shrink the pool, begin evicting blocks: val spaceFreedByEviction = memoryStore.evictBlocksToFreeSpace(None, remainingSpaceToFree, memoryMode) // When a block is released, BlockManager.dropFromMemory() calls releaseMemory(), so we do // not need to decrement _memoryUsed here. However, we do need to decrement the pool size. spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory + spaceFreedByEviction } else { spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory } }- 计算
MemoryManager
抽象类,用于存储部分的内存管理器,下面是重要的成员对象
numCores: CPU核心数onHeapStorageMemory: 用于存储的堆内内存大小onHeapExecutionMemory: 用于计算的堆内内存大小onHeapStorageMemoryPool,offHeapStorageMemoryPool,onHeapExecutionMemoryPool,offHeapExecutionMemoryPool: 用于计算和存储的堆内堆外内存池maxOffHeapMemory: 堆外内存的最大值。通过spark.memory.offHeap.size指定offHeapStorageMemory: 用于储存的堆外内存大小。最大堆外内存的最大值的一部分,默认为0.5,通过spark.memory.storageFraction指定
下面是重要的成员方法,大部分方法都用synchronized保证线程安全
maxOnHeapStorageMemory(): 最大堆内存储内存,由子类实现maxOffHeapStorageMemory(): 最大堆外存储内存,由子类实现acquireStorageMemory(): 为存储block,从堆内或堆外内存获取指定大小的内存,由子类实现acquireUnrollMemory(): 为展开block,从堆内或堆外内存获取指定大小的内存,由子类实现setMemoryStore(): 给堆内堆外内存池设置MemoryStore
如下所示,对计算内存和存储内存的操作都将直接对相应的内存池进行操作,比较简单
/**
* Release numBytes of execution memory belonging to the given task.
*/
private[memory]
def releaseExecutionMemory(
numBytes: Long,
taskAttemptId: Long,
memoryMode: MemoryMode): Unit = synchronized {
memoryMode match {
case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.releaseMemory(numBytes, taskAttemptId)
case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.releaseMemory(numBytes, taskAttemptId)
}
}
/**
* Release all memory for the given task and mark it as inactive (e.g. when a task ends).
*
* @return the number of bytes freed.
*/
private[memory] def releaseAllExecutionMemoryForTask(taskAttemptId: Long): Long = synchronized {
onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.releaseAllMemoryForTask(taskAttemptId) +
offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.releaseAllMemoryForTask(taskAttemptId)
}
/**
* Release N bytes of storage memory.
*/
def releaseStorageMemory(numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Unit = synchronized {
memoryMode match {
case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => onHeapStorageMemoryPool.releaseMemory(numBytes)
case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => offHeapStorageMemoryPool.releaseMemory(numBytes)
}
}
/**
* Release all storage memory acquired.
*/
final def releaseAllStorageMemory(): Unit = synchronized {
onHeapStorageMemoryPool.releaseAllMemory()
offHeapStorageMemoryPool.releaseAllMemory()
}
/**
* Release N bytes of unroll memory.
*/
final def releaseUnrollMemory(numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Unit = synchronized {
releaseStorageMemory(numBytes, memoryMode)
}
/**
* Execution memory currently in use, in bytes.
*/
final def executionMemoryUsed: Long = synchronized {
onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.memoryUsed + offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.memoryUsed
}
/**
* Storage memory currently in use, in bytes.
*/
final def storageMemoryUsed: Long = synchronized {
onHeapStorageMemoryPool.memoryUsed + offHeapStorageMemoryPool.memoryUsed
}
/**
* Returns the execution memory consumption, in bytes, for the given task.
