Spark SQL对Join的解析和执行过程
ANTLR4文法
// ?表示可选结构
fromClause
: FROM relation (',' relation)* lateralView* pivotClause?
;
relation
: relationPrimary joinRelation*
;
joinRelation
: (joinType) JOIN right=relationPrimary joinCriteria?
| NATURAL joinType JOIN right=relationPrimary
;
joinType
: INNER?
| CROSS
| LEFT OUTER?
| LEFT SEMI
| RIGHT OUTER?
| FULL OUTER?
| LEFT? ANTI
;
joinCriteria
: ON booleanExpression
| USING '(' identifier (',' identifier)* ')'
;
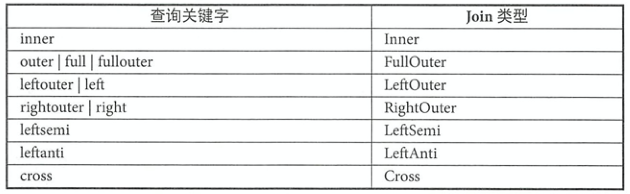
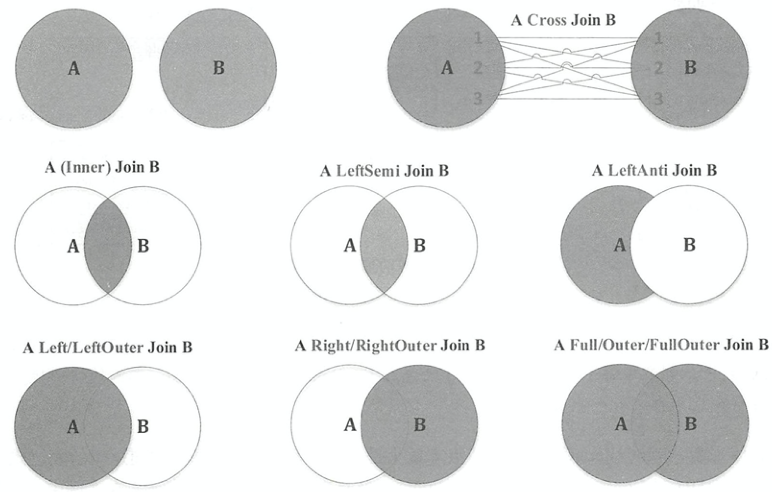
由ANTLR4文法所示,Spark SQL支持如下七种Join。Cross和Inner继承自抽象类InnerLike
逻辑计划
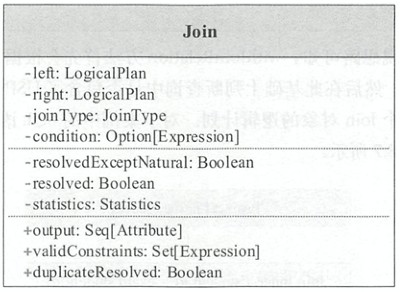
逻辑计划Join表示Join操作,其结构如下图所示,其中duplicateResolved左右逻辑计划的输出是否一致
物理计划
HashJoin
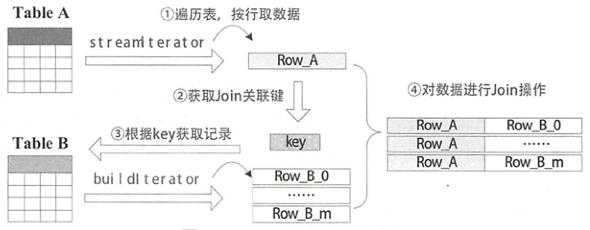
根据数据表的角色不同分为streamedTable流式表和BuildTable构建表,通常将大表设定为流式表,将小表设定为构建表。如下图所示,在一次Build过程中,流式表迭代器streamedlter遍历流式表的每条记录,然后在构建表迭代器buildlter中查找相匹配的记录,每次Build的结果为一条JoinedRow(left, right)。如果left来自streamedlter,right来自buildlter,则为BuildRight操作;如果right来自 streamedlter,left来自 buildlter,则为BuildLeft操作
对于LeftOuter、RightOuter、LeftSemi和LeftAnti ,它们的Build类型是确定的,即LeftOuter、 LeftSemi、LeftAnti为BuildRight,RightOuter为BuildLeft。
特质HashJoin的操作框架如下所示,除了一些基本信息,其中,buildPlan, streamedPlan与buildKeys, streamedKeys是根据buildSide将左右表和左右连接键区分为流式表和构建表角色。
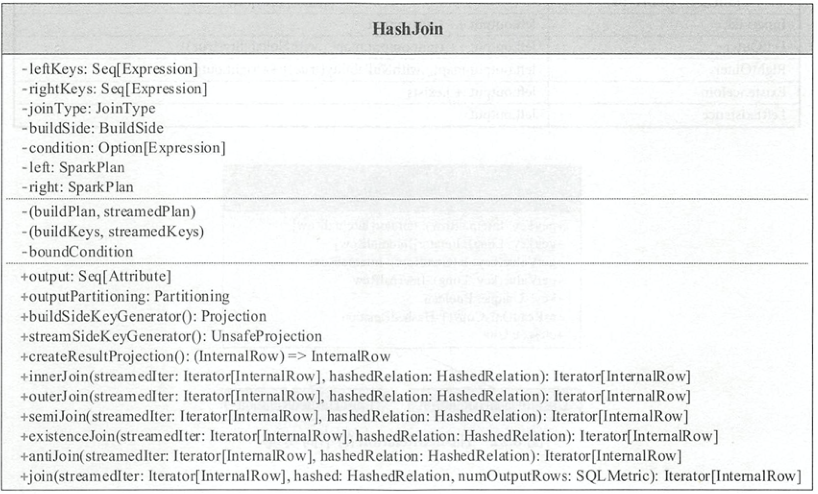
output(): 如下所示,根据Join类型的不同,输出的列属性也不同override def output: Seq[Attribute] = { joinType match { case _: InnerLike => left.output ++ right.output case LeftOuter => left.output ++ right.output.map(_.withNullability(true)) case RightOuter => left.output.map(_.withNullability(true)) ++ right.output case j: ExistenceJoin => left.output :+ j.exists case LeftExistence(_) => left.output case x => throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"HashJoin should not take $x as the JoinType") } }outputPartitioning(): 输出数据的分区模式,由streamedPlan决定innerJoin(): 对应的JoinType为Inner和Cross。hashedRelation对应的是构建表的HashMap结构,遍历流式表,将连接键相同的构建表的行与流式表的当前行组合成JoinedRow,流式表的一行可能和多个构建表的行对应。从代码中可以看出此函数中对JoinRow进行了复用,如果直接物化返回的迭代器将会导致重复。但是由于函数返回的是迭代器类型,最后进行计算ResultTask时,遍历innerJoin()返回的迭代器的同时从内存中取出对应数据,这样就不会产生重复private def innerJoin( streamIter: Iterator[InternalRow], hashedRelation: HashedRelation): Iterator[InternalRow] = { val joinRow = new JoinedRow val joinKeys = streamSideKeyGenerator() streamIter.flatMap { srow => joinRow.withLeft(srow) val matches = hashedRelation.get(joinKeys(srow)) if (matches != null) { matches.map(joinRow.withRight(_)).filter(boundCondition) } else { Seq.empty } } } // JoinRow def withRight(newRight: InternalRow): JoinedRow = { row2 = newRight this }outerJoin(): 对应的JoinType为LeftOuter和RightOuter。如下代码可以看出,如果流式表中的连接键在构建表中没有,则会返回流式表对应行和空值连接的行。