*/
private[memory] def getExecutionMemoryUsageForTask(taskAttemptId: Long): Long = synchronized {
onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.getMemoryUsageForTask(taskAttemptId) +
offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.getMemoryUsageForTask(taskAttemptId)
}
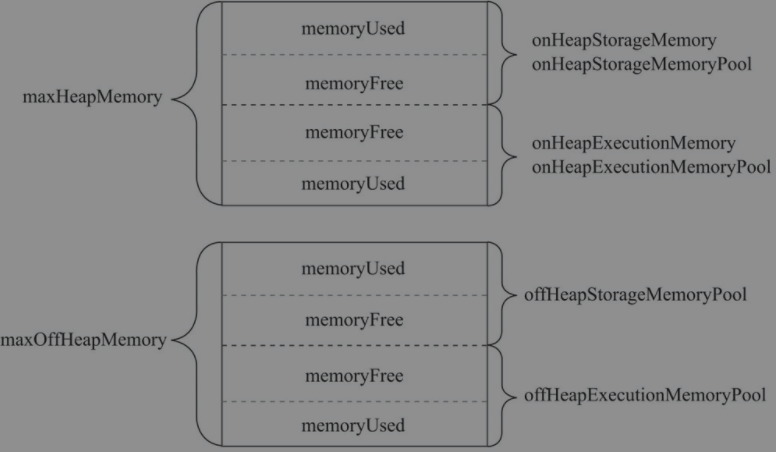
MemoryManager有两个子类,分别是StaticMemoryManager和UnifiedMemoryManager。在静态内存管理机制下,Spark应用程序在运行期的存储内存和执行内存的大小均为固定的。现在Spark默认使用UnifiedMemoryManager可以动态调节存储内存和执行内存的空间大小。
UnifiedMemoryManager
维护在计算内存和存储内存之间的软边界,可以相互借用内存。计算和存储的占比由spark.memory.fraction 配置,默认是0.6,即偏向于存储内存池。其中存储内存池的堆内内存默认占比是由 spark.memory.storageFraction 参数决定,默认是 0.5 ,即存储内存池的堆内内存默认占比为0.3。
计算内存和存储内存可以相互借用,但是缓存block时可能会因为计算内存池占用了大量的内存池不能释放导致缓存block失败,在这种情况下,新的block会根据StorageLevel做相应处理。
以下只介绍存储体系方面的内容,下面是特有的成员变量
maxHeapMemory: 最大堆内内存。大小为系统可用内存与spark.memory.fraction属性值(默认为0.6)的乘积
下面是实现的方法,使用了synchronized保证线程安全
maxOnHeapStorageMemory(): 最大堆内储存内存。最大堆内内存减去堆内计算内存已使用的内存量override def maxOnHeapStorageMemory: Long = synchronized { maxHeapMemory - onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.memoryUsed }maxOffHeapStorageMemory(): 最大堆外存储内存。最大堆外内存减去堆外计算内存已使用的内存量override def maxOffHeapStorageMemory: Long = synchronized { maxOffHeapMemory - offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.memoryUsed }acquireStorageMemory(): 为存储block从存储内存池中获取所需大小的内存- 根据内存模式获取对应的计算内存池,存储内存池和最大存储内存大小
- 如果所需内存大于存储内存池中的空闲内存大小,则减少执行内存池的大小以增加存储内存池的大小,向执行内存池借空闲内存
- 获取所需的内存大小
override def acquireStorageMemory( blockId: BlockId, numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Boolean = synchronized { assertInvariants() assert(numBytes >= 0) val (executionPool, storagePool, maxMemory) = memoryMode match { case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => ( onHeapExecutionMemoryPool, onHeapStorageMemoryPool, maxOnHeapStorageMemory) case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => ( offHeapExecutionMemoryPool, offHeapStorageMemoryPool, maxOffHeapStorageMemory) } if (numBytes > maxMemory) { // Fail fast if the block simply won't fit logInfo(s"Will not store $blockId as the required space ($numBytes bytes) exceeds our " + s"memory limit ($maxMemory bytes)") return false } if (numBytes > storagePool.memoryFree) { // There is not enough free memory in the storage pool, so try to borrow free memory from // the execution pool. val memoryBorrowedFromExecution = Math.min(executionPool.memoryFree, numBytes - storagePool.memoryFree) executionPool.decrementPoolSize(memoryBorrowedFromExecution) storagePool.incrementPoolSize(memoryBorrowedFromExecution) } storagePool.acquireMemory(blockId, numBytes) }acquireUnrollMemory(): 为展开block从存储内存池获取所需大小内存,其实就是调用了acquireStorageMemory()方法
MemoryEntry
特质,内存中的block抽象。主要包含size,memoryMode和classTag保存block大小,内存类型和数据类型信息。有两个实现类
DeserializedMemoryEntry: 未序列化的MemoryEntry,一定是存储在堆内内存上SerializedMemoryEntry: 序列化的MemoryEntry
MemoryStore
在内存上存储的block底层管理器。这里多了用于展开block的内存的概念,是用于将迭代器类型的数据放入内存而不断获取使用的内存,其实最终获取的就是存储内存。下面是重要的成员对象
blockInfoManager:BlockInfoManagermemoryManager:MemoryManagerblockEvictionHandler: block驱逐处理器。用于将block从内存中驱逐出去entries:LinkedHashMap[BlockId, MemoryEntry[_]],存储BlockId和MemoryEntry的映射关系onHeapUnrollMemoryMap,offHeapUnrollMemoryMap: 任务attempt id 和在堆内或堆外用于展开block所占内存大小的映射unrollMemoryThreshold: 用来展开block请求的初始内存大小。由spark.storage.unrollMemoryThreshold,默认1M
下面是一些对MemoryStore描述的方法,就是对成员对象的进一步封装
maxMemory(): 最大存储内存包含堆内和堆外。memoryManager.maxOnHeapStorageMemory + memoryManager.maxOffHeapStorageMemorymemoryUsed(): 已使用存储内存包含堆内和堆外。memoryManager.storageMemoryUsedcurrentUnrollMemory(): 用于展开block的内存。onHeapUnrollMemoryMap.values.sum + offHeapUnrollMemoryMap.values.sumcurrentUnrollMemoryForThisTask(): 当前用于展开block所使用的内存。onHeapUnrollMemoryMap.getOrElse(currentTaskAttemptId(), 0L) + offHeapUnrollMemoryMap.getOrElse(currentTaskAttemptId(), 0L)blocksMemoryUsed(): 用于存储block的大小。memoryUsed - currentUnrollMemory
下面MemoryStore中对block处理的方法
getSize(): 通过entries获得对应block的大小evictBlocksToFreeSpace(): 驱逐block,释放已使用的存储空间来存储新的blockfreeMemory表示已经释放的内存,space表示需要释放的内存- 不断迭代,将
entries中的符合条件的block(内存模式一样并且不能和当前block属于同一RDD或者不是RDD)添加进selectedBlocks并获得其写锁,直到满足释放内存的要求 - 释放
selectedBlocks中的block,调用BlockManager.dropFromMemory()迁移到其他存储或者直接清除 - 如果即使驱逐符合条件block也无法满足内存要求,则释放写锁。如果有block释放失败,则释放最后一个成功释放block之后block的写锁
private[spark] def evictBlocksToFreeSpace( blockId: Option[BlockId], space: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Long = { assert(space > 0) memoryManager.synchronized { var freedMemory = 0L val rddToAdd = blockId.flatMap(getRddId) val selectedBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[BlockId] def blockIsEvictable(blockId: BlockId, entry: MemoryEntry[_]): Boolean = { entry.memoryMode == memoryMode && (rddToAdd.isEmpty || rddToAdd != getRddId(blockId)) } // This is synchronized to ensure that the set of entries is not changed // (because of getValue or getBytes) while traversing the iterator, as that // can lead to exceptions. entries.synchronized { val iterator = entries.entrySet().iterator() while (freedMemory < space && iterator.hasNext) { val pair = iterator.next() val blockId = pair.getKey val entry = pair.getValue if (blockIsEvictable(blockId, entry)) { // We don't want to evict blocks which are currently being read, so we need to obtain // an exclusive write lock on blocks which are candidates for eviction. We perform a // non-blocking "tryLock" here in order to ignore blocks which are locked for reading: if (blockInfoManager.lockForWriting(blockId, blocking = false).isDefined) { selectedBlocks += blockId freedMemory += pair.getValue.size } } } } def dropBlock[T](blockId: BlockId, entry: MemoryEntry[T]): Unit = { val data = entry match { case DeserializedMemoryEntry(values, _, _) => Left(values) case SerializedMemoryEntry(buffer, _, _) => Right(buffer) } val newEffectiveStorageLevel = blockEvictionHandler.dropFromMemory(blockId, () => data)(entry.classTag) if (newEffectiveStorageLevel.isValid) { // The block is still present in at least one store, so release the lock // but don't delete the block info blockInfoManager.unlock(blockId) } else { // The block isn't present in any store, so delete the block info so that the // block can be stored again blockInfoManager.removeBlock(blockId) } } if (freedMemory >= space) { var lastSuccessfulBlock = -1 try { logInfo(s"${selectedBlocks.size} blocks