其余情况与innerJoin()一致private def outerJoin( streamedIter: Iterator[InternalRow], hashedRelation: HashedRelation): Iterator[InternalRow] = { val joinedRow = new JoinedRow() val keyGenerator = streamSideKeyGenerator() val nullRow = new GenericInternalRow(buildPlan.output.length) streamedIter.flatMap { currentRow => val rowKey = keyGenerator(currentRow) joinedRow.withLeft(currentRow) val buildIter = hashedRelation.get(rowKey) new RowIterator { private var found = false override def advanceNext(): Boolean = { while (buildIter != null && buildIter.hasNext) { val nextBuildRow = buildIter.next() if (boundCondition(joinedRow.withRight(nextBuildRow))) { found = true return true } } if (!found) { joinedRow.withRight(nullRow) found = true return true } false } override def getRow: InternalRow = joinedRow }.toScala } }semiJoin(): 对应的JoinType为LeftSemi。当流式表的连接键不为空且构建表中存在对应的行时,返回流式表的行private def semiJoin( streamIter: Iterator[InternalRow], hashedRelation: HashedRelation): Iterator[InternalRow] = { val joinKeys = streamSideKeyGenerator() val joinedRow = new JoinedRow streamIter.filter { current => val key = joinKeys(current) lazy val buildIter = hashedRelation.get(key) !key.anyNull && buildIter != null && (condition.isEmpty || buildIter.exists { (row: InternalRow) => boundCondition(joinedRow(current, row)) }) } }antiJoin(): 对应的JoinType为LeftAnti。当流式表的连接键不为空且构建表中不存在对应的行时,返回流式表的行private def antiJoin( streamIter: Iterator[InternalRow], hashedRelation: HashedRelation): Iterator[InternalRow] = { val joinKeys = streamSideKeyGenerator() val joinedRow = new JoinedRow streamIter.filter { current => val key = joinKeys(current) lazy val buildIter = hashedRelation.get(key) key.anyNull || buildIter == null || (condition.isDefined && !buildIter.exists { row => boundCondition(joinedRow(current, row)) }) } }join(): 由对应的JoinType,调用不同的Join函数protected def join( streamedIter: Iterator[InternalRow], hashed: HashedRelation, numOutputRows: SQLMetric): Iterator[InternalRow] = { val joinedIter = joinType match { case _: InnerLike => innerJoin(streamedIter, hashed) case LeftOuter | RightOuter => outerJoin(streamedIter, hashed) case LeftSemi => semiJoin(streamedIter, hashed) case LeftAnti => antiJoin(streamedIter, hashed) case j: ExistenceJoin => existenceJoin(streamedIter, hashed) case x => throw new IllegalArgumentException( s"BroadcastHashJoin should not take $x as the JoinType") }
BroadcastHashJoinExec
BroadcastHashJoinExec主要对小表进行广播操作,避免大表shuffle
在外连接中,基表不能被广播
使用了hint(
MAPJOIN(table)、BROADCASTJOIN(table)、BROADCAST(table))会强制开启指定表广播小表的数据必须很小,通过
spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold参数来配置,默认是10MB
doExecute()函数返回RDD[InternalRow],显示了具体的运算逻辑。利用构建表物理计划建立广播的HashedRelation,调用流式表物理计划的RDD[InternalRow]的mapPartitions()函数转化为新的RDD,在RDD内调用其父类的HashJoin.join()函数计算出Join后的行。
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
val broadcastRelation = buildPlan.executeBroadcast[HashedRelation]()