selected for dropping " + s"(${Utils.bytesToString(freedMemory)} bytes)") (0 until selectedBlocks.size).foreach { idx => val blockId = selectedBlocks(idx) val entry = entries.synchronized { entries.get(blockId) } // This should never be null as only one task should be dropping // blocks and removing entries. However the check is still here for // future safety. if (entry != null) { dropBlock(blockId, entry) afterDropAction(blockId) } lastSuccessfulBlock = idx } logInfo(s"After dropping ${selectedBlocks.size} blocks, " + s"free memory is ${Utils.bytesToString(maxMemory - blocksMemoryUsed)}") freedMemory } finally { // like BlockManager.doPut, we use a finally rather than a catch to avoid having to deal // with InterruptedException if (lastSuccessfulBlock != selectedBlocks.size - 1) { // the blocks we didn't process successfully are still locked, so we have to unlock them (lastSuccessfulBlock + 1 until selectedBlocks.size).foreach { idx => val blockId = selectedBlocks(idx) blockInfoManager.unlock(blockId) } } } } else { blockId.foreach { id => logInfo(s"Will not store $id") } selectedBlocks.foreach { id => blockInfoManager.unlock(id) } 0L } } }putBytes(): 将序列化的block写入内存中- 判断
BlockId是否在entries中,即这个BlockId已经存在 - 调用
memoryManager.acquireStorageMemory(),为存储block从堆外或堆内存储内存获取所需大小 - 如果在借完执行内存的空闲内存后,自身的空闲内存仍不足,会调用自身的
evictBlocksToFreeSpace()方法释放已使用内存 - 封装为
SerializedMemoryEntry并放入entries记录映射关系
def contains(blockId: BlockId): Boolean = { entries.synchronized { entries.containsKey(blockId) } } def putBytes[T: ClassTag]( blockId: BlockId, size: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode, _bytes: () => ChunkedByteBuffer): Boolean = { require(!contains(blockId), s"Block $blockId is already present in the MemoryStore") if (memoryManager.acquireStorageMemory(blockId, size, memoryMode)) { // We acquired enough memory for the block, so go ahead and put it val bytes = _bytes() assert(bytes.size == size) val entry = new SerializedMemoryEntry[T](bytes, memoryMode, implicitly[ClassTag[T]]) entries.synchronized { entries.put(blockId, entry) } logInfo("Block %s stored as bytes in memory (estimated size %s, free %s)".format( blockId, Utils.bytesToString(size), Utils.bytesToString(maxMemory - blocksMemoryUsed))) true } else { false } }- 判断
reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask(): 为展开block申请内存- 调用
memoryManager.acquireUnrollMemory(),为展开block从堆外或堆内存储内存获取所需大小,与putBytes()方法中的这一步操作类似 - 更新
unrollMemoryMap
def reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask( blockId: BlockId, memory: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Boolean = { memoryManager.synchronized { val success = memoryManager.acquireUnrollMemory(blockId, memory, memoryMode) if (success) { val taskAttemptId = currentTaskAttemptId() val unrollMemoryMap = memoryMode match { case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => onHeapUnrollMemoryMap case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => offHeapUnrollMemoryMap } unrollMemoryMap(taskAttemptId) = unrollMemoryMap.getOrElse(taskAttemptId, 0L) + memory } success } }- 调用
releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask(): 释放在当前任务中用于展开block使用的堆内或堆外内存def releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask(memoryMode: MemoryMode, memory: Long = Long.MaxValue): Unit = { val taskAttemptId = currentTaskAttemptId() memoryManager.synchronized { val unrollMemoryMap = memoryMode match { case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => onHeapUnrollMemoryMap case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => offHeapUnrollMemoryMap } if (unrollMemoryMap.contains(taskAttemptId)) { val memoryToRelease = math.min(memory, unrollMemoryMap(taskAttemptId)) if (memoryToRelease > 0) { unrollMemoryMap(taskAttemptId) -= memoryToRelease memoryManager.releaseUnrollMemory(memoryToRelease, memoryMode) } if (unrollMemoryMap(taskAttemptId) == 0) { unrollMemoryMap.remove(taskAttemptId) } } } }putIterator(): 因为Iterator可能很大无法物化并放入内存中避免发生OOM。逐步展开Iterator,并定期检查是否有足够的可用内存。ValueHolder用于不断添加数据并将已添加的数据封装为MemoryEntry- 调用
reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask()指定保留用来展开block的初始内存 - 每展开
memoryCheckPeriod个元素后就要检查一下是否大于memoryThreshold,否则就要调用reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask()去申请更多的保留内存,内存增长的公式为currentSize * memoryGrowthFactor - memoryThreshold value迭代器中的数据不断追加到ValuesHolder中,直到获取不到多余的内存- 获取
ValuesHolder中的精确大小,并调整已获取到的内存大小 - 将
ValuesHolder中的数据封装为MemoryEntry,并且调用releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask()释放当前任务的展开block内存,调用memoryManager.acquireStorageMemory()获得存储内存,这一步实际上将展开block的内存将转移到存储内存中 - 如果没有足够内存,返回
Left,已使用展开block的内存大小
private def putIterator[T]( blockId: BlockId, values: Iterator[T], classTag: ClassTag[T], memoryMode: MemoryMode, valuesHolder: ValuesHolder[T]): Either[Long, Long] = { require(!contains(blockId), s"Block $blockId is already present in the MemoryStore") // Number of elements unrolled so far var elementsUnrolled = 0 // Whether there is still enough memory for us to continue unrolling this block var keepUnrolling = true // Initial per-task memory to request for unrolling blocks (bytes). val initialMemoryThreshold = unrollMemoryThreshold // How often to check whether we need to request more memory val memoryCheckPeriod = conf.get(UNROLL_MEMORY_CHECK_PERIOD) // Memory currently reserved by this task for this particular unrolling operation var memoryThreshold = initialMemoryThreshold // Memory to request as a multiple of current vector size val memoryGrowthFactor = conf.get(UNROLL_MEMORY_GROWTH_FACTOR) // Keep track of unroll memory used by this particular block / putIterator() operation var unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock = 0L // Request enough memory to begin unrolling keepUnrolling = reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask(blockId, initialMemoryThreshold, memoryMode) if (!keepUnrolling) { logWarning(s"Failed to reserve initial memory threshold of " + s"${Utils.bytesToString(initialMemoryThreshold)} for computing block $blockId in memory.") } else { unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock += initialMemoryThreshold } // Unroll this block safely, checking whether we have exceeded our threshold periodically while (values.hasNext && keepUnrolling) { valuesHolder.storeValue(values.next()) if (elementsUnrolled % memoryCheckPeriod == 0) { val currentSize = valuesHolder.estimatedSize() // If our vector's size has exceeded the threshold, request more memory if (currentSize >= memoryThreshold) { val amountToRequest = (currentSize * memoryGrowthFactor - memoryThreshold).toLong keepUnrolling = reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask(blockId, amountToRequest, memoryMode) if (keepUnrolling) { unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock += amountToRequest } // New threshold is currentSize * memoryGrowthFactor memoryThreshold += amountToRequest } } elementsUnrolled += 1 } // Make sure that we have enough memory to store the block. By this point, it is possible that // the block's actual memory usage has exceeded the unroll memory by a small amount, so we // perform one final call to attempt to allocate additional memory if necessary. if (keepUnrolling) { val entryBuilder = valuesHolder.getBuilder() val size = entryBuilder.preciseSize if (size > unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock) { val amountToRequest = size - unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock keepUnrolling = reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask(blockId, amountToRequest, memoryMode) if (keepUnrolling) { unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock += amountToRequest } } if (keepUnrolling) { val entry = entryBuilder.build() // Synchronize so that transfer is atomic memoryManager.synchronized { releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask(memoryMode, unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock) val success = memoryManager.acquireStorageMemory(blockId, entry.size, memoryMode) assert(success, "transferring unroll memory to storage memory failed") } entries.synchronized { entries.put(blockId, entry) } logInfo("Block %s stored as values in memory (estimated size %s, free %s)".format(blockId, Utils.bytesToString(entry.size), Utils.bytesToString(maxMemory - blocksMemoryUsed))) Right(entry.size) } else { // We ran out of space while unrolling the values for this block logUnrollFailureMessage(blockId, entryBuilder.preciseSize) Left(unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock) } } else { // We ran out of space while unrolling the values for this block logUnrollFailureMessage(blockId, valuesHolder.estimatedSize()) Left(unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock) } }- 调用
putIteratorAsValues(),putIteratorAsBytes(): 分别是写入未序列化(堆内内存)和序列化后的数据,内部调用了putIterator()getBytes(),getValues(): 分别从是entries中获取序列化和未序列的MemoryEntryremove(),clear(): 分别是从内存中移除block和清除所有block
总结
UnifiedMemoryManager: 在堆内和堆外内存中,计算内存和存储内存中间间隔一条虚线是可以互相借用的计算内存主要用于 shuffle、join、sort、aggregation 中的缓存
存储内存主要用于缓存 RDD、展开 partition、存放广播变量
计算和存储的占比由
spark.memory.fraction配置,默认是0.6,即偏向于存储内存池。其中存储内存池的堆内内存默认占比是由spark.memory.storageFraction参数决定,默认是 0.5 ,即存储内存池的堆内内存默认占比为0.3。计算内存和存储内存可以相互借用,但是缓存block时可能会因为计算内存池占用了大量的内存池不能释放导致缓存block失败,在这种情况下,新的block会根据
StorageLevel做相应处理
MemoryStore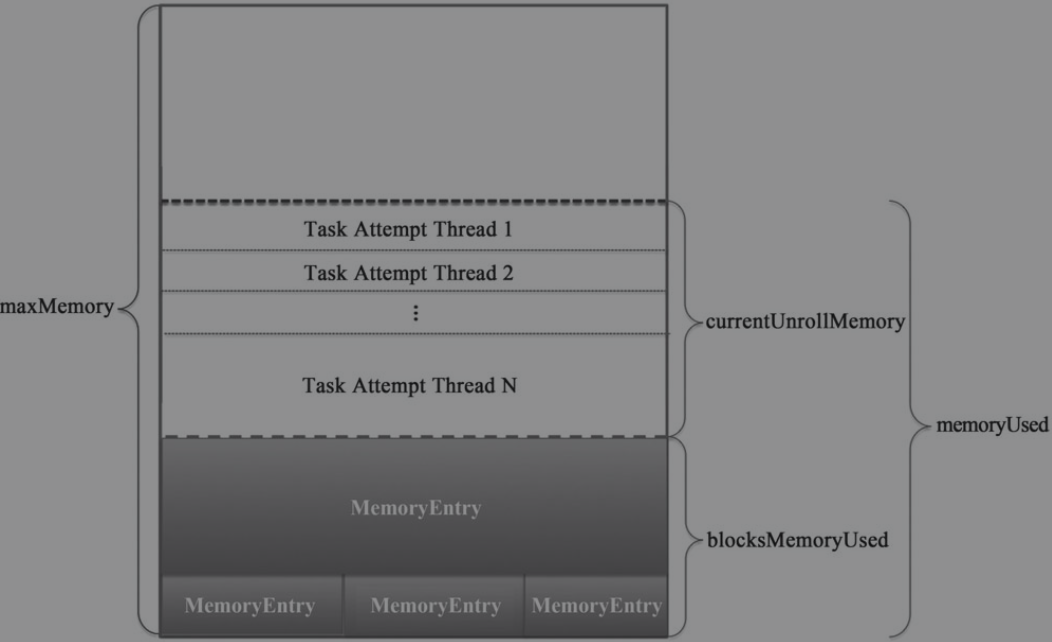
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/09/09/store-memory/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)