streamedPlan.execute().mapPartitions { streamedIter =>
val hashed = broadcastRelation.value.asReadOnlyCopy()
TaskContext.get().taskMetrics().incPeakExecutionMemory(hashed.estimatedSize)
join(streamedIter, hashed, numOutputRows)
}
}
ShuffledHashJoinExec
在外连接中,基表不能被广播
spark.sql.join.preferSortMergeJoin参数必须设置为 false- 小表小于
spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold*spark.sql.shuffle.partitions - 小表远远小于(
muchSmaller())大表
doExecute()函数返回RDD[InternalRow],显示了具体的运算逻辑。在调用prepareForExecution()进行准备工作时,会添加 Exchange物理计划对流式表和构建表分别进行shuffle,让两张表中拥有相同连接键哈希值的行分到相同的分区中。调用流式表物理计划的RDD[InternalRow]的zipPartitions()函数转化为新的RDD,在RDD内将构建表构造成HashedRelation,然后调用其父类的HashJoin.join()函数计算出Join后的行。
private def buildHashedRelation(iter: Iterator[InternalRow]): HashedRelation = {
val buildDataSize = longMetric("buildDataSize")
val buildTime = longMetric("buildTime")
val start = System.nanoTime()
val context = TaskContext.get()
val relation = HashedRelation(iter, buildKeys, taskMemoryManager = context.taskMemoryManager())
buildTime += (System.nanoTime() - start) / 1000000
buildDataSize += relation.estimatedSize
// This relation is usually used until the end of task.
context.addTaskCompletionListener[Unit](_ => relation.close())
relation
}
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
streamedPlan.execute().zipPartitions(buildPlan.execute()) { (streamIter, buildIter) =>
val hashed = buildHashedRelation(buildIter)
join(streamIter, hashed, numOutputRows)
}
}
SortMergeJoinExec
当两个表的数据量都非常大时,会使用SortMergeJoin方式进行Join。对两张表参与Join的连接键使用相同的分区算法和分区数进行分区,目的就是保证相同的连接键的行都落到相同的分区里面。之后再对每个分区按照连接键进行排序,最后Reduce端获取两张表相同分区的数据进行Merge Join。条件如下所示
- 不满足
BroadcastHashJoin和ShuffledHashJoin - 只支持等值连接,并且要求参与Join的连接键可排序
Iterator
特质RowIterator主要定义了advanceNext()方法将Iterator向前移动一行,和getRow()获取当前行。在具体子类现中,是通过调用对应的JoinScanner来实现父类的那两个方法
SortMergeJoinScanner
在SortMergeJoinScanner的构造参数中会传递
streamedlter: streamedTable的迭代器bufferedlter: bufferedTable的迭代器streamedKeyGenerator,bufferedKeyGenerator: streamedTable和bufferedTable的连接键keyOrdering: 连接键的排序器
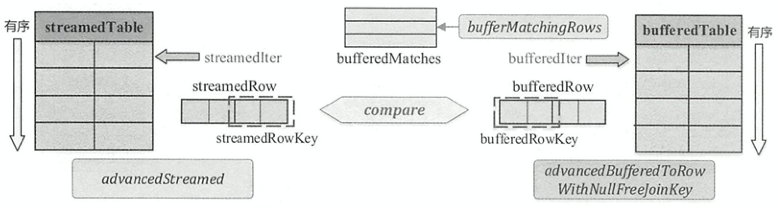
如图所示,streamedTable与bufferedTable都是shuffle后的数据,所以都是已经排好序的,因此在匹配满足条件数据的过程中只需要不断移动迭代器,得到新的数据行进行比较再Join即可,与当前steamedTable行匹配的所有bufferedTable缓存在bufferedMatches中。
在SortMergeJoinScanner中,两个表迭代器所指向的数据行分别用streamedRow和bufferedRow表示。 数据行对应的Join操作的连接键分别为streamedRowKey与bufferedRowKey。advancedStreamed()函数用于获得下一个streamedRow和streamedRowKey。advancedBufferedToRowWithNullFreeJoinKey()函数用于获得下一个bufferedRow和bufferedRowKey,跳过包含 null 的数据行。
对于findNextInnerJoinRows()方法用来得到满足内连接条件的数据,算法流程如下所示
final def findNextInnerJoinRows(): Boolean = {
while (advancedStreamed() && streamedRowKey.anyNull) {
// Advance the streamed side of the join until we find the next row whose join key contains
// no nulls or we hit the end of the streamed iterator.
}
val found = if (streamedRow == null) {
// We have consumed the entire streamed iterator, so there can be no more matches.
matchJoinKey = null
bufferedMatches.clear()
false
} else if (matchJoinKey != null && keyOrdering.compare(streamedRowKey, matchJoinKey) == 0) {
// The new streamed row has the same join key as the previous row, so return the same matches.
true
} else if (bufferedRow == null) {
// The streamed row's join key does not match the current batch of buffered rows and there are
// no more rows to read from the buffered iterator, so there can be no more matches.
matchJoinKey = null
bufferedMatches.clear()
false
} else {
// Advance both the streamed and buffered iterators to find the next pair of matching rows.
var comp = keyOrdering.compare(streamedRowKey, bufferedRowKey)
do {
if (streamedRowKey.anyNull) {
advancedStreamed()
} else {
assert(!bufferedRowKey.anyNull)
comp = keyOrdering.compare(streamedRowKey, bufferedRowKey)
if (comp > 0) advancedBufferedToRowWithNullFreeJoinKey()
else if (comp < 0) advancedStreamed()
}
} while (streamedRow != null && bufferedRow != null && comp != 0)
if (streamedRow == null || bufferedRow == null) {
// We have either hit the end of one of the iterators, so there can be no more matches.
matchJoinKey = null
bufferedMatches.clear()
false
} else {
// The streamed row's join key matches the current buffered row's join, so walk through the
// buffered iterator to buffer the rest of the matching rows.
assert(comp == 0)
bufferMatchingRows()
true
}
}
if (!found) eagerCleanupResources()
found
}
- 循环调用
advancedStreamed()直到当前streamedTable连接键streamRowKey不包含null字段 - 如果streamedTable行
streamRow为null或者bufferedTable行bufferedRow为null,说明streamedTable或者bufferedTable处理完毕,清空bufferedMatches,返回false - 如果streamedTable连接键
streamedRowKey和bufferedTable连接键bufferedRowKey相等,那么bufferedMatches数组已经是可以和streamRow连接的bufferedTable中的所有行 - 不断比较
streamedRowKey和bufferedRowKey,如果streamedRowKey值较小,则调用advancedStreamed()获取streamedTable下一行。如果bufferedRowKey值较小,则调用advancedBufferedToRowWithNullFreeJoinKey()获取bufferedTable下一行。直到两者相等或者其中一行为null - 当满足Join条件时,执行
bufferMatchingRows()方法得到bufferedMatches数组
对于findNextInnerOuterJoinRows()方法用来得到满足外连接条件的数据,算法流程如下所示
final def findNextOuterJoinRows(): Boolean = {
val found = if (!advancedStreamed()) {
// We have consumed the entire streamed iterator, so there can be no more matches.
matchJoinKey = null
bufferedMatches.clear()
false
} else {
if (matchJoinKey != null && keyOrdering.compare(streamedRowKey, matchJoinKey) == 0) {
// Matches the current group, so do nothing.
} else {
// The streamed row does not match the current group.
matchJoinKey = null
bufferedMatches.clear()
if (bufferedRow != null && !streamedRowKey.anyNull) {
var comp = 1
do {
comp = keyOrdering.compare(streamedRowKey, bufferedRowKey)
} while (comp > 0 && advancedBufferedToRowWithNullFreeJoinKey())
if (comp == 0) {
// We have found matches, so buffer them (this updates matchJoinKey)
bufferMatchingRows()
} else {
// We have overshot the position where the row would be found, hence no matches.
}
}
}
// If there is a streamed input then we always return true
true
}
if (!found) eagerCleanupResources()
found
}
- 如果streamedTable全部行都已经处理完,则清空
bufferedMatches,并返回false - 如果两个连接键相等,则直接返回true
- 如果不相等,那么不断迭代bufferedTable直到当前
bufferedRowKey值比streamedRowKey值大或两者相等。如果相等则调用bufferMatchingRows()方法获得bufferedMatches并返回true,否则直接返回true
SortMergeFullOuterJoinScanner
用于处理Full Outer的情况。
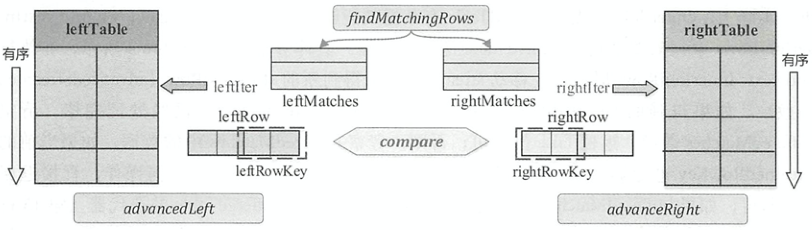
如图所示,左表和右表分别前移的方法为advancedLeft()和advancedRight(),在SortMergeFullOuterJoinScanner遍历数据过程中会构造两个缓冲区leftMatches和rightMatches,来缓存匹配右表当前数据行的数据与缓存匹配左表当前数据行的数据。 scanNextlnBuffered()方法返回两个缓冲区full join的数据放入joinedRow
private def scanNextInBuffered(): Boolean = {
while (leftIndex < leftMatches.size) {
while (rightIndex < rightMatches.size) {
joinedRow(leftMatches(leftIndex), rightMatches(rightIndex))
if (boundCondition(joinedRow)) {
leftMatched.set(leftIndex)
rightMatched.set(rightIndex)
rightIndex += 1
return true
}
rightIndex += 1
}
rightIndex = 0
if (!leftMatched.get(leftIndex)) {
// the left row has never matched any right row, join it with null row
joinedRow(leftMatches(leftIndex), rightNullRow)
leftIndex += 1
return true
}
leftIndex += 1
}
while (rightIndex < rightMatches.size) {
if (!rightMatched.get(rightIndex)) {
// the right row has never matched any left row, join it with null row
joinedRow(leftNullRow, rightMatches(rightIndex))
rightIndex += 1
return true
}
rightIndex += 1
}
// There are no more valid matches in the left and right buffers
false
}
private def findMatchingRows(matchingKey: InternalRow): Unit = {
leftMatches.clear()
rightMatches.clear()
leftIndex = 0
rightIndex = 0
while (leftRowKey != null && keyOrdering.compare(leftRowKey, matchingKey) == 0) {
leftMatches += leftRow.copy()
advancedLeft()
}
while (rightRowKey != null && keyOrdering.compare(rightRowKey, matchingKey) == 0) {
rightMatches += rightRow.copy()
advancedRight()
}
if (leftMatches.size <= leftMatched.capacity) {
leftMatched.clearUntil(leftMatches.size)
} else {
leftMatched = new BitSet(leftMatches.size)
}
if (rightMatches.size <= rightMatched.capacity) {
rightMatched.clearUntil(rightMatches.size)
} else {
rightMatched = new BitSet(rightMatches.size)
}
}
如上所示,findMatchingRows()方法不断地比较左右表当前数据行中的,缓存相等的行
doExecute
在调用prepareForExecution()进行准备工作时,会添加 Exchange物理计划对流式表和构建表分别进行shuffle,让两张表中拥有相同连接键哈希值的行分到相同的分区中并且排序好。如下所示,SortMergeJoinExec.doExecute()方法返回RDD[InternalRow]显示了具体的运算逻辑
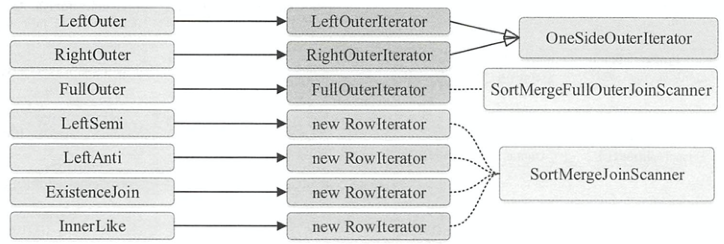
- 调用左表物理计划的
RDD[InternalRow]的zipPartitions()函数转化为新的RDD - 在每个分区内,根据Join type的不同,由该分区内的左右表迭代器构造不同的
RowIterator,OneSideOuterIterator依赖于SortMergeJoinScanner
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
val spillThreshold = getSpillThreshold
val inMemoryThreshold = getInMemoryThreshold
left.execute().zipPartitions(right.execute()) { (leftIter, rightIter) =>
val boundCondition: (InternalRow) => Boolean = {
condition.map { cond =>
newPredicate(cond, left.output ++ right.output).eval _
}.getOrElse {
(r: InternalRow) => true
}
}
// An ordering that can be used to compare keys from both sides.
val keyOrdering = newNaturalAscendingOrdering(leftKeys.map(_.dataType))
val resultProj: InternalRow => InternalRow = UnsafeProjection.create(output, output)
joinType match {
case _: InnerLike =>
new RowIterator {
private[this] var currentLeftRow: InternalRow = _
private[this] var currentRightMatches: ExternalAppendOnlyUnsafeRowArray = _
private[this] var rightMatchesIterator: Iterator[UnsafeRow] = null
private[this] val smjScanner = new SortMergeJoinScanner(
createLeftKeyGenerator(),
createRightKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
cleanupResources
)
private[this] val joinRow = new JoinedRow
if (smjScanner.findNextInnerJoinRows()) {
currentRightMatches = smjScanner.getBufferedMatches
currentLeftRow = smjScanner.getStreamedRow
rightMatchesIterator = currentRightMatches.generateIterator()
}
override def advanceNext(): Boolean = {
while (rightMatchesIterator != null) {
if (!rightMatchesIterator.hasNext) {
if (smjScanner.findNextInnerJoinRows()) {
currentRightMatches = smjScanner.getBufferedMatches
currentLeftRow = smjScanner.getStreamedRow
rightMatchesIterator = currentRightMatches.generateIterator()
} else {
currentRightMatches = null
currentLeftRow = null
rightMatchesIterator = null
return false
}
}
joinRow(currentLeftRow, rightMatchesIterator.next())
if (boundCondition(joinRow)) {
numOutputRows += 1
return true
}
}
false
}
override def getRow: InternalRow = resultProj(joinRow)
}.toScala
case LeftOuter =>
val smjScanner = new SortMergeJoinScanner(
streamedKeyGenerator = createLeftKeyGenerator(),
bufferedKeyGenerator = createRightKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
streamedIter = RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
bufferedIter = RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
cleanupResources
)
val rightNullRow = new GenericInternalRow(right.output.length)
new LeftOuterIterator(
smjScanner, rightNullRow, boundCondition, resultProj, numOutputRows).toScala
case RightOuter =>
val smjScanner = new SortMergeJoinScanner(
streamedKeyGenerator = createRightKeyGenerator(),
bufferedKeyGenerator = createLeftKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
streamedIter = RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
bufferedIter = RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
cleanupResources
)
val leftNullRow = new GenericInternalRow(left.output.length)
new RightOuterIterator(
smjScanner, leftNullRow, boundCondition, resultProj, numOutputRows).toScala
case FullOuter =>
val leftNullRow = new GenericInternalRow(left.output.length)
val rightNullRow = new GenericInternalRow(right.output.length)
val smjScanner = new SortMergeFullOuterJoinScanner(
leftKeyGenerator = createLeftKeyGenerator(),
rightKeyGenerator = createRightKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
leftIter = RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
rightIter = RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
boundCondition,
leftNullRow,
rightNullRow)
new FullOuterIterator(
smjScanner,
resultProj,
numOutputRows).toScala
case LeftSemi =>
new RowIterator {
private[this] var currentLeftRow: InternalRow = _
private[this] val smjScanner = new SortMergeJoinScanner(
createLeftKeyGenerator(),
createRightKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
cleanupResources
)
private[this] val joinRow = new JoinedRow
override def advanceNext(): Boolean = {
while (smjScanner.findNextInnerJoinRows()) {
val currentRightMatches = smjScanner.getBufferedMatches
currentLeftRow = smjScanner.getStreamedRow
if (currentRightMatches != null && currentRightMatches.length > 0) {
val rightMatchesIterator = currentRightMatches.generateIterator()
while (rightMatchesIterator.hasNext) {
joinRow(currentLeftRow, rightMatchesIterator.next())
if (boundCondition(joinRow)) {
numOutputRows += 1
return true
}
}
}
}
false
}
override def getRow: InternalRow = currentLeftRow
}.toScala
case LeftAnti =>
new RowIterator {
private[this] var currentLeftRow: InternalRow = _
private[this] val smjScanner = new SortMergeJoinScanner(
createLeftKeyGenerator(),
createRightKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
cleanupResources
)
private[this] val joinRow = new JoinedRow
override def advanceNext(): Boolean = {
while (smjScanner.findNextOuterJoinRows()) {
currentLeftRow = smjScanner.getStreamedRow
val currentRightMatches = smjScanner.getBufferedMatches
if (currentRightMatches == null || currentRightMatches.length == 0) {
numOutputRows += 1
return true
}
var found = false
val rightMatchesIterator = currentRightMatches.generateIterator()
while (!found && rightMatchesIterator.hasNext) {
joinRow(currentLeftRow, rightMatchesIterator.next())
if (boundCondition(joinRow)) {
found = true
}
}
if (!found) {
numOutputRows += 1
return true
}
}
false
}
override def getRow: InternalRow = currentLeftRow
}.toScala
case j: ExistenceJoin =>
new RowIterator {
private[this] var currentLeftRow: InternalRow = _
private[this] val result: InternalRow = new GenericInternalRow(Array[Any](null))
private[this] val smjScanner = new SortMergeJoinScanner(
createLeftKeyGenerator(),
createRightKeyGenerator(),
keyOrdering,
RowIterator.fromScala(leftIter),
RowIterator.fromScala(rightIter),
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
cleanupResources
)
private[this] val joinRow = new JoinedRow
override def advanceNext(): Boolean = {
while (smjScanner.findNextOuterJoinRows()) {
currentLeftRow = smjScanner.getStreamedRow
val currentRightMatches = smjScanner.getBufferedMatches
var found = false
if (currentRightMatches != null && currentRightMatches.length > 0) {
val rightMatchesIterator = currentRightMatches.generateIterator()
while (!found && rightMatchesIterator.hasNext) {
joinRow(currentLeftRow, rightMatchesIterator.next())
if (boundCondition(joinRow)) {
found = true
}
}
}
result.setBoolean(0, found)
numOutputRows += 1
return true
}
false
}
override def getRow: InternalRow = resultProj(joinRow(currentLeftRow, result))
}.toScala
case x =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
s"SortMergeJoin should not take $x as the JoinType")
}
}
}
BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec
可以看成以下执行方式,在每个分区内使用嵌套的循环,时间复杂度很高
for record_1 in relation_1:
for record_2 in relation_2:
# join condition is executed
BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec会根据相关条件对小表进行广播,以减少表的扫描次数。触发广播的需要满足以下三个条件之一
right outer join是会广播左表
- left outer, left semi, left anti或者 existence join时会广播右表
- inner join的时候两张表都会广播
CartesianProductExec
如果两张参与Join的表没有连接条件且是内连接类型,那么会产生CartesianProduct,得到笛卡尔积
选择过程
先介绍一下JoinSelection中的比较函数
canBroadcast(): 判断逻辑计划的输出是否足够小进而可以被广播。该逻辑计划的统计大小在广播阈值spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold(默认为10M)之内则返回trueprivate def canBroadcast(plan: LogicalPlan): Boolean = { plan.stats.sizeInBytes >= 0 && plan.stats.sizeInBytes <= conf.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold }canBuildLocalHashMap(): 判断逻辑计划的分区足够小进而可以构建一个本地哈希表。进行了粗粒度的比较,比较逻辑计划的统计大小是否比广播阈值和spark.sql.shuffle.partitions的乘积private def canBuildLocalHashMap(plan: LogicalPlan): Boolean = { plan.stats.sizeInBytes < conf.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold * conf.numShufflePartitions }muchSmaller(): 判断a逻辑计划是否远远小于(3倍)b逻辑计划canBuildRight(): 是否可构建右表private def canBuildRight(joinType: JoinType): Boolean = joinType match { case _: InnerLike | LeftOuter | LeftSemi | LeftAnti | _: ExistenceJoin => true case _ => false }canBuildLeft(): 是否可构建左表private def canBuildLeft(joinType: JoinType): Boolean = joinType match { case _: InnerLike | RightOuter => true case _ => false }broadcastSide(): 是否可以广播左表或者右表private def broadcastSide( canBuildLeft: Boolean, canBuildRight: Boolean, left: LogicalPlan, right: LogicalPlan): BuildSide = { def smallerSide = if (right.stats.sizeInBytes <= left.stats.sizeInBytes) BuildRight else BuildLeft if (canBuildRight && canBuildLeft) { // Broadcast smaller side base on its estimated physical size // if both sides have broadcast hint smallerSide } else if (canBuildRight) { BuildRight } else if (canBuildLeft) { BuildLeft } else { // for the last default broadcast nested loop join smallerSide } }canBroadcastByHints(),broadcastSideByHints(): 结合hint和Join type判断是否可以广播,广播左表还是右表private def canBroadcastByHints(joinType: JoinType, left: LogicalPlan, right: LogicalPlan) : Boolean = { val buildLeft = canBuildLeft(joinType) && left.stats.hints.broadcast val buildRight = canBuildRight(joinType) && right.stats.hints.broadcast buildLeft || buildRight } private def broadcastSideByHints(joinType: JoinType, left: LogicalPlan, right: LogicalPlan) : BuildSide = { val buildLeft = canBuildLeft(joinType) && left.stats.hints.broadcast val buildRight = canBuildRight(joinType) && right.stats.hints.broadcast broadcastSide(buildLeft, buildRight, left, right) }canBroadcastBySizes(),broadcastSideBySizes(): 结合广播阈值和Join type判断是否可以广播,广播左表还是右表private def canBroadcastBySizes(joinType: JoinType, left: LogicalPlan, right: LogicalPlan) : Boolean = { val buildLeft = canBuildLeft(joinType) && canBroadcast(left) val buildRight = canBuildRight(joinType) && canBroadcast(right) buildLeft || buildRight } private def broadcastSideBySizes(joinType: JoinType, left: LogicalPlan, right: LogicalPlan) : BuildSide = { val buildLeft = canBuildLeft(joinType) && canBroadcast(left) val buildRight = canBuildRight(joinType) && canBroadcast(right) broadcastSide(buildLeft, buildRight, left, right) }
下面分析一下构造Join物理计划的函数apply()
- 结合hint和Join type判断是否可以广播表并分析广播左表还是右表,构造
BroadcastHashJoinExec - 结合广播阈值和Join type判断是否可以广播并分析广播左表还是右表,构造
BroadcastHashJoinExec spark.sql.join.preferSortMergeJoin参数为true,并且结合是否可以本地建哈希表和Join type判断,并且是否有一个表远远小于(muchSmaller())另一个表,分析shuffle左表还是右表,构造ShuffledHashJoinExec- 如果其中参与Join的字段不可以排序,则shuffle该表,构造
ShuffledHashJoinExec - 如果参与Join的字段可以排序,则构造
SortMergeJoinExec - 如果不含Join条件
- 结合hint和Join type判断是否可以广播表并分析广播左表还是右表,构造
BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec - 如果Join type是InnerLike,构建
CartesianProductExec
- 结合hint和Join type判断是否可以广播表并分析广播左表还是右表,构造
- 其他情况,选择两个数据表中数据量相对较少的数据表来做广播,构建
BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec,这可能会很慢或导致OOM
def apply(plan: LogicalPlan): Seq[SparkPlan] = plan match {
// --- BroadcastHashJoin --------------------------------------------------------------------
// broadcast hints were specified
case ExtractEquiJoinKeys(joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, condition, left, right)
if canBroadcastByHints(joinType, left, right) =>
val buildSide = broadcastSideByHints(joinType, left, right)
Seq(joins.BroadcastHashJoinExec(
leftKeys, rightKeys, joinType, buildSide, condition, planLater(left), planLater(right)))
// broadcast hints were not specified, so need to infer it from size and configuration.
case ExtractEquiJoinKeys(joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, condition, left, right)
if canBroadcastBySizes(joinType, left, right) =>
val buildSide = broadcastSideBySizes(joinType, left, right)
Seq(joins.BroadcastHashJoinExec(
leftKeys, rightKeys, joinType, buildSide, condition, planLater(left), planLater(right)))
// --- ShuffledHashJoin ---------------------------------------------------------------------
case ExtractEquiJoinKeys(joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, condition, left, right)
if !conf.preferSortMergeJoin && canBuildRight(joinType) && canBuildLocalHashMap(right)
&& muchSmaller(right, left) ||
!RowOrdering.isOrderable(leftKeys) =>
Seq(joins.ShuffledHashJoinExec(
leftKeys, rightKeys, joinType, BuildRight, condition, planLater(left), planLater(right)))
case ExtractEquiJoinKeys(joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, condition, left, right)
if !conf.preferSortMergeJoin && canBuildLeft(joinType) && canBuildLocalHashMap(left)
&& muchSmaller(left, right) ||
!RowOrdering.isOrderable(leftKeys) =>
Seq(joins.ShuffledHashJoinExec(
leftKeys, rightKeys, joinType, BuildLeft, condition, planLater(left), planLater(right)))
// --- SortMergeJoin ------------------------------------------------------------
case ExtractEquiJoinKeys(joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, condition, left, right)
if RowOrdering.isOrderable(leftKeys) =>
joins.SortMergeJoinExec(
leftKeys, rightKeys, joinType, condition, planLater(left), planLater(right)) :: Nil
// --- Without joining keys ------------------------------------------------------------
// Pick BroadcastNestedLoopJoin if one side could be broadcast
case j @ logical.Join(left, right, joinType, condition)
if canBroadcastByHints(joinType, left, right) =>
val buildSide = broadcastSideByHints(joinType, left, right)
joins.BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec(
planLater(left), planLater(right), buildSide, joinType, condition) :: Nil
case j @ logical.Join(left, right, joinType, condition)
if canBroadcastBySizes(joinType, left, right) =>
val buildSide = broadcastSideBySizes(joinType, left, right)
joins.BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec(
planLater(left), planLater(right), buildSide, joinType, condition) :: Nil
// Pick CartesianProduct for InnerJoin
case logical.Join(left, right, _: InnerLike, condition) =>
joins.CartesianProductExec(planLater(left), planLater(right), condition) :: Nil
case logical.Join(left, right, joinType, condition) =>
val buildSide = broadcastSide(
left.stats.hints.broadcast, right.stats.hints.broadcast, left, right)
// This join could be very slow or OOM
joins.BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec(
planLater(left), planLater(right), buildSide, joinType, condition) :: Nil
// --- Cases where this strategy does not apply ---------------------------------------------
case _ => Nil
}
解析过程
如下所示,一条简单的带有Join的SQL语句SELECT STUDENT.ID FROM STUDENT JOIN EXAM ON STUDENT.ID = EXAM.STUDENTID解析成执行计划的过程
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
'Project ['STUDENT.NAME, 'EXAM.SCORE]
+- 'Join Inner, ('STUDENT.ID = 'EXAM.STUDENTID)
:- 'UnresolvedRelation `STUDENT`
+- 'UnresolvedRelation `EXAM`
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
NAME: string, SCORE: string
Project [NAME#11, SCORE#28]
+- Join Inner, (ID#10 = STUDENTID#29)
:- SubqueryAlias `student`
: +- Relation[ID#10,NAME#11,AGE#12] csv
+- SubqueryAlias `exam`
+- Relation[CLASSID#26,GRADEID#27,SCORE#28,STUDENTID#29] csv
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Project [NAME#11, SCORE#28]
+- Join Inner, (ID#10 = STUDENTID#29)
:- Project [ID#10, NAME#11]
: +- Filter isnotnull(ID#10)
: +- Relation[ID#10,NAME#11,AGE#12] csv
+- Project [SCORE#28, STUDENTID#29]
+- Filter isnotnull(STUDENTID#29)
+- Relation[CLASSID#26,GRADEID#27,SCORE#28,STUDENTID#29] csv
== Physical Plan ==
*(2) Project [NAME#11, SCORE#28]
+- *(2) BroadcastHashJoin [ID#10], [STUDENTID#29], Inner, BuildLeft
:- BroadcastExchange HashedRelationBroadcastMode(List(input[0, string, true]))
: +- *(1) Project [ID#10, NAME#11]
: +- *(1) Filter isnotnull(ID#10)
: +- *(1) FileScan csv [ID#10,NAME#11] Batched: false, Format: CSV, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/wzx/Documents/tmp/spark_tmp/STUDENT.csv], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(ID)], ReadSchema: struct<ID:string,NAME:string>
+- *(2) Project [SCORE#28, STUDENTID#29]
+- *(2) Filter isnotnull(STUDENTID#29)
+- *(2) FileScan csv [SCORE#28,STUDENTID#29] Batched: false, Format: CSV, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/wzx/Documents/tmp/spark_tmp/EXAM.csv], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(STUDENTID)], ReadSchema: struct<SCORE:string,STUDENTID:string>
- 由ANTLR4将SQL字符串解析成ANTLR4解析树
- 由
SparkSqlParser将ANTLR4解析树转化为Unresolved逻辑计划树 Analyzer对Unresolved逻辑计划树应用解析规则,解析为Analyzed逻辑计划树。在本例中,应用了ResolveRelations规则,是从Catalog中找到STUDENT表和EXAM表的基本信息。应用了ResolveReferences规则,解析所有列信息,将所有UnresolvedAttribute与UnresolvedExtractValue类型的表达式转换成对应的列信息Optimizer对Analyzed逻辑计划树应用优化规则。在本例中经过了别名消除EliminateSubqueryAliases规则与列剪裁ColumnPruning规则的处理,以及InferFiltersFromConstraints规则保证连接条件两边的列都不为空,在Join条件中增加对左表和右表的列的判空,而PushPredicateThroughJoin规则将两个判空语句进行下推SparkPlanner对逻辑计划树应用生成物理计划规则,转化为物理计划树。使用了ExtractEquiJoinKeys模式匹配提取出 Join type, left keys, right keys, condition, left child, right child。对于Join Inner, (ID#10 = STUDENTID#29)算子提取出了Inner, [ID#10], [STUDENTID#29], None, Project[ID#10, NAME#11], Project[SCORE#28, STUDENTID#29]- 对于
Join算子来说,应用JoinSelection策略构造对应的物理算子,由于数据表数据量很小,所以选择了BroadcastHashJoin
REFERENCE
- Spark SQL内核剖析
- 每个 Spark 工程师都应该知道的五种 Join 策略——过往记忆大数据
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://masterwangzx.com/2020/11/13/spark-sql-join